John A. Moran Eye Center Neuro-Ophthalmology Collection: A variety of lectures, videos and images relating to topics in Neuro-Ophthalmology created by faculty at the Moran Eye Center, University of Utah, in Salt Lake City.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
Filters: Collection: "ehsl_novel_jmec"
| Title | Description | Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 76 |
 |
Dysthyroid Optic Neuropathy: A Preventable Cause of Blindness | Dysthyroid Optic Neuropathy (DON) is a treatable cause of visual loss in ~5% of pts w/ ted. Monitor closely those pts with risk factors (proptosis, tight orbit, restricted motility, strabismus, smoker, diabetic). Oral prednisone is often effective, but frequent relapses after tapering. Orbital xrt ... | |
| 77 |
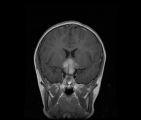 |
See-saw Nystagmus MRI 1 | MRI; See-saw Nystagmus | Image |
| 78 |
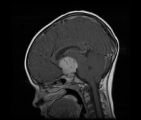 |
See-saw Nystagmus MRI 2 | MRI; See-saw Nystagmus | Image |
| 79 |
 |
Why Don't You See Double? | This presentation was given at the Neurology Grand Rounds in Fall 2011 at the University of Utah. A number of Duane Syndrome cases are covered. Related video can be found in this collection at: Duane's Syndrome Type I: http://content.lib.utah.edu/u?/EHSL-Moran-Neuro-opth,130 Duane's Syndrome Type I... | Text |
| 80 |
 |
B-scan Technique | This video describes and demonstrates the B-scan examination technique for examination of the eye using ultrasonography. | Image/MovingImage |
| 81 |
 |
Ultrasonography Techniques | This video describes and demonstrates the various techniques for examination of the eye using ultrasonography, including A-scan, B-scan and immersion. | Image/MovingImage |
| 82 |
 |
Ultrasonography: Immersion Technique | This video describes and demonstrates the immersion technique for examination of the eye using ultrasonography. | Image/MovingImage |
| 83 |
 |
The Orbital Exam | Comprehensive demonstration of the entire orbital examination. | |
| 84 |
 |
Fluoresein Angiography | Comprehensive description of using fluoresein angiography in examinations. | |
| 85 |
 |
Clover-leaf Visual Field Defects | Description of clover-leaf visual field defects. | |
| 86 |
 |
The Wall-Eyed Potato Farmer | Young man presenting with apparent episodic neurologic evants that initially was thought to be multiple sclerosis, but as time went on, he had progressive changes in his neurologic exam and in his imaging findings. Brain biopsy revealed Gliomatosis cerebri. Anatomy: Brain Stem; Pons; Midbrain. Patho... | |
| 87 |
 |
Introduction to Fogging Refraction | An introduction to fogging refraction. | |
| 88 |
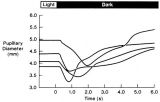 |
Pupillogram Demonstrating Paradoxical Pupillary Constriction to Darkness | Pupillogram demonstrating paradoxical pupillary constriction to darkness in four patients with congenital achromatopsia. Note that the pupils initially constrict when the light is extinguished. (Price MJ, Thompson HS, Judisch GF et al: Pupillary constriction to darkness. Br J Ophthalmol 1981;69:205-... | Image |
| 89 |
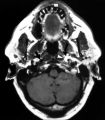 |
Left-sided Internal Carotid Artery Dissection | Left-sided internal carotid artery dissection identified on T-1 weighted magnetic resonance image from a 52-year-old man who suddenly developed left-sided neck and orbital pain along with a droopy left upper eyelid while dragging a deer out of the woods during hunting season. The normal dark flow vo... | Image |
| 90 |
 |
How to Use the Direct Ophthalmoscope in an Exam | Demonstration of using the direct ophthalmoscope to examine the optic disc. Covers hand placement , which eye to use, and distance from patient. | Image/MovingImage |
| 91 |
 |
Tour of the Direct Ophthalmoscope | This clip describes the parts and operation of the ophthalmoscope as an ocular examination tool. Includes adjustment of aperture size and adjustment of lenses. | Image/MovingImage |
| 92 |
 |
Cochet-Bonnet Esthesiometer (similar to Von Frey Hair) Exam | The Cochet-Bonnet esthesiometer , similar to Von Frey Hair testing, has been used in studies to quantify sensory changes in the trigeminal system, especially the cornea. The device uses a thin fiber to test sensation. The shorter the fiber, the more sensation is felt. The monofilament is applied per... | |
| 93 |
 |
Amsler Grid Testing | Demonstration of Amsler Grid examination. | Text |
| 94 |
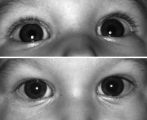 |
Right-sided Pseudo-Horner's Syndrome | Right-sided pseudo-Horner's syndrome in an 8-month-old infant referred because her mother had noted a larger pupil on the left for a few months and her pediatrician thought the right upper lid was droopy. Both pupils reacted normally to light and darkness, the degree of anisocoria was similar in bot... | Image |
| 95 |
 |
Tour of the Fundus | This clip demonstrates the funduscopic examination technique. | Image/MovingImage |
| 96 |
 |
Fusional Vergence Amplitudes | Demonstration of fusional vergence amplitudes examination. Incluudes: a. Convergence Amplitudes b. Divergence Amplitudes c. Vertical Ampitudes | Text |
| 97 |
 |
Gaze Palsy with Facial Weakness from Pontine AVM | Example of a patient with torsional nystagmus in both eyes and pendular nystagmus in the left eye. Patient is led through instructions for direction of gaze. | Image/MovingImage |
| 98 |
 |
Exophthalmometry | Demonstration of exophthalmometry examination. | Text |
| 99 |
 |
Pupil Exam | Demonstration of pupil examination. | Text |
| 100 |
 |
Color Vision Testing | Demonstration of color vision examination. | Text |
