The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
TO
Filters: Collection: "ehsl_heal" Format: image
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 101 |
 |
Lingual tonsil ('lymphoepithelial tissue', 'gut-associated lymphatic tissue' or GALT) (human) | Stain: Azan. A: Left side shows a secondary lymphatic follicle (1) separated by the connective tissue of the proper lamina (2) from the lining non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium (3). The mantle zone (4) is indicated by the peripheral dense aggregations of (memory) B lymphocytes. (5) diff... | lingual tonsil; GALT; non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 102 |
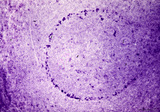 |
Border of white pulp in spleen (mouse) | Monoaminooxidase (enzyme histochemistry on frozen section) with Nitro-BT as staining substrate resulting in a blue formazan precipitate. Despite the general activity of most cells in the spleen, the border cells or so-called metallophilic cells (1) or dendritic antigen-presenting cells (APC) show th... | monoamino oxidase; ED3 antibody; follicle; white pulp | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 103 |
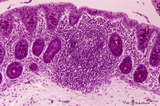 |
Colon ('gut-associated lymphatic tissue' or GALT) (human) | Stain: Hematoxylin-PAS. Solitary lymphatic nodule in colon (see also Digestive System: Colon) A large amount of non-encapsulated diffuse lymphatic tissue or mucosa-associated lymphatic tissue (MALT) is located in the subepithelial lamina propria of the colon and called gut-associated lymphatic tiss... | GALT; follicle; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 104 |
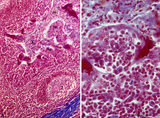 |
Palatine tonsil ('lymphoepithelial tissues', 'gut-associated lymphatic tissue' or GALT) (human) | Stain: Azan. A low magnification in A shows the thick blue connective septum (1) with a secondary lymphatic nodule (2). (3) is a cross-section of a crypt filled with detached squamous epithelium (3a) mixed up with keratinized material (red) and a huge amount of lymphocytes (3b). A higher magnificati... | follicle; germinal center; mantle layer; stratified squamous epithelium | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 105 |
 |
Hassall's corpuscle in thymus (human, puberty) | Stain: Hematoxylin. A larger magnification of the thymic medulla reveals the purple-stained structures in the centre of a so-called Hassall's (or thymic) corpuscle consisting of keratinized (*) epithelial cells. It is surrounded by recognizable flattened cells showing keratohyalin granules (-->). T... | thymic corpuscle (Hassalls); epithelioreticular cell (ERC); lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 106 |
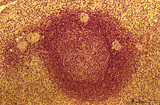 |
Spleen with secondary lymphatic nodule (human) | Stain: Hematoxylin & eosin. The splenic follicle as part of the white pulp is arranged around the cross sectioned central artery (1).The lymphatic sheath or PALS is composed of T cells (2). The darker stained mantle zone of mainly nave B lymphocytes (3) encompasses the lighter stained germinal centr... | white pulp; PALS; marginal zone; mantle layer | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 107 |
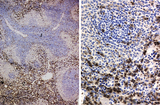 |
Immunohistochemistry of ED1-positive subset of macrophages in spleen (rat) | Stain: Immunoperoxidase staining using diaminobenzidin (DAB)/ hematoxylin counterstained on frozen section with the anti-macrophage antibody ED1. Most of the labeled (brown) macrophages are found in the red pulp (2) up to the marginal zone border (B). The PALS area (1) contains sparsely spread ED1 ... | ED1 ; macrophages; immunohistochemistry; marginal zone | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 108 |
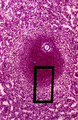 |
Spleen with secondary lymphatic nodule (human) | Stain: Azan. The white pulp of this perfused spleen consists of: at (1) a cross-section of the central artery, (2) tangential cut mantle zone and (3) the marginal zone. The red pulp contains empty venous sinusoids (4) and the perilymphoid zone (3a) is the zone of red pulp immediately surrounding ... | white pulp; germinal center; follicle; white pulp | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 109 |
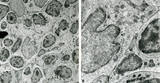 |
Part of lymphatic nodule in spleen (rat) | Electron microscopy. The left image (A) reveals part of a white pulp area stuffed with a dendritic cell (1) between a majority of different types of lymphocytes (2, 3). The right image shows a larger magnification of the same area with the dendritic cell (1) sandwiched in between the enclosing lymp... | dendritic cell; electron microscopy; white pulp | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 110 |
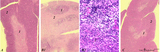 |
Thymus after cyclophosphamide treatment (rat) | Stain: Hematoxylin & eosin. A single injection with cyclophosphamide (CP, 4 70 mg/ml) induces a transient cortical involution, i.e. inhibition of the cell proliferation and maturation. A: Normal thymus with medulla (1) and cortex (2). B1: Inversion of thymic cortex and medulla 4 to 8 days after CP ... | cyclophosphamide; immunosuppression; involution; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 111 |
 |
Lymphoblast in splenic white pulp (rat, human) | Electron microscopy (A, rat) and Methyl green (B, human). Upon antigenic stimulation the lymphocytes in the germinal centre proliferate and generate activated B cells or lymphoblasts which seed towards marginal zone and red pulp while differentiating. Due to the increased number of lymphoblasts, ret... | electron microscopy; lymphoblast | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 112 |
 |
Phagocytosis in small splenic blood vessel (mouse) | Electron microscopy. Stain: Peroxidase reaction with diaminobenzidin staining. A diversity of red blood cells is black-stained due to the staining of hemoglobin by oxidized benzidin. Circulating lymphocytes (2) in the lumen (*) remain unstained. An oblong monocyte (1) developing into a macrophage h... | electron microscopy; phagocytosis | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 113 |
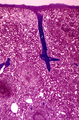 |
Survey of spleen (human) | Stain: Azan. The spleen is covered by a capsule (1) of dense connective tissue and elastic fibers. The capsule continues into the spleen as trabeculae (2) carrying blood vessels and nerve fibers. As arteries leave the trabeculae it becomes invested by a sheath of T cells forming a PALS (3) or periar... | white pulp; sinusoid; red pulp; PALS | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 114 |
 |
: Lymph node (human) | Stain: Azan. Specialized venules (1) or so-called high endothelial venules (HEV) are here located in the paracortical area (4) close to the lymphatic follicle (2+3). The HEVs are lined by cuboidal or columnar endothelial cells that possess specific homing receptors for antigen-primed B- and T ly... | paracortex; high endothelial venule (HEV); germinal center | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 115 |
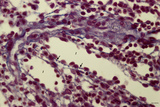 |
Red pulp of spleen with perfused venous sinusoids (human) | Stain: Azan. Cross-sectioned venous sinusoids with splenic cord (1). The wall of a sinusoid is composed of elongated rod-like endothelial cells that are orientated parallel to each other in the long axis of the sinusoid. There is a discontinuous pale-stained basement membrane (difficult to observe i... | sinusoid ; red pulp; splenic cord; central arteriole | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 116 |
 |
Venous circulation pattern in perfused spleen (human) | Stain: Azan. The composed picture shows part of the splenic circulation system at several enlargements (inset, A, B). The open venous sinusoids (1) drain via short pulp veins into thin-walled trabecular veins (2), subsequently into thick-walled trabecular veins (4). The trabeculae originate from the... | splenic circulation; trabecular veins; sinusoid ; PALS | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 117 |
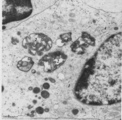 |
Thymus medulla (rat, young adult) | Electron microscopy. Epithelioreticular cells of the medulla (1) close to each other. The electron-light cytoplasm contains many small vesicles (1, Golgi area) as well as cross-sections of vacuoles (2) with small finger-like cytoplasmic extrusions in the lumen. Electron-dense lysosomal structures (3... | medullar epithelioreticular cell ; thymus medulla; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 118 |
 |
Thymus medulla (rat, young adult) | Electron microscopy. Surrounded by thymocytes (3) a medullary macrophage with an electron-light nucleus (1). The cytoplasm contains many electron-dense lysosomes of varying sizes and forms (2). | medullar macrophage; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 119 |
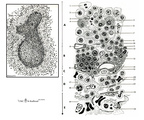 |
Scheme electron microscopy of the border of secondary nodule/red pulp in spleen | The left figure POJA-L974 shows a scheme of histological impression of a survey of a secondary splenic follicle or nodule. The rectangle is enlarged in the right figure POJA-L976B and shows the following elements: A. germinal centre; B. mantle zone; C. dendritic cell area; D. marginal zone; E. ... | white pulp; marginal zone; red pulp; antigen presenting cell (APC) | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 120 |
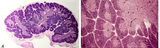 |
Thymus (human, newborn, low and higher magnification) | Stain: Hematoxylin & eosin. The infantile thymus is surrounded by connective tissue capsule (3) from where vascularized interlobular septa (or trabeculae, 3) penetrate into the lobulated organ. Each lobule consists of a darker stained cortex (2) and a lighter stained medulla (1). The medulla has a l... | Zhen; thymus cortex; thymus medulla; Hassall's corpuscle ; Lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 121 |
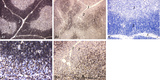 |
The effect of cyclophosphamide on the CD8-thymocytes in thymus (rat) | Stain: Immunoperoxidase staining with diaminobenzidin (DAB) and hematoxylin counterstained on frozen section. A single injection with cyclophosphamide (CP, 70 mg/ml) induces a transient cortical involution after 4 days, i.e. the darkly stained cortex and the lightly stained medulla in normal thymus ... | cyclophosphamide; CD8 monoclonal antibody; immunosuppression; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 122 |
 |
Detailed localization of heparan sulfate (HS) in spleen (rat) | Stain: Immunofluorescence of Alexa 594 red labeled single chain antibody 3C3 for heparan sulfate (HS). The antibody stains HS epitopes of the meshwork of reticulum cells and the basal membrane of blood vessels. A: survey white pulp spleen. B: marginal sinuses between PALS area and red pulp. C: red... | white pulp; PALS; heparan sulfate | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 123 |
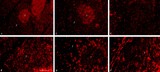 |
Immunohistochemistry with cellular markers in thymus (rat) | Stain: Alexa-594 red immunofluorescence. (1) medulla. (2) cortex. (A-survey, B-cortex): ER13 antibody stains for MHC-class II antigens on reticular cell types in medulla and cortex. (C): ED1 monoclonal antibody stains a single chain glycoprotein of 110 kDa on the lysosomal membrane of myeloid cel... | ER13 antibody; ED1 monoclonal antibody; ED2 monoclonal antibody; ER2 monoclonal antibody | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 124 |
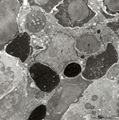 |
Phagocytosis in splenic red pulp (mouse) | Electron microscopy. Stain: Peroxidase reaction with diaminobenzidin staining. A diversity of red blood cells in the red pulp can be discerned due to the DAB staining of hemoglobin by oxidized benzidin (dark and light staining). The macrophage (1) shows peroxidase activity along the nuclear membran... | electron microscopy; phagocytosis | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 125 |
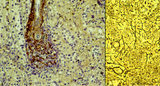 |
Red pulp of spleen with venous sinusoids (monkey, human) | Stain: A: Silver stain (Movat) (monkey); B: Silver stain (Gomori) (human). (A): The darkly stained fibres are conspicuous in the PALS (1) area arranged in parallel rows. The blood vessels continue in the surrounding splenic sinusoids (4). The wall of the sinusoid is built as a grid, the space is su... | sinusoid; reticular fibres | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
