The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
TO
Filters: Collection: "ehsl_heal"
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 101 |
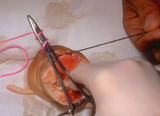 |
Suturing | The needle holder is placed on the inside of the long arm (needle bearing end) of the V, and the suture is wrapped twice around the needle holder. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 102 |
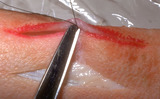 |
Suturing | This demonstrates cutting the deep dermal suture just above the knot. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 103 |
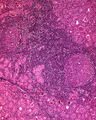 |
Chronic thyroiditis | Chronic thyroiditis | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 104 |
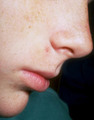 |
Electrocautery | This shows the biopsy site after light electrocautery. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 105 |
 |
Seborrheic dermatitis | Seborrheic dermatitis involving the beard. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 106 |
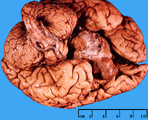 |
Pituitary adenoma | Pituitary adenoma | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 107 |
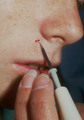 |
Electrocautery | Very light electrocautery can be used to smooth any uneven edges. If using the hyfrecator model, it should be plugged into low and a setting of 30 on the older machines, or setting of 3 watts on the newer machines should be used, and a very light brush kind of stroke should be used to smooth out the... | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 108 |
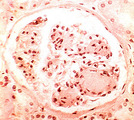 |
Nodular glomerulosclerosis | Nodular glomerulosclerosis | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 109 |
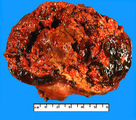 |
Anaplastic carcinoma | Anaplastic carcinoma | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 110 |
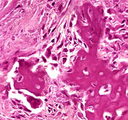 |
Osteosarcoma | Osteosarcoma | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 111 |
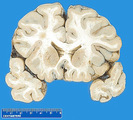 |
Normal brain | Normal brain | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 112 |
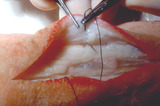 |
Suturing | The other side of the wound is then rolled open to expose the underlying dermis, and I placed the suture in the under-portion of the dermis as far away from the wound edge as possible. I enter from the side where the wound center, and then exit away from the wound center. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 113 |
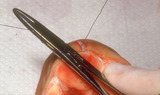 |
Excision: suturing | Two loops are placed around the needle holder to initiate the first throw. The short end of the suture is then grasped, and the hand holding the long(needle bearing) end of the suture crosses over the hand with the needle holder. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 114 |
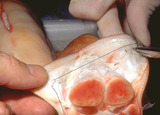 |
Excision procedure | Deep dermal suture is placed as far away from the wound edge as possible. It's initiated on the non-dominant (left) side, and final exit is on the dominant (right) side as shown here. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 115 |
 |
Scirrhous carcinoma, breast | Scirrhous carcinoma, breast | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 116 |
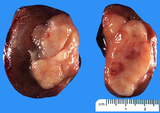 |
Seminoma | Seminoma | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 117 |
 |
Lamellar ichthyosis | Lamellar ichthyosis. The abnormal stratum corneum has produced what appears as very thick scale on the skin, and with an abnormal barrier layer these patients commonly get secondary staphylococcal and yeast infections. Note that there are other associated ectodermal problems such as the teeth, hair,... | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 118 |
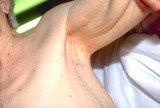 |
Scabies | A nursing home patient who was infested with scabies. Shows the typical pruritic red papules in the axilla. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 119 |
 |
Ingrown nail | This shows the nail plate and part of the attached matrix having been removed. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
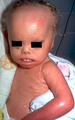
| 120 |
 |
Atopic dermatitis | Atopic dermatitis (eczema) involving the cheeks of a child. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 121 |
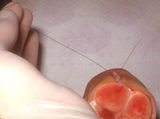 |
Suturing | As the suture exits from the wound, the ends of the suture can be lifted to form aV. The long arm of the V is formed by the needle bearing end of the suture. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 122 |
 |
Epinephrine | Epinephrine also comes in a crystalline form, and the brand name is Sus-Phrine. This is a Depo form of epinephrine. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 123 |
 |
mosquito | Mosquitos are not known to be vectors for significant diseases in Utah. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 124 |
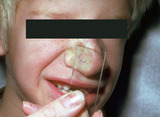 |
Spider telangiectasia | A spider telangiectasia is compressible and blanchable with adequate pressure. Generally, as the pressure is released the central feeding vessel can be seen and often pulsates. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 125 |
 |
Hair regrowth | Rogaine helps to restore hair regrowth of some degree in about a third of men. | Dermatology; Hair | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology |
