John A. Moran Eye Center Neuro-Ophthalmology Collection: A variety of lectures, videos and images relating to topics in Neuro-Ophthalmology created by faculty at the Moran Eye Center, University of Utah, in Salt Lake City.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
| Title | Description | Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 26 |
 |
Hand-held Equipment Used to Measure a Relative Afferent Pupillary Defect | Hand-held equipment used to measure a relative afferent pupillary defect and to record pupil sizes. Four neutral density filters (0.3, 0.6, 0.9, 1.2 log units) are conveniently carried in a soft cloth carrying pouch. A bright light source (a Finhoff model illuminator is shown here) is ideal for stim... | Image |
| 27 |
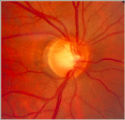 |
Notching of the Neuro-retinal Rim | The neuro-retinal rim becomes thinner; in particular the rim superotemporally and inferortemporally may develop a notch which is usually superior or inferior and rarely nasal or temporal. These notches are believed to be due to focal ischemic damage to the neuro-retinal rim. Glaucoma with Notching a... | Image |
| 28 |
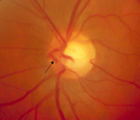 |
3-65 - Shunt Vessels (Glaucoma) | Chronic end-stage glaucoma produces high pressure that interferes with venous drainage from the disc and broad smooth venous collaterals drain the disc centrifugally to the disc margin where they drain. | Image |
| 29 |
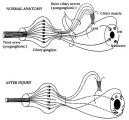 |
Pathophysiology of Signs Associated with a Tonic Pupil | Pathophysiology of signs associated with a tonic pupil. Normally, all parasympathetic fibers of the third cranial nerve synapse in the ciliary ganglion (top). Most postganglionic fibers innervate the ciliary muscle (dashed lines). After injury to the ciliary ganglion, the pupil becomes denervated an... | Image |
| 30 |
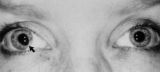 |
Tadpole-shaped Pupil | Tadpole-shaped pupil in a 20-year-old women with frequent episodes of blurred vision and achiness of the right eye lasting several minutes. The patient took a photograph of her eyes during an attack to document the peaked, segmental dilation of her right pupil (black arow). (Thompson HS, Zackon DH, ... | Image |
| 31 |
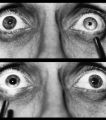 |
Right-sided Relative Afferent Pupillary Defect | Right-sided relative afferent pupillary defect in a man with optic nerve glioma. When the unaffected left eye is stimulated by light, both pupils constrict (top). When the light is then swung over to the affected right eye, both pupils dilate (bottom). This indicates that pupillomotor conduction thr... | Image |
| 32 |
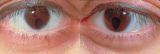 |
Bilateral Iris Colobomas | Coloboma literally means a "gap"-and can be used to describe any fissure, hole, or gap in the eye. The term most often is used to refer to a congenital gap in the disc, retina, the choroid, and the iris. Colobomas occur because the embryonic fissure fails to fuse. Since the fissure closure begins in... | Image |
| 33 |
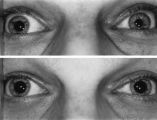 |
Left-sided Dilation Lag in a Man with Horner's Syndrome | Left-sided dilation lag in a 29-year-old man with Horner's syndrome caused by a posterior mediastinal ganglioneuroma. Note that the degree of anisocoria is greater after 5 seconds in darkness (top) compared with findings after 15 seconds in darkness (bottom). | Image |
| 34 |
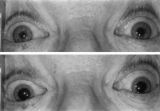 |
Enhanced Mydriasis in Response to Hydroxyamphetamine | Enhanced mydriasis in response to hydroxyamphetamine in a 77-year-old woman with a long-standing, preganglionic, right-sided Horner's syndrome that occurred following cervical neck dissection for thoracic outlet syndrome 30 years earlier. Miosis of the right pupil is apparent in room light (top). Th... | Image |
| 35 |
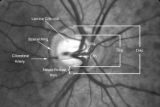 |
2-4a - Disc Anatomy | The optic disc appearance is determined by: the size of the eye, the size of the scleral canal, how the nerve is inserted into the globe, the appearance of the lamina cribrosa, where myelination stops, and what is left behind in normal development. Even though this is a disc with a very large cup, i... | Image |
| 36 |
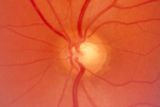 |
2-53a - Venous Pulsations | On the disc, look for spontaneous venous pulsations. Spontaneous venous pulsations can be seen in the large trunks of veins at the level of the disc margin. They are normally present and seen in 37-90% of normals -- depending on the experience of the examiner and the shape of the disc. The spontaneo... | Image |
| 37 |
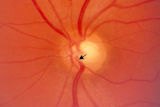 |
2-53b - Venous Pulsations | On the disc, look for spontaneous venous pulsations. Spontaneous venous pulsations can be seen in the large trunks of veins at the level of the disc margin. They are normally present and seen in 37-90% of normals -- depending on the experience of the examiner and the shape of the disc. The spontaneo... | Image |
| 38 |
 |
2-6a - Little Red Discs | Image | |
| 39 |
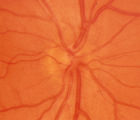 |
2-6b - Little Red Discs | Image | |
| 40 |
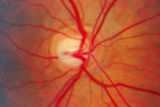 |
2-7a - Disc Anatomy | The optic disc appearance is determined by: the size of the eye, the size of the scleral canal, how the nerve is inserted into the globe, the appearance of the lamina cribrosa, where myelination stops, and what is left behind in normal development. Even though this is a disc with a very large cup, i... | Image |
| 41 |
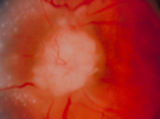 |
3-56a - Sarcoid | Image | |
| 42 |
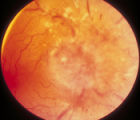 |
3-59a - Glioma | This 45-year-old man presented with vision loss in his right eye; his examination showed severe disc swelling in this eye and vision loss on visual field testing (3-59a). MRI with fat saturation and enhancement and MRI with T2 signals also confirm an enlarged optic nerve. (3-59c) Excisional biopsy o... | Image |
| 43 |
 |
3-59c - Glioma | This 45-year-old man presented with vision loss in his right eye; his examination showed severe disc swelling in this eye and vision loss on visual field testing (3-59a). MRI with fat saturation and enhancement and MRI with T2 signals also confirm an enlarged optic nerve. (3-59c) Excisional biopsy o... | Image |
| 44 |
 |
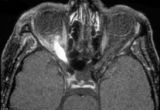
3-60a - Meningioma | This 35 year old woman presented with slowly progressive loss of central acuity to 20/30. 3-60a: Her visual field shows progressive restriction over time. 3-60b: Her disc was chronically swollen, with refractile bodies on the disc surface. 3-60d: The CT axial scan showed an enlarged calcified optic... | Image |
| 45 |
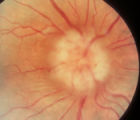 |
3-60b - Meningioma | This 35 year old woman presented with slowly progressive loss of central acuity to 20/30. 3-60a: Her visual field shows progressive restriction over time. 3-60b: Her disc was chronically swollen, with refractile bodies on the disc surface. 3-60d: The CT axial scan showed an enlarged calcified optic... | Image |
| 46 |
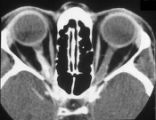 |
3-60d - Meningioma | This 35 year old woman presented with slowly progressive loss of central acuity to 20/30. 3-60a: Her visual field shows progressive restriction over time. 3-60b: Her disc was chronically swollen, with refractile bodies on the disc surface. 3-60d: The CT axial scan showed an enlarged calcified optic... | Image |
| 47 |
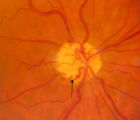 |
3-64a - Shunt Vessels (CRVO) | This man with a chronic CRVO and retino-choroidal collaterals developed AION and his collaterals disappeared. CRVO with retinochoroidal collaterals is almost always associated with multiple peripheral dot and blot hemorrhages as well as nerve fiber layer infarcts of various ages. Notice the retino-c... | Image |
| 48 |
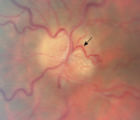 |
3-66a - Shunt Vessels (Post-papilledema) | The retino-choroidal collaterals seen with chronic papilledema begin with a "Hairnet" of telangiectasias that gradually winnow down to one or more large collateral tortuous draining channel. The presence of these vessels is evidence of long standing disc swelling. When the CSF pressure is lowered, t... | Image |
| 49 |
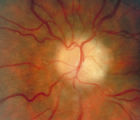 |
3-66d - Shunt Vessels (Post-papilledema) | The retino-choroidal collaterals seen with chronic papilledema begin with a "Hairnet" of telangiectasias that gradually winnow down to one or more large collateral tortuous draining channel. The presence of these vessels is evidence of long standing disc swelling. When the CSF pressure is lowered, t... | Image |
| 50 |
 |
4-35 - Cupped Optic Nerve | Atrophic Glaucoma Atrophic glaucomatous discs show thinning of the neuro-retinal rim, "saucerization" (which is shallow cupping), evidence of peripapillary atrophy, and pallor of the very narrow neuroretinal rim. Notice that there is severe atrophy of the nerve fiber layer. | Image |
