John A. Moran Eye Center Neuro-Ophthalmology Collection: A variety of lectures, videos and images relating to topics in Neuro-Ophthalmology created by faculty at the Moran Eye Center, University of Utah, in Salt Lake City.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
Filters: Collection: "ehsl_novel_jmec"
| Title | Description | Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 26 |
 |
Dissection of the Carotid Artery | ||
| 27 |
 |
Macula | Overview of the structure and viewing of the macula. | Text |
| 28 |
 |
Mimics of Atrophy | Text | |
| 29 |
 |
Optic Nerve Tumors Benign and Malignant | Discussion of optic nerve tumors including meningioma and glioma. | Text |
| 30 |
 |
Retinal Fluorescein Angiography | This slide set provides a brief description of Retinal Fluorescein Angiography. First introduced in 1960, sodium fluorescein, a dye, is administered through an angiocatheter (3-5cc) by a nurse or technician. The dye reaches the central retinal artery after passing through the heart and lungs. | Text |
| 31 |
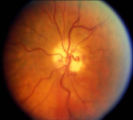 |
Shunt Vessel Meningioma | RETINO-CHOROIDAL (OPTO-CILIARY) COLLATERAL VESSELS: (also known as Retinal-choroidal venous collaterals, opticociliary veins or ciliary shunt vessels) Retino-choroidal collaterals are potential telangiectatic connections between the retina and choroidal circulation. Although sometimes called "shunts... | Image |
| 32 |
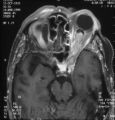 |
Shunt Vessel Meningioma - MRI | Meningiomas block venous egress and open potential venous channels known as retinochoroidal (optociliary) collateral vein. This meningioma extends from the back of the globe through the optic canal. | Image |
| 33 |
 |
Stargardt's Disease | Discussion of Stargardt's disease, an inherited maculopathy which frequently presents with a loss of central vision. | Text |
| 34 |
 |
Third Nerve Palsy | Patient with third nerve palsy (no audio) | Image/MovingImage |
| 35 |
 |
Tilted Discs | Short PowerPoint discussion of tilted discs with illustrations and images. | |
| 36 |
 |
Vestibular Nystagmus | Example of patient with vestibular nystagmus. Patient is led through instructions for direction of gaze. Shown also with Frenzel goggles. | Image/MovingImage |
| 37 |
 |
Abducting (Dissociated) Nystagmus | Example of a patient with abducting (dissociated) nystagmus. Patient has a subtle internuclear ophthalmoplegia. Right eye has right-beating jerk nystagmus, with smaller oscillations in the left eye. Disease/Diagnosis: Abducting Nystagmus | Image/MovingImage |
| 38 |
 |
Congenital Ocular Motor Apraxia | Two examples of congenital ocular motor apraxia. Patients have trouble initiating saccades, and compensate with head movement. Discussion of how to distinguish this condition from simply not seeing well. | Image/MovingImage |
| 39 |
 |
Dissociated Nystagmus | Example of a patient with dissociated nystagmus. Demonstrates difference in movements between each eye. | Image/MovingImage |
| 40 |
 |
Internuclear Ophthalmoplegia (2 Examples) | Two examples of patients with internuclear ophthalmoplegia. First patient has a right internuclear ophthalmoplegia. Patient had subacute bacterial endocarditis with a bacterial abscess in the brain stem. Ductions and gaze to the right look good, but when gazing to the left, the right eye does not ad... | Image/MovingImage |
| 41 |
 |
Latent Nystagmus | Example of a patient with latent nystagmus. Demonstrates a lack of oscillations in forward gaze, followed by the occlusion of each eye, showing how this generates a jerking oscillation in the non-occluded eye away from the occluded eye. | Image/MovingImage |
| 42 |
 |
Opsoclonus | Example of patients with opsoclonus, a saccadic abnormality. | Image/MovingImage |
| 43 |
 |
Paradoxical Constriction of Pupils to Darkness (Flynn Phenomenon) | Example of patients both with and without paradoxical constriction of pupils. Observed in many congenital retinal disorders, such as achromatopsia, congenital stationary night-blindness, and Leber's congenital amaurosis. Sometimes seen in optic nerve disorders, such as dominant optic atrophy. | Image/MovingImage |
| 44 |
 |
Physiologic (End-Gaze) Nystagmus | Demonstration of physiological nystagmus, where oscillations do not represent pathology, but occur when the patient's gaze is drawn too far laterally. | Image/MovingImage |
| 45 |
 |
Spasm of the Near Reflex | Example of patient with spasm of the near reflex and voluntary nystagmus. Discussion of similar-looking conditions (e.g. six nerve palsy, limitation of abduction, lateral rectus muscle problems) and how to tell them apart from spasm of the near reflex by observing the myosis evoked by the near respo... | Image/MovingImage |
| 46 |
 |
Transillumination Ocular Melanoma | Video describing condition. | Image/MovingImage |
| 47 |
 |
Upbeat Nystagmus | Example of a patient with upbeat nystagmus. Shows vertical jerk nystagmus with fast phases in the up direction. Localizes to brain stem, and occurs with strokes, demyelination, and tumors. | Image/MovingImage |
| 48 |
 |
Vestibular Nystagmus | Discussion of vestibular nystagmus. Seen with peripheral disorders and central disorders, and in two varieties: spontaneous and positional. Horizontal jerk with small amplitude. | Image/MovingImage |
| 49 |
 |
Aberrant Regeneration of the Third and Sixth Nerves | Image/MovingImage | |
| 50 |
 |
The Multifocal Electroretinogram: Clinical Applications | The most important development in ERGs is the multifocal ERG (mfERG). Erich Sutter adapted the mathematical sequences called binary m-sequences creating a program that can extract hundreds of focal ERGs from a single electrical signal. This system allows assessment of ERG activity in small areas of ... | Text |
