The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
TO
Filters: Collection: "ehsl_heal"
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 76 |
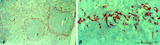 |
: Localization of ED3-positive subpopulation of macrophages in spleen (rat) | Stain: Immunohistochemistry of Vector red staining using the antibody ED3. The survey in (A) shows that the ED3-positive macrophages are found as a ring in the marginal zone border, as well as spread in the red pulp area (2). The cells are sometimes referred as marginal metallophilic macrophages. T... | metallophilic macrophages; ED3 antibody; marginal zone | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 77 |
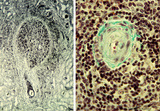 |
Spleen with central artery in lymphatic nodule (human) | Stain: A: Silver stain (Gomori). B: Trichrome (Goldner). In A: the reticular fibers (2) around the PALS (periarteriolar lymphatic sheath) and continuing in and around the marginal zone are stained black, illustrating the reticular framework of the lymphatic nodule. (1) central arteries. (4) red pulp... | central artery; PALS; white pulp; T cells | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 78 |
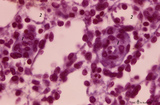 |
Macrophage-sheathed capillaries in spleen (human) | Azan. The branching of each penicillar arteriole gives rise to capillaries and a slow-down of the blood stream. In certain regions monocyte-derived macrophages leave the capillary and enter its wall where they develop into macrophages. Together with the present reticular cells these cell accumulatio... | macrophage-sheathed capillaries; penicillar arterioles; sinusoid | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 79 |
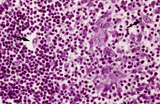 |
Medulla of thymus (human, puberty) | Stain: Hematoxylin. The light-stained medulla consists of a loosened framework of epithelial reticular cells, macrophages, thymocytes and capillaries. Accumulations of a specialized type of epithelial reticular cells (1) are localized between the thymocytes. These clusters represent precursors of fu... | thymic corpuscle (Hassalls); epithelioreticular cell (ERC); thymus medulla; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 80 |
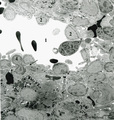 |
Splenic venous sinusoid in red pulp (rat) | Immunoelectron microscopy (gold labeling of heparan sulfate in Lowicryl embedding, using the single chain antibody HS4C3). (1) shows the open lumen of a venous sinusoid filled with few electron-dense erythrocytes and lining cells (2). (3) marks a neutrophilic granulocyte. (4) points to the diaped... | sinusoid; immuno electron microscopy; heparan sulfate | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 81 |
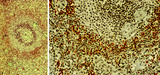 |
Secondary lymphatic nodule in the spleen (human) | Stain: Trichrome (Goldner). A: Survey of a follicle in the spleen. B: a higher magnification of a similar section shows part of a lymphatic nodule (follicle, white pulp) with cross-sections of the central artery (6). (1) germinal centre (filled with reticular cells, B-memory lymphocytes and macroph... | white pulp; PALS; germinal center; marginal zone | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 82 |
 |
Immunoperoxidase stained CD8 positive T cells in spleen (rat) | Stain: Immunoperoxidase staining using diaminobenzidin (DAB)/ hematoxylin counterstained on frozen section with anti-CD8 antibodies. A, B and C show brown-stained CD8-positive T cells or Tc cells at different enlargements. The CD8 Tc/s cells are localised predominantly in the PALS area (1), while th... | CD8 lymphocytes; immunohistochemistry; PALS | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 83 |
 |
Thymus (human, fetus) | Stain: Silver stain (Gomori). Reticular fibers are demonstrated in the interlobular septa in the thymic cortical area (2) of this lobule. In the medulla (1) the more loosened reticular framework is more distinct. The reticular fibers are produced by the epithelioreticular cells and are particular ... | thymic corpuscle (Hassalls); epithelioreticular cell (ERC); reticular fibers; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 84 |
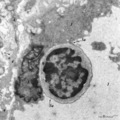 |
Thymus cortex (rat, young adult) | Electron microscopy. Type I epithelioreticular cells (4) separate connective tissue compartment (capsule, trabeculae, blood vessels) from the thymic parenchyma. At the left the capsule is bordered by a basal lamina (4a) of two projections (4) of type I epithelioreticular cells. Close to them, part o... | lymphoid tissue ; epithelioreticular cell type I; diapedesis | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 85 |
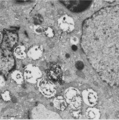 |
Thymus cortex (rat, young adult) | Electron microscopy. Two epithelioreticular cells type II or TEC2 (1) show the characteristic vacuoles (*) partly filled with granules (thymulin, lymphokines). At (--><--) small desmosomes. Apart from the mitochondria electron-dense lysosomal structures are present as well as tonofilaments (1, kera... | epithelioreticular cell II ; desmosome; MHC-II expression; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 86 |
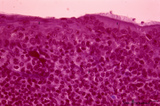 |
Detail of pharyngeal tonsils (human) | Stain: Azan. In contrast to the palatine and lingual tonsils, the epipharyngeal tonsil has a ciliated epithelium (1). Islands of multilayered squamous epithelium may interrupt it (transition zone, 2). The epithelium may be infiltrated with lymphocytes. The surface of this tonsil can be enlarged by m... | pharyngeal tonsil; GALT; squamous epithelium; ciliated epithelium | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 87 |
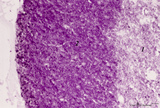 |
Thymus cortex (mouse, young adult) | Stain: Hematoxylin. Autoradiography after pulse labeling with tritiated thymidin. Most of the (black) radioactive labeling is found in the outer thymic cortex (3) where pre-T cells divide and subsequently migrate to the lighter stained medulla (1) that consists of a more loosened framework of epith... | thymus cortex; thymus medulla; thymidin labeling; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 88 |
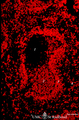 |
Localization of B cells in spleen (rat) | Stain: Immunofluorescence of Vector red using Mark-1 antibody against B cells. The T cells in the PALS (periarteriolar lymphatic sheath) remain unstained (1, dark). The red-stained B cells are packed in the germinal centre (2), the corona (3) or mantle layer that diffuses into the marginal zone and... | B lymphocytes; immunofluorescence; PALS | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 89 |
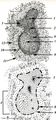 |
Scheme of secondary lymphatic nodule in spleen (human) | A. histological impression of a follicle or nodule B. outline of impression 1. pulpa artery; 2. central artery ; 3. lymphatic sheath; 4. lymphatic nodule; 5. thymus-dependent area (periarteriolar lymphatic sheath or PALS), composed of Th subset lymphocytes; 6. mantle zone with mainly nave B l... | white pulp; marginal zone; antigen presenting cell (APC) | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 90 |
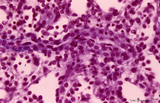 |
Splenic sheathed capillaries (human) | Stain: Azan. The blood flow in the spleen goes from splenic artery to trabecular artery to central or follicular artery (with a periarteriolar lymphatic sheath or PALS), and upon leaving the follicle the blood flows through penicillar arterioles and sheathed capillaries and terminal arterial capilla... | penicillar arterioles; red pulp; sheathed capillaries | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 91 |
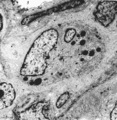 |
Thymus medulla (rat, neonate) | Electron microscopy. An interdigitating cell in the thymic corticomedullary region shows a large electron-light cytoplasm with a complex branching (7) at the periphery. The nucleus is sectioned twice (1). There is abundance of organelles as well as of quite uniform electron-dense lysosomal structure... | medullar epithelioreticular cell; interdigitating cell; corticomedullar region; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 92 |
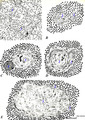 |
Scheme of the thymus medulla (human) | A-B: medullar epithelioreticular cells; C-D-E: development stages of thymic corpuscles (or Hassall bodies) (1): branching (-->) epithelioreticular cells in the medulla forming a meshwork (cytoreticulum) that normally is populated by thymocytes; (2): specialized epithelioreticular cells (2) often... | thymic corpuscle; Hassall ; epithelioreticular cells ; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 93 |
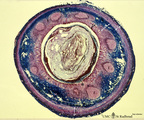 |
Appendix ('gut-associated lymphatic tissue' or GALT) (human) | Stain: Azan. Survey of vermiform appendix (see also Digestive System: Appendix) A large amount of non-encapsulated diffuse lymphatic tissue or mucosa-associated lymphatic tissue (MALT) is located in the subepithelial lamina propria/submucosa of the appendix and called gut-associated lymphatic tissue... | GALT; follicle; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 94 |
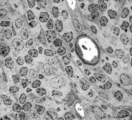 |
Survey of part of splenic lymphatic nodule (rat) | Electron microscopy. (1) shows an arteriolar branch of a central artery, and cross-sections of capillary branches (1a). Within the periarteriolar lymphatic sheath (PALS) mostly T lymphocytes (5) are present between concentric arranged reticular cells (2). Cells with larger lighter stained nuclei rep... | central artery ; electron microscopy; PALS; Antigen presenting cells (APC) | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 95 |
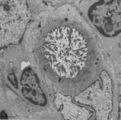 |
Cystic corpuscle in thymus (mouse, young adult) | Electron microscopy. This cystic corpuscle is lined by specialized epithelioreticular cells and exhibits a lumen (1) which is filled with long microvilli however, curiously derived from a flattened epithelial cell (2, nucleus). The cell contains few electron-dense keratohyalin granules (3). (-->) po... | epithelioreticular cells; thymic corpuscle; thymic cyst; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 96 |
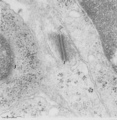 |
Thymus cortex (mouse, young adult) | Electron microscopy. (1) A well developed desmosome (1) of an epithelioreticular cells type II (TEC2). Apart from few free ribosomes, glycogen granules (2) are present in the electron-light cytoplasm. (3) part of an electron-grey thymocyte with many ribosomes. | epithelioreticular cell type II ; desmosome; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 97 |
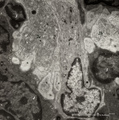 |
Dendritic cells in spleen (mouse) | Electron microscopy. The interdigitations (*) of the left dendritic cells (antigen-presenting cell or APC) (1 and 2a) are clearly shown. The right (2b) is a neighbour dendritic cell sectioned at the level of the Golgi area. (3) lymphocyte and (4) reticular cell. | electron microscopy; dendritic cell | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 98 |
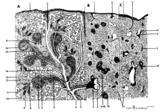 |
Scheme of the spleen (human) | Spleen: A. general diagram; B. adult; C. senium 1. capsule of dense irregular connective tissue with few elastic and smooth muscle fibers (it varies with the species); 2. trabecula (septum); 3. trabecular artery derived from the splenic artery; 4. trabecular vein; 5. when the pulpa artery ... | white pulp; red pulp | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 99 |
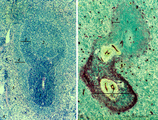 |
White pulp of spleen (mouse) | Stain: Hematoxylin & eosin in A and alkaline phosphatase in B (with substrate Naphtol Fast Blue RR). The general structure of the white pulp of the spleen and its specific microenvironment for T and B cells is well illustrated using alkaline phosphatase that strongly stains the capillaries around th... | alkaline phosphatase; PALS; T lymphocytes; white pulp | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 100 |
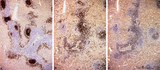 |
The effect of cyclophosphamide treatment on the B and T cells in spleen (rat) | Stain: Immunoperoxidase staining using diaminobenzidin (DAB)/ hematoxylin counterstained on frozen section with antibodies to B cells (Mark 1), CD3 and CD8 T cells. (A): B cells in the follicles, germinal centres (2) and corona are stained positive brown, while the PALS area (1) is negative (blue)... | CD3 lymphocytes; CD8 lymphocytes; B lymphocytes; cyclophosphamide | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
