The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
TO
Filters: Collection: "ehsl_heal"
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 101 |
 |
Dentinoenamel junction in the tooth (human, adult). Thin ground section of crown. | From left to right: Enamel with fine striation (composition of enamel rods or prisms); darker zones almost perpendicular to the striation are the incremental lines (Retzius) due to successive apposition of layers of enamel as the crown is formed. Dentinoenamel junction is shown as a narrow fissure f... | oral cavity; dentinal tubules; dentinoenamel junction; interglobular dentin; lines of Retzius | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 102 |
 |
Dentinoenamel junction in the tooth - human, adult. Thin ground section of crown. | From left to right: Superficial dentin (bluish) in the crown with S-shaped course of dentinal tubules; They pass uninterrupted through the irregular black structures (due to filling with air) representing hypocalcified areas (interglobular dentin); Mineralization of dentin starts in small globular ... | oral cavity; dentinal tubules; dentinoenamel junction; interglobular dentin; lines of Retzius | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 103 |
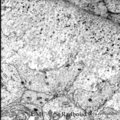 |
Dentinogenesis in tooth development - bell stage, gerbil, postnatal | Electronmicroscopy. At the top right corner side the distal cytoplasmic parts of presecretory ameloblasts resting on a thin grey basal lamina. In the central area predentin with collagen fibers (grey patches) and cross-sectioned small odontoblastic branches. In between them dispersed numerous dark-s... | oral cavity; predentin; matrix vesicles | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 104 |
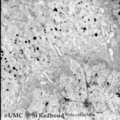 |
Dentinogenesis in tooth development - bell stage, gerbil, postnatal | Electronmicroscopy. At the bottom side of the predentin partly cross-sectioned odontoblasts with some organelles and many vesicular structures, the dark ones containing hydroxyapatite. Close to the odontoblasts a high concentration of secreted collagen fibers. Further away numerous matrix vesicles (... | oral cavity; predentin; matrix vesicles | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 105 |
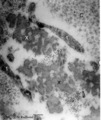 |
Detail of elastin in an alveolar tip in lung tissue (human, adult) | Electron microscopy. Note the lace-like pattern of lumps of amorph elastin (X) that appears more electron-dense than the collagen fibers (C). At this high magnification cross-sectioned microfibrils (that contain among others fibrillin) are present in close association (*) with different areas of ela... | Elastin-associated proteins; Elastoblast; Myofibroblast | Poja Histology Collection - Respiratory System Subset |
| 106 |
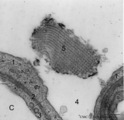 |
Detail of lamellar body (surfactant) and type I alveolar cell in lung (rat) | Electron microscopy. After fixation the extracellular lining of surfactant (phosphatidylcholine, phosphoglycerol, cholesterol and proteins) will often be present as free packed lamellae in the alveolar space (4). This so-called tubular myelin is observed as stacks (5) of lipid crystals and aqueous l... | Pneumocyte I ; Pneumocyte II; Alveolar cells; Tubular myelin | Poja Histology Collection - Respiratory System Subset |
| 107 |
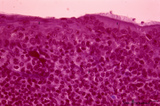 |
Detail of pharyngeal tonsils (human) | Stain: Azan. In contrast to the palatine and lingual tonsils, the epipharyngeal tonsil has a ciliated epithelium (1). Islands of multilayered squamous epithelium may interrupt it (transition zone, 2). The epithelium may be infiltrated with lymphocytes. The surface of this tonsil can be enlarged by m... | pharyngeal tonsil; GALT; squamous epithelium; ciliated epithelium | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 108 |
 |
Detailed localization of heparan sulfate (HS) in spleen (rat) | Stain: Immunofluorescence of Alexa 594 red labeled single chain antibody 3C3 for heparan sulfate (HS). The antibody stains HS epitopes of the meshwork of reticulum cells and the basal membrane of blood vessels. A: survey white pulp spleen. B: marginal sinuses between PALS area and red pulp. C: red... | white pulp; PALS; heparan sulfate | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 109 |
 |
Developing conchae in a frontal section of head (pig, fetus) | Stain: Azan. The fetal conchae develop like a branched gland (1) within the blue-stained trabecular bone (2) of the future skull. The fetal skin (3) is present at the top and bottom. Groups of cheek musculature (4) in middle left and right side. A broad sleeve of chin muscles below (5). The developi... | Conchae nasales; Trabecular bone | Poja Histology Collection - Respiratory System Subset |
| 110 |
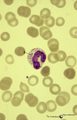 |
Dhle bodies in mature neutrophils in peripheral blood smear (human) | : May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). In adults the usual response to a bacterial infection is a neutrophil leukocytosis with a shift to the left, toxic granulation, Dhle bodies and, when the infection is severe, cytoplasmic vacuolation and swelling occur. Dhle bodies (1, arrow) are small, pale-blue-grey cyto... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 111 |
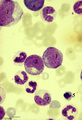 |
Differentiation stages of myeloid cells in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). (1) Promyelocytes with coarse primary azurophilic granules and nucleoli. (2) Myelocyte with starting indentation of the nucleus (primary plus secondary granules). (3) Neutrophilic metamyelocytes with kidney shaped nuclei. (4) Band form of neutrophilic granulocytes (b... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 112 |
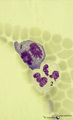 |
Dividing cells (mitosis) in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). (1) Shows a dividing cell (mitotic figure) possibly an erythroblast cell type. (2) Shows two segmented neutrophils. | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 113 |
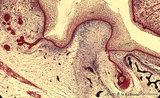 |
Early cap stage in tooth development - human, embryo; low magnification | Stain: Azan. From top to bottom: top left vestibular groove with gland formation; stratified ectoderm with dark red rim of basal cells from which a dental lamina sprouts downwards into the dental crypt (bony cavity) (bottom right corner); bone stains dark blue; connective tissue/mesenchym stains lig... | oral cavity; tooth development; dental lamina | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 114 |
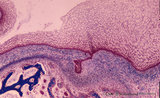 |
Early cap stage in tooth development - human, embryo; low magnification | Stain: Azan. From top to bottom: top left vestibular groove with gland formation; stratified ectoderm with ingrowth of the dental lamina (in the middle); bulbous growing end of dental lamina; bottom left alveolar bone formation (dark blue); and connective tissue/mesenchym stains light blue. | oral cavity; tooth development; dental lamina | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 115 |
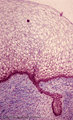 |
Early cap stage in tooth development - human, embryo | Stain: Azan. From top to bottom: stratified ectoderm with ingrowth of the dental lamina; knob-like end of the dental lamina; and collagen fibers of lamina propria are blue. | oral cavity; tooth development; dental lamina | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 116 |
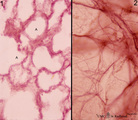 |
Elastic fibers in the lung (human) | Stain: Orcein. At the left (1) several alveoli (A) are depicted with a faint staining of cellular elements. The elastic fibers within the alveoli are stained reddish-purple. At the right (2) a high magnification of a tangential-sectioned alveolus shows the thicker bundles as well as very thin branch... | Elastic fibers | Poja Histology Collection - Respiratory System Subset |
| 117 |
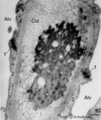 |
Elastin close near the alveolar tip in lung tissue (human, adult) | Electron microscopy. The alveolar tip in the alveolar spaces (Alv) is covered with flattened type I alveolar cells (2). The arrows at (↓1) indicate the junctions between these flattened cells. The amorph elastin (*) in the alveolar tip appears more electron-dense than the collagen fibers (Col). No... | Type I alveolar cells; Elastin-associated proteins | Poja Histology Collection - Respiratory System Subset |
| 118 |
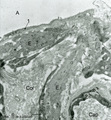 |
Elastin in alveolar tip in lung tissue (human, adult) | Immuno-electron microscopy (embedded in Lowicryl HM 20). The amorph elastin (E) appears pale after embedding in this type of resin, but is antibody-labeled with electron-dense gold particles of 10 nm. (Col) indicate bundles of collagen fibers which are intermingled with swollen cytoplasmic extension... | Alveolar cell type I; Myofibroblast; Immuno-electron microscopy; Immuno-staining | Poja Histology Collection - Respiratory System Subset |
| 119 |
 |
Elastin in alveolus of lung tissue (human, adult) | Immuno-electron microscopy (embedded in Lowicryl HM 20). Elastin (E) is labeled with electron-dense gold particles of 10 nm. Note that the amorph elastin appears pale after embedding in this type of resin. (A) indicates alveolar space, (F) unlabelled myofibrolast, (C) collagen fibers, and (1) the th... | Alveolar cells type I; Myofibroblasts; Immuno-electron microscopy; Immuno-staining | Poja Histology Collection - Respiratory System Subset |
| 120 |
 |
Elastin in alveolus of lung tissue (human, adult) | Immuno-electron microscopy (embedded in Lowicryl HM 20). The amorph elastin (E) appears pale after embedding in this type of resin, but is antibody-labeled with electron-dense gold particles of 10 nm. (C) indicate bundles of collagen fibers (unlabeled) which are intermingled with swollen cytoplasmic... | Immuno-staining; Immuno-electron microscopy | Poja Histology Collection - Respiratory System Subset |
| 121 |
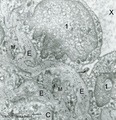 |
Elastin in lung arteriole (human, adult) | Immuno-electron microscopy (embedded in Lowicryl HM 20). The alveolar septa contain a muscular pulmonary arteriole (lumen = X) with unlabelled endothelial cells (1). The elastic membranes in the arteriolar walls consist of more or less continuous bands of amorphous elastic lumps (E) antibody-labeled... | Alveolar septum; Immuno-electron microscopy; Immuno-staining | Poja Histology Collection - Respiratory System Subset |
| 122 |
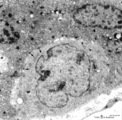 |
Electron microscopy of cytotrophoblast cell (human placenta, early pregnancy) | Below a single electron-light cytotrophoblast cell (CTC or Langhans cell, 1) covered by a syncytiotrophoblast cell (STC, 2) with two nuclei. A continuous basal lamina (3) separates the CTC and STC from the embryonic connective tissue. The CTC appears as a blast-like cell with a large electron-l... | placenta; tertiary villi; syncytiotrophoblast; placental barrier | Poja Histology Collection - Placenta |
| 123 |
 |
Electron microscopy of syncytiotrophoblast cells in tertiary villus (human placenta, midpregnancy) | The left photograph (A) shows the apical cytoplasm of a syncytiotrophoblast cell (STC, nucleus). The free cell surface displays small protrusions and a characteristic pattern of differently shaped microvilli; pinocytotic invaginations and a single macropinocytotic vacuole. Note the apical localized ... | placenta; tertiary villi; syncytiotrophoblast; electron microscopy | Poja Histology Collection - Placenta |
| 124 |
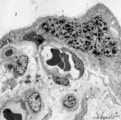 |
Electron microscopy of syncytiotrophoblast knot in tertiary villus (human placenta, almost full-term) | Electron microscopy. The mature villus, surrounded by intervillous space (1), contains capillaries (2) with erythrocytes and pericytes (3) embedded in fetal connective tissue elements (4). Two capillaries are localised close to the covering multinucleated syncytiotrophoblast cell (STC, 5) (vasculosy... | placenta; chorionic villi; syncytial knot; electron microscopy; vasculosyncytial membrane | Poja Histology Collection - Placenta |
| 125 |
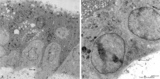 |
Electron microscopy of tertiary villus (human placenta, early pregnancy) | At the left (A), part of a tertiary (terminal) villus with the multinucleated syncytiotrophoblast cell (1) (STC) at the top. The apex shows protrusions and extensive microvilli of varying sizes (brushborder). Nuclei (1a) are sectioned at different levels and the cytoplasm contains abundant organelle... | placenta; chorionic villi; placental barrier; syncytiotrophoblast; electron microscopy | Poja Histology Collection - Placenta |
