John A. Moran Eye Center Neuro-Ophthalmology Collection: A variety of lectures, videos and images relating to topics in Neuro-Ophthalmology created by faculty at the Moran Eye Center, University of Utah, in Salt Lake City.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
Filters: Collection: "ehsl_novel_jmec"
| Title | Description | Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 76 |
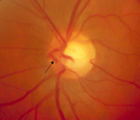 |
3-65 - Shunt Vessels (Glaucoma) | Chronic end-stage glaucoma produces high pressure that interferes with venous drainage from the disc and broad smooth venous collaterals drain the disc centrifugally to the disc margin where they drain. | Image |
| 77 |
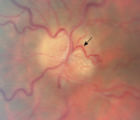 |
3-66a - Shunt Vessels (Post-papilledema) | The retino-choroidal collaterals seen with chronic papilledema begin with a "Hairnet" of telangiectasias that gradually winnow down to one or more large collateral tortuous draining channel. The presence of these vessels is evidence of long standing disc swelling. When the CSF pressure is lowered, t... | Image |
| 78 |
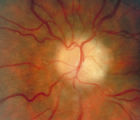 |
3-66d - Shunt Vessels (Post-papilledema) | The retino-choroidal collaterals seen with chronic papilledema begin with a "Hairnet" of telangiectasias that gradually winnow down to one or more large collateral tortuous draining channel. The presence of these vessels is evidence of long standing disc swelling. When the CSF pressure is lowered, t... | Image |
| 79 |
 |
4-35 - Cupped Optic Nerve | Atrophic Glaucoma Atrophic glaucomatous discs show thinning of the neuro-retinal rim, "saucerization" (which is shallow cupping), evidence of peripapillary atrophy, and pallor of the very narrow neuroretinal rim. Notice that there is severe atrophy of the nerve fiber layer. | Image |
| 80 |
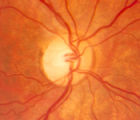 |
4-52b - Dominant Optic Neuropathy | A son presented with bilateral optic atrophy of unknown etiology after he failed a school visual exam. When looking for dominant optic atrophy, look at the parents. Mother was examined to find similar kind of atrophy. 4-52a mother, 4-52b son. | Image |
| 81 |
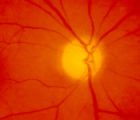 |
4-54a -Optic Neuropathy, Ischemic: Posterior | Image | |
| 82 |
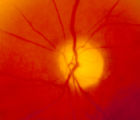 |
4-54b - Optic Neuropathy, Ischemic: Posterior | Image | |
| 83 |
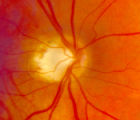 |
4-60a - Dominant Optic Neuropathy | A son presented with bilateral optic atrophy of unknown etiology after he failed a school visual exam. When looking for dominant optic atrophy, look at the parents. Mother was examined to find similar kind of atrophy. 4-60a mother, 4-60b son. | Image |
| 84 |
 |
A-scan Technique | This video describes and demonstrates the A-scan examination technique for examination of the eye using ultrasonography. | Image/MovingImage |
| 85 |
 |
Amsler Grid Testing | Demonstration of Amsler Grid examination. | Text |
| 86 |
 |
B-scan Technique | This video describes and demonstrates the B-scan examination technique for examination of the eye using ultrasonography. | Image/MovingImage |
| 87 |
 |
Basal Encephaloceles | Text | |
| 88 |
 |
Basic Headache | Presentation covering an overview of headache and migraine. | Text |
| 89 |
 |
Basic Eye Alignment Exam | Demonstration of basic eye alignment examination. Includes: a. Tools b. Cover-Uncover and SPCT c. Alternate Cover and APCT d. Maddox Rod Testing | Image/MovingImage |
| 90 |
 |
Duane's Syndrome Type 1 | Clip of patient with Duane's Syndrome Type I. Presented at the Neurology Grand Rounds in Fall 2011 at the University of Utah. Presentation can be found in this collection at: Why Don't You See Double? http://content.lib.utah.edu/u?/EHSL-Moran-Neuro-opth,132 Disease/Diagnosis: Duane's Syndrome Type ... | Image/MovingImage |
| 91 |
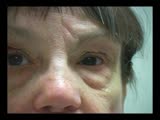 |
Duane's Syndrome Type 3 | Clip of patient with Duane's Syndrome Type III. Presented at the Neurology Grand Rounds in Fall 2011 at the University of Utah. Presentation can be found in this collection at: Why Don't You See Double? http://content.lib.utah.edu/u?/EHSL-Moran-Neuro-opth,132 Disease/Diagnosis: Duane's Syndrome Ty... | Image/MovingImage |
| 92 |
 |
Why Don't You See Double? | This presentation was given at the Neurology Grand Rounds in Fall 2011 at the University of Utah. A number of Duane Syndrome cases are covered. Related video can be found in this collection at: Duane's Syndrome Type I: http://content.lib.utah.edu/u?/EHSL-Moran-Neuro-opth,130 Duane's Syndrome Type I... | Text |
| 93 |
 |
Color Vision Testing | Demonstration of color vision examination. | Text |
| 94 |
 |
Cone Dystrophy | PPT covering Cone Dystrophy - An inherited degeneration that presents between 10 - 30 years of age. Symptoms are decreased visual acuity, poor color vision, and sometimes light sensitivity. | Text |
| 95 |
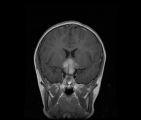 |
See-saw Nystagmus MRI 1 | MRI; See-saw Nystagmus | Image |
| 96 |
 |
Anterior Ischemic Optic Neuropathy | PPT describing Anterior Ischemic Optic Neuropathy (AION). Covers clinical signs, such as monocular vision loss, swollen nerve, and visual field defects, as well as risk factors. | Text |
| 97 |
 |
Dissection of the Carotid Artery | ||
| 98 |
 |
Exophthalmometry | Demonstration of exophthalmometry examination. | Text |
| 99 |
 |
Documenting the Neuro-ophthalmic Patient: External Photography | Description of documenting the neuro-ophthalmic patient using external photography. This covers pupils and extra ocular muscles. | |
| 100 |
 |
Structures of the iris | Structures of the iris. The a indicates the anterior border layer that terminates at the pigmentary ruff of the pupillary border (b). The c indicates the iris sphincter muscle, which is oriented circumferentially within the stroma and located deep to the anterior border layer; d indicates vessels th... | Image |
