The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
TO
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 101 |
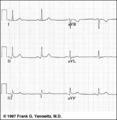 |
Frontal plane QRS axis = +30 degrees | Frontal plane QRS axis = +30 degrees | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 102 |
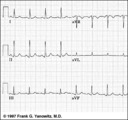 |
Frontal plane QRS axis = +50 degrees | 1) lead aVL is the smallest QRS and closest to being the isoelectric lead; 2) perpendiculars to aVL are +60 and -120 degrees; 3) lead I is positive; 4) therefore, the axis is closest to being +60 degrees. Because aVL is actually slightly positive, the axis is only about +50 degrees (i.e., slightly ... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 103 |
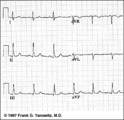 |
Frontal plane QRS axis = +75 degrees | Since there is no isoelectric lead in this ECG, the two closest leads are I and aVL. If I were isoelectric, the axis would be +90 degrees; if aVL were isoelectric, the axis would be +60 degrees. A nice compromize is +75 degrees. (The two closest leads are always 30 degrees apart.) | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 104 |
 |
Frontal plane QRS axis = +90 degrees | 1) Lead I is isoelectric; 2) perpendiculars to lead I are +90 and -90 degrees; 3) leads II, III, aVF are positive; 4) therefore, the axis must be +90 degrees. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 105 |
 |
Frontal plane QRS axis = -15 degrees | Frontal plane QRS axis = -15 degrees | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 106 |
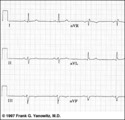 |
Frontal plane QRS axis = -45 degrees | Frontal plane QRS axis = -45 degrees | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 107 |
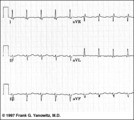 |
Frontal plane QRS axis = -45 degrees | Frontal plane QRS axis = -45 degrees | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 108 |
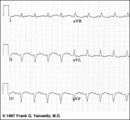 |
Frontal plane QRS axis = -75 degrees | Frontal plane QRS axis = -75 degrees | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 109 |
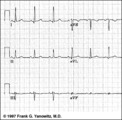 |
Frontal plane QRS axis = 0 degrees | Frontal plane QRS axis = 0 degrees | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 110 |
 |
Frontal plane QRS axis = 90 degrees | Frontal plane QRS axis = 90 degrees | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 111 |
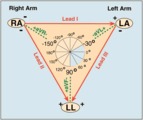 |
Frontal plane lead diagram | The six frontal plane leads are illustrated with their respective positive and negative poles.When forced to intersect at a center point, the six leads inscribe a 360 degree circle. The normal frontal plane axis is from -30 degrees to + 90 degrees, shaded in grey. Left axis deviation is from -30 d... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 112 |
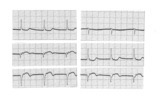 |
Frontal plane: accelerated junctional rhythm and inferior MI | Frontal plane: accelerated junctional rhythm and inferior MI | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 113 |
 |
Fully evolved inferior MI: frontal plane | Fully evolved inferior MI: frontal plane | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 114 |
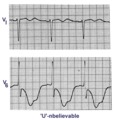 |
Giant TU fusion waves | TU fusion waves are often seen in long QT syndromes. The differential diagnosis of this ECG abnormality includes electrolyte abnormalities -hypokalemia, CNS disease, e.g., subarachnoid hemorrhage; hereditary long QT syndromes, and drugs such as quinidine. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 115 |
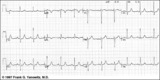 |
High lateral wall MI (seen in aVL) | High lateral wall MI (seen in aVL) | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 116 |
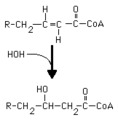 |
Hydration of an enoyl CoA | Hydration of the double bond is catalyzed by enoyl CoA hydratase. The product is an L-3-hydroxyacyl CoA. This reaction is a step in the beta-oxidation of fatty acids. | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids | |
| 117 |
 |
Hydroxymethylglutaryl CoA lyase reaction | In this mitochondrial process hydroxymethylglutaryl CoA is converted to acetoacetate, a ketone body. Acetyl CoA is another product. | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids | |
| 118 |
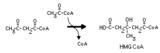 |
Hydroxymethylglutaryl CoA synthase reaction | This irreversible reaction occurs in the mitochondria, where it is the first step in ketone body synthesis. It also occurs in the cytoplasm, where it leads to isoprenoid and steroid synthesis. | Biosynthesis | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids |
| 119 |
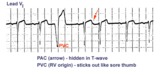 |
Identification of PVC's and PAC's | PVC's usually stick out like sore thumbs; PAC's are often difficult to see because they are hidden in the preceding ST-T wave. The PVC in this example is mostly negative in lead V1 suggesting RV origin; i.e., most of activation is moving in posterior direction towards the left ventricle. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 120 |
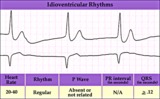 |
Idioventricular escape rhythm | Idioventricular escape rhythm | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 121 |
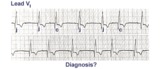 |
Incomplete AV dissociation due To 2nd degree AV block | 2nd degree AV block is evident from the nonconducted P waves. Junctional escapes, labled J, terminate the long pauses because that's the purpose of escape pacemakers....to protect us from too slow heart rates. All QRSs with shorter RR intervals are capture beats, labeled c. Atypical RBBB with a q... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 122 |
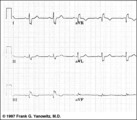 |
Indeterminate frontal plane QRS axis | Indeterminate frontal plane QRS axis | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 123 |
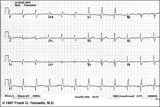 |
Inferior & Anteroseptal MI + RBBB | Pathologic Q waves are seen in leads II, III, aVF (inferior MI) and in leads V1-3 (anteroseptal MI). RBBB is recognized by the wide QRS (>0.12s) and the anterior/rightwards orientation of terminal QRS forces. When an anteroseptal MI complicates RBBB (or visa versa) the rSR' complex in V1 (typical ... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 124 |
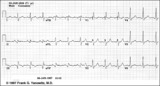 |
Inferior MI and RBBB | Inferior MI and RBBB | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 125 |
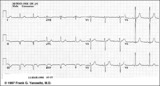 |
Inferior MI: fully evolved | Significant pathologic Q-waves are seen in leads II, III, aVF along with resolving ST segment elevation and symmetrical T wave inversion. This is a classic inferior MI. | Knowledge Weavers ECG |
