The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
TO
Filters: Collection: "ehsl_heal"
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 51 |
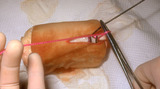 |
Suturing | The short arm of the suture is then grasped with the needle holder, and then the non-dominant (left) hand crosses over the right hand as one tightens the knot pulling along the long axis of the wound. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 52 |
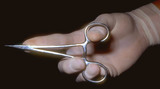 |
Needle holder | The needle holder (sometimes called needle driver) can be held as shown, or | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 53 |
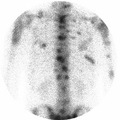 |
Metastatic prostatic carcinoma | Metastatic prostatic carcinoma | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 54 |
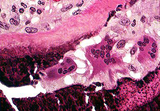 |
Renal osteodystrophy | Renal osteodystrophy | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 55 |
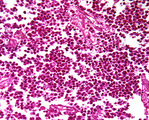 |
Testis seminoma | Testis seminoma | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 56 |
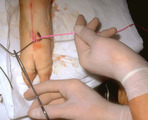 |
Excision procedure | This suture is tightened by crossing the non-dominant (left) and over the dominant (right) hand. This same sequence is continued until four loops have been thrown and then the suture is cut leaving ends approximately .5 cm long. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 57 |
 |
Skin tags | Skin tags. They are rather small, and have a pedunculated base giving them the appearance of a teardrop. | Skin Tags | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology |
| 58 |
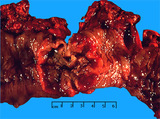 |
Adenocarcinoma, colon | Adenocarcinoma, colon | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 59 |
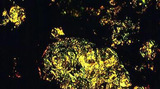 |
Medullary carcinoma | Medullary carcinoma | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 60 |
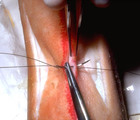 |
Suturing | I exit through the other side of the wound as superficially and closely as possible to the wound edge. Generally, I am about a mm away from the wound edge, and just barely entering the dermis. It is crucial to be as superficial within the dermis and as close to the wound edge on the second pass as i... | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 61 |
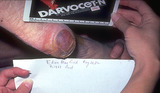 |
Necrosis | The purple/red area on the heel is an area of necrosis of the entire epidermis and dermis that is induced by the person lying in one position for too long. Again, the entire epidermis and dermis are necrotic, and need to be surgically removed. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 62 |
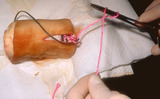 |
Excision: suturing | The needle holder is then placed inside the long arm of the V, and a single loop is thrown around the needle holder. The short arm of the suture is then grasped. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 63 |
 |
Excision procedure | The central specimen is then removed ensuring that there is same thickness throughout the specimen. | Surgical Methods | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology |
| 64 |
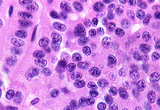 |
Islet cell carcinoma | Islet cell carcinoma | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 65 |
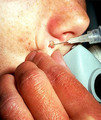 |
Shave technique | This demonstrates the shave technique. Local anesthetic can be injected into the fat beneath the target lesion, or within the lesion itself. One should be extremely careful to inject as little anesthetic as necessary to anesthetize the skin, because the anesthetic will artifactually enlarge and dist... | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 66 |
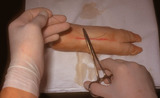 |
Suturing | This demonstrates placing the needle holder on the inside of the long arm of the V using actual suture. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 67 |
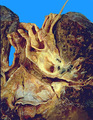 |
Bronchogenic carcinoma | Bronchogenic carcinoma | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 68 |
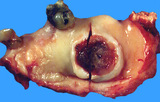 |
Hard palate carcinoma | Hard palate carcinoma | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 69 |
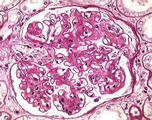 |
Diabetes mellitus | Diabetes mellitus | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 70 |
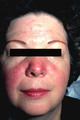 |
Rosacea | The typical appearance of a patient with rosacea. The patient usually has underlying erythema on the nose and cheeks, and generally has superimposed red papules and pustules on these areas. The first stage of rosacea consists of only erythema, and the second stage consists of the superimposed red pa... | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 71 |
 |
Excision: suturing | A single loop is thrown around the needle holder. The short arm of the suture is then grasped. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 72 |
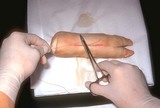 |
Suturing | This demonstrates a single loop of suture thrown around the needle holder. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 73 |
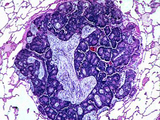 |
Metastatic colon adenocarcinoma | Metastatic colon adenocarcinoma | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 74 |
 |
Epinephrine | If a patient is on beta-blockers and experiences severe urticaria or anaphylaxis, often epinephrine does not work. Glucagon can be used in lieu of epinephrine, and generally 1 mg (regardless of body size) is given in the subcutaneous fat | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 75 |
 |
Prolactinoma | Prolactinoma | Knowledge Weavers Pathology |
