John A. Moran Eye Center Neuro-Ophthalmology Collection: A variety of lectures, videos and images relating to topics in Neuro-Ophthalmology created by faculty at the Moran Eye Center, University of Utah, in Salt Lake City.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
Filters: Collection: "ehsl_novel_jmec"
| Identifier | Title | Description | Subject | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 101 |
 |
Exophthalmometry | Exophthalmometry | Demonstration of exophthalmometry examination. | Examination, Ocular; Exophthalmometry |
| 102 |
 |
1-20 | Facial Myokymia Unilateral | Example of patient with facial myokymia, a disorder of the seventh nerve, probably due to brain stem involvement. Patient has multiple sclerosis. Discussion of characteristics, such as continuous, undulating, contractions in the distribution of the seventh nerve, and a spreading of these movements t... | Superior Oblique Myokymia; Facial Myokymia Unilateral; Facial Myokymia |
| 103 |
 |
facial_nerve_exam | Facial Nerve Exam | Explanation of a facial nerve exam. | Facial Nerve |
| 104 |
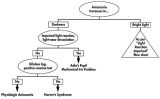 |
Figure-26 | Flow Chart for Sorting Out Anisocoria - Bright Light and Darkness | Flow chart for sorting out anisocoria based initially on how it is influenced by bright light and darkness. | Anisocoria; Adie Syndrome; Diagnostic Use, Cocaine; Constriction; Dark Adaptation; Diagnosis, Differential; Dilatation; Diagnosis, Eye Diseases; Physiopathology, Eye Diseases; Horner Syndrome; Humans; Innervation, Iris; Diagnostic Use, Methacholine Compounds; Diagnostic Use, Pilocarpine; Physiology,... |
| 105 |
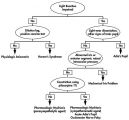 |
Figure-25 | Flow Chart for Sorting Out Anisocoria - Direct Light Reaction of the Pupil | Flow chart for sorting out anisocoria based initially on the integrity of the direct light reaction of the pupil. | Anisocoria; Adie Syndrome; Diagnostic Use, Cocaine; Constriction; Dark Adaptation; Diagnosis, Differential; Dilatation; Diagnosis, Eye Diseases; Physiopathology, Eye Diseases; Horner Syndrome; Humans; Innervation, Iris; Diagnostic Use, Methacholine Compounds; Diagnostic Use, Pilocarpine; Physiology,... |
| 106 |
 |
FluoreseinAngiography | Fluoresein Angiography | Comprehensive description of using fluoresein angiography in examinations. | Fluoresein Angiography |
| 107 |
 |
NOVEL_Moran_3a-8 | Flutter in Downgaze | Examination of patient with flutter in downgaze (no audio) | Downgaze, Eye Flutter |
| 108 |
 |
NOVEL_Moran_2-22 | Fourth Nerve Palsy | Demonstration of examination of patient who experienced blurry vision and pain in the left eye. Demonstrates checking of eye movements, focusing on object while each eye is covered and uncovered, turning head both ways and repeating. Shows limitation of depression in adduction of left eye, left hype... | Fourth Nerve Palsy; 3 Step Test |
| 109 |
 |
Fusional_Vergence | Fusional Vergence Amplitudes | Demonstration of fusional vergence amplitudes examination. Incluudes: a. Convergence Amplitudes b. Divergence Amplitudes c. Vertical Ampitudes | Examination, Ocular; Fusional Vergence Amplitudes |
| 110 |
 |
NOVEL_Moran_2-6 | Gaze Palsy with Facial Weakness from Pontine AVM | Example of a patient with torsional nystagmus in both eyes and pendular nystagmus in the left eye. Patient is led through instructions for direction of gaze. | Gaze Palsy, Facial Weakness, Pontine AVM |
| 111 |
 |
Glaucoma the basics.pdf | Glaucoma: The Basics | Glaucoma is the most common optic neuropathy. Progressive cupping of the optic disc due to increased intraocular pressure together with visual field abnormalities and local disc susceptibility factors characterize this neuropathy. This PowerPoint lecture covers the basics of Glaucoma and includes ma... | Glaucoma; Optic Neuropathy |
| 112 |
 |
Figure-11 | Hand-held Equipment Used to Measure a Relative Afferent Pupillary Defect | Hand-held equipment used to measure a relative afferent pupillary defect and to record pupil sizes. Four neutral density filters (0.3, 0.6, 0.9, 1.2 log units) are conveniently carried in a soft cloth carrying pouch. A bright light source (a Finhoff model illuminator is shown here) is ideal for stim... | RAPD; Relative Afferent Pupillary Defect; Pupil; Reflex, Pupillary; Pupil Disorders; Afferent Pupillary Defect |
| 113 |
 |
1-18 | Hemifacial Spasm | Example of patients with hemifacial spasm. First patient has a sequela of Bell's palsy, and is seen to have mainly clonic movements around the eye, with occasional tonic movements around the mouth. Second patient has a cerebellopontine angle epidurmoid tumor, and is seen to have movements around the... | Hemifacial Spasm |
| 114 |
 |
Herpes Zoster: Zoster Ophthalmicus with Third Nerve Palsy | Herpes Zoster Ophthalmicus with Third Nerve Palsy | Images showing presentation of Herpes Zoster (Zoster Ophthalmicus). | Herpes Zoster (Zoster Ophthalmicus) |
| 115 |
 |
1-1 | How to Measure the RAPD | This clip demonstrates the examination technique for measuring the Relative Afferent Pupillary Defect (RAPD). Demonstration of balancing an afferent papillary defect using filters in a patient with a resolving optic neuritis and an afferent papillary defect on the left. | Relative Afferent Pupillary Defect (RAPD); Examination, Pupillary |
| 116 |
 |
ophthalmoscope | How to Use the Direct Ophthalmoscope in an Exam | Demonstration of using the direct ophthalmoscope to examine the optic disc. Covers hand placement , which eye to use, and distance from patient. | Direct Ophthalmoscope; Examination, Ocular |
| 117 |
 |
Hydroxychloroquine Maculopathy (Plaquenil).pdf | Hydroxychloroquine Maculopathy (Plaquenil) | An overview of Chloroquine Maculopathy. | Maculopathy; Hydroxychloroquine; Plaquenil |
| 118 |
 |
NOVEL_Moran_3a-12 | Intermittent Square Wave Jerks | Patient with intermittent square wave jerks (no audio) | Intermittent Square Wave Jerks |
| 119 |
 |
1-8 | Internuclear Ophthalmoplegia (2 Examples) | Two examples of patients with internuclear ophthalmoplegia. First patient has a right internuclear ophthalmoplegia. Patient had subacute bacterial endocarditis with a bacterial abscess in the brain stem. Ductions and gaze to the right look good, but when gazing to the left, the right eye does not ad... | Internuclear Ophthalmoplegia; Abducting Nystagmus |
| 120 |
 |
fog_refraction_Warner | Introduction to Fogging Refraction | An introduction to fogging refraction. | Fogging Refraction |
| 121 |
 |
Introduction_headache_migraine_secondary_headaches | Introduction to Headache, Migraine and Secondary Headaches | Video lecture covering an introduction to headache, migraine, and secondary headaches by Kathleen Digre, MD. | Migraine, Secondary Headache |
| 122 |
 |
neuro-exam_intro | Introduction to the Basic Neurologic Exam | Introduction to the neurological examinations section of NExT. | Neurology; Examinations |
| 123 |
 |
2-2 | Latent Nystagmus | Example of a patient with latent nystagmus. Demonstrates a lack of oscillations in forward gaze, followed by the occlusion of each eye, showing how this generates a jerking oscillation in the non-occluded eye away from the occluded eye. | Latent Nystagmus; Fusional Maldevelopment Nystagmus Syndrome |
| 124 |
 |
Leber's Hereditary Optic Neuropathy | Leber's Hereditary Optic Neuropathy | Images and visual fields from a boy with acute visual loss. | Leber's Optic Neuropathy |
| 125 |
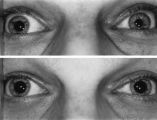 |
Figure-21 | Left-sided Dilation Lag in a Man with Horner's Syndrome | Left-sided dilation lag in a 29-year-old man with Horner's syndrome caused by a posterior mediastinal ganglioneuroma. Note that the degree of anisocoria is greater after 5 seconds in darkness (top) compared with findings after 15 seconds in darkness (bottom). | Diagnosis, Horner Syndrome; Physiopathology, Horner Syndrome; Reflex, Pupillary; Dilation Lag; Horner's Syndrome |
