The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
TO
Filters: Format: "image/png" Collection: ehsl_heal
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 76 |
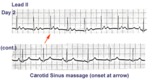 |
ECG of the century - part II: dual AV pathways | An astute cardiology fellow, yours truly, went to the patient's bedside on Day 2 and massaged the right carotid sinus as indicated by the arrow. Four beats later at a slightly slower heart rate the PR interval suddenly normalized suggesting an abrupt change from a slow AV nodal pathway to a fast AV... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 77 |
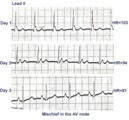 |
ECG of the century: A most unusual 1st degree AV block | On Day 1, at a heart rate of 103 bpm the P waves are not clearly defined suggesting an accelerated junctional rhythm. However, on Day 2, at a slightly slower heart rate the sinus P wave suddenly appears immediately after the QRS complex. In retrospect, the sinus P wave in Day 1 was found burried i... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 78 |
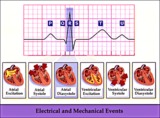 |
Electrical and mechanical events diagram - marquette | Electrical and mechanical events diagram - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 79 |
 |
Electronic atrial pacing - marquette | Electronic atrial pacing - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 80 |
 |
Electronic ventricular pacemaker rhythm - marquette | Electronic ventricular pacemaker rhythm - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 81 |
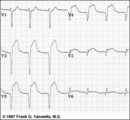 |
Extensive anterior/anterolateral MI: precordial leads | Extensive anterior/anterolateral MI: precordial leads | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 82 |
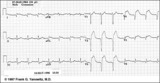 |
Extensive anterior/anterolateral MI: recent | Significant pathologic Q-waves (V2-6, I, aVL) plus marked ST segment elevation are evidence for this large anterior/anterolateral MI. The exact age of the infarction cannot be determined without clinical correlation and previous ECGs, but this is likely a recent MI. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 83 |
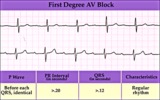 |
First degree AV block - marquette | First degree AV block - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 84 |
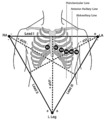 |
Frontal and horizontal plane lead diagram | Frontal and horizontal plane lead diagram | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 85 |
 |
Frontal plane QRS axis = +15 degrees | Frontal plane QRS axis = +15 degrees | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 86 |
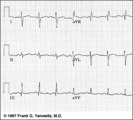 |
Frontal plane QRS axis = +150 degrees (RAD) | This is an unusual right axis deviation (RAD). Lead I is negative, which usually means RAD. Lead II is the isoelectric lead, which almost always means -30 degrees; but in this example the axis is 180 degrees away from -30, or +150 degrees. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 87 |
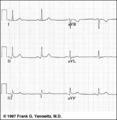 |
Frontal plane QRS axis = +30 degrees | Frontal plane QRS axis = +30 degrees | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 88 |
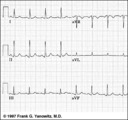 |
Frontal plane QRS axis = +50 degrees | 1) lead aVL is the smallest QRS and closest to being the isoelectric lead; 2) perpendiculars to aVL are +60 and -120 degrees; 3) lead I is positive; 4) therefore, the axis is closest to being +60 degrees. Because aVL is actually slightly positive, the axis is only about +50 degrees (i.e., slightly ... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 89 |
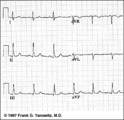 |
Frontal plane QRS axis = +75 degrees | Since there is no isoelectric lead in this ECG, the two closest leads are I and aVL. If I were isoelectric, the axis would be +90 degrees; if aVL were isoelectric, the axis would be +60 degrees. A nice compromize is +75 degrees. (The two closest leads are always 30 degrees apart.) | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 90 |
 |
Frontal plane QRS axis = +90 degrees | 1) Lead I is isoelectric; 2) perpendiculars to lead I are +90 and -90 degrees; 3) leads II, III, aVF are positive; 4) therefore, the axis must be +90 degrees. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 91 |
 |
Frontal plane QRS axis = -15 degrees | Frontal plane QRS axis = -15 degrees | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 92 |
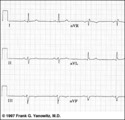 |
Frontal plane QRS axis = -45 degrees | Frontal plane QRS axis = -45 degrees | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 93 |
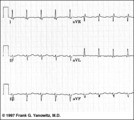 |
Frontal plane QRS axis = -45 degrees | Frontal plane QRS axis = -45 degrees | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 94 |
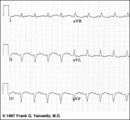 |
Frontal plane QRS axis = -75 degrees | Frontal plane QRS axis = -75 degrees | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 95 |
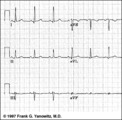 |
Frontal plane QRS axis = 0 degrees | Frontal plane QRS axis = 0 degrees | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 96 |
 |
Frontal plane QRS axis = 90 degrees | Frontal plane QRS axis = 90 degrees | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 97 |
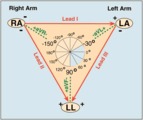 |
Frontal plane lead diagram | The six frontal plane leads are illustrated with their respective positive and negative poles.When forced to intersect at a center point, the six leads inscribe a 360 degree circle. The normal frontal plane axis is from -30 degrees to + 90 degrees, shaded in grey. Left axis deviation is from -30 d... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 98 |
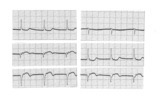 |
Frontal plane: accelerated junctional rhythm and inferior MI | Frontal plane: accelerated junctional rhythm and inferior MI | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 99 |
 |
Fully evolved inferior MI: frontal plane | Fully evolved inferior MI: frontal plane | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 100 |
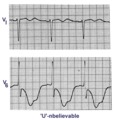 |
Giant TU fusion waves | TU fusion waves are often seen in long QT syndromes. The differential diagnosis of this ECG abnormality includes electrolyte abnormalities -hypokalemia, CNS disease, e.g., subarachnoid hemorrhage; hereditary long QT syndromes, and drugs such as quinidine. | Knowledge Weavers ECG |
