The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
TO
Filters: Collection: ehsl_heal
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 101 |
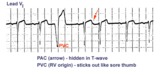 |
Identification of PVC's and PAC's | PVC's usually stick out like sore thumbs; PAC's are often difficult to see because they are hidden in the preceding ST-T wave. The PVC in this example is mostly negative in lead V1 suggesting RV origin; i.e., most of activation is moving in posterior direction towards the left ventricle. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 102 |
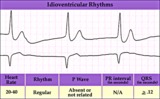 |
Idioventricular escape rhythm | Idioventricular escape rhythm | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 103 |
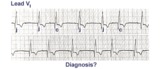 |
Incomplete AV dissociation due To 2nd degree AV block | 2nd degree AV block is evident from the nonconducted P waves. Junctional escapes, labled J, terminate the long pauses because that's the purpose of escape pacemakers....to protect us from too slow heart rates. All QRSs with shorter RR intervals are capture beats, labeled c. Atypical RBBB with a q... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 104 |
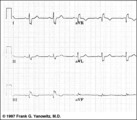 |
Indeterminate frontal plane QRS axis | Indeterminate frontal plane QRS axis | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 105 |
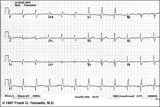 |
Inferior & Anteroseptal MI + RBBB | Pathologic Q waves are seen in leads II, III, aVF (inferior MI) and in leads V1-3 (anteroseptal MI). RBBB is recognized by the wide QRS (>0.12s) and the anterior/rightwards orientation of terminal QRS forces. When an anteroseptal MI complicates RBBB (or visa versa) the rSR' complex in V1 (typical ... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 106 |
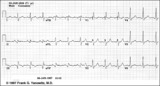 |
Inferior MI and RBBB | Inferior MI and RBBB | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 107 |
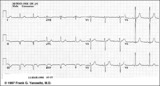 |
Inferior MI: fully evolved | Significant pathologic Q-waves are seen in leads II, III, aVF along with resolving ST segment elevation and symmetrical T wave inversion. This is a classic inferior MI. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 108 |
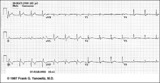 |
Infero-posterior MI | Infero-posterior MI | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 109 |
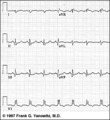 |
Infero-posterior MI & RBBB: Frontal Plane Leads + V1 | Infero-posterior MI & RBBB: Frontal Plane Leads + V1 | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 110 |
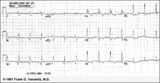 |
Infero-posterior MI with RBBB | This is an unusual RBBB because the initial R wave is taller than the R wave in lead V1. This is the clue for true posterior MI. The tall initial R wave in V1 is a pathologic R wave analagous to the pathologic Q wave of an anterior MI. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 111 |
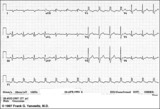 |
Infero-posterior MI&RBBB | Deep Q waves in II, III, aVF plus tall R waves in V1-2 are evidence for this infero-posterior MI. The wide QRS (>0.12s) and RR' complex in V1 are evidence for RBBB. Any time RBBB has an initial R in V1 equal to or greater than the R', true posterior MI must be considered. Q waves in V5-6 suggest a... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 112 |
 |
Inferolateral ST segment elevation | ST Segment elevation with a straight or convex upwards configuration usually means transmural ischemia (or injury) and is seen in the setting of acute myocardial infarction. This ECG finding may also be seen transiently during coronary artery spasm. Unlike ST depression, ST elevation is often loca... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 113 |
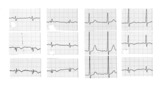 |
Inferoposterior MI | Inferoposterior MI | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 114 |
 |
Inferoposterior MI | Inferoposterior MI | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 115 |
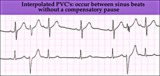 |
Interpolated PVCs - marquette | Interpolated PVCs - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 116 |
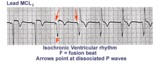 |
Isochronic ventricular rhythm | An isochronic ventricular rhythm is also called an accelerated ventricular rhythm because it represents an active ventricular focus. This arrhythmia is a common reperfusion arrhythmia in acute MI patients. It often begins and ends with fusion beats and there is AV dissociation. Treatment is usuall... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 117 |
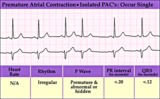 |
Isolated PAC - marquette | Isolated PAC - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 118 |
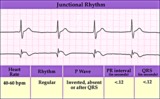 |
Junctional escape rhythm | Junctional escape rhythm | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 119 |
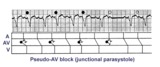 |
Junctional parasystole and pseudo-AV block | This complicated rhythm strip shows normal sinus rhythm and a competing junctional parasystolic focus. Solid circles indicate junctional premature beats from the parasystolic focus. Open circles indicate non-conducted junctional prematures; the first open circle is a nonconducted junctional prematur... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 120 |
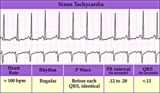 |
Junctional tachycardia - marquette | Junctional tachycardia - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 121 |
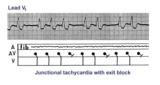 |
Junctional tachycardia with exit block: a manifestation of digitalis intoxication | Theladder diagramsays it all: the atria are fibrillating; there is complete heart block in the AV junction; a junctional tachycardia focus is firing at about 130 bpm, but not all junctional impulses reach the ventricles due to 2nd degree exit block. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 122 |
 |
LAFB: frontal plane leads | LAFB: frontal plane leads | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 123 |
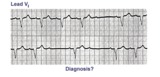 |
LBBB and 2nd degree AV block, mobitz type I | Mobitz II 2nd degree AV block is usually a sign of bilateral bundle branch disease. One of the two bundle branches should be completely blocked; in this example the left bundle is blocked. The nonconducted sinus P waves are most likely blocked in the right bundle which exhibits 2nd degree block. ... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 124 |
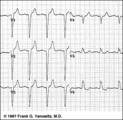 |
LBBB: precordial leads | LBBB: precordial leads | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 125 |
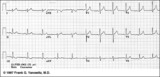 |
Lead Error: V1 & V3 are Transposed | In this normal 12-lead ECG the V1 and V3 chest electrodes are interchanged. Experienced ECG interpreters should be able to spot this lead placement error. | Knowledge Weavers ECG |
