John A. Moran Eye Center Neuro-Ophthalmology Collection: A variety of lectures, videos and images relating to topics in Neuro-Ophthalmology created by faculty at the Moran Eye Center, University of Utah, in Salt Lake City.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
Filters: Collection: "ehsl_novel_jmec"
| Title | Description | Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 26 |
 |
Spontaneous Venous Pulsations | This clips shows a spontaneous venous pulsation viewed during an ocular examination. | Image/MovingImage |
| 27 |
 |
Duane's Retraction Syndrome Type 3 | Example of a patient with Type 3 Duane's Retraction Syndrome, as well as bilateral Duane's Syndrome. Shows limitation of abduction in both eyes and adduction in the left eye. Also shows side-view of globe retraction in abduction. | Image/MovingImage |
| 28 |
 |
Blepharospasm | Example of patient with blepharospasm. Patient is led through instructions for direction of gaze and opening and closing of eyes. Patient is led through same exercises again after receiving indomethacin treatment. | Image/MovingImage |
| 29 |
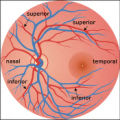 |
2-37a - Vascular Features | When looking at the disc, the central retinal artery and vein should be visible. The central retinal artery is usually slightly narrower than the vein. When the central retinal artery goes though the lamina cribrosa, the artery becomes smaller because of diminution of the muscular layer and loss of ... | Image |
| 30 |
 |
Bilateral Ptosis | Video of patient with bilateral ptosis. | Image/MovingImage |
| 31 |
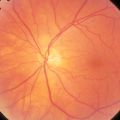 |
2-37b - Vascular Features | When looking at the disc, the central retinal artery and vein should be visible. The central retinal artery is usually slightly narrower than the vein. When the central retinal artery goes though the lamina cribrosa, the artery becomes smaller because of diminution of the muscular layer and loss of ... | Image |
| 32 |
 |
Central Retinal Artery Occlusion | Video of central retinal artery occlusion. | Image/MovingImage |
| 33 |
 |
Binocular Pendular Nystagmus | Example of a patient with binocular pendular nystagmus. Patient has somewhat dissociated nystagmus, with nystagmus seen more prominently in the left eye. Patient shows an occasional jerk nystagmus to the right in the right eye. Left eye oscillations are mostly pendular. | Image/MovingImage |
| 34 |
 |
Superior Oblique Myokymia | Close-up video of a patient with superior oblique myokymia (no audio.) | Image/MovingImage |
| 35 |
 |
Rebound Nystagmus | Example of a patient with rebound nystagmus, where the oscillations alternate direction as the patient shifts gaze in different directions. Discussion of relationship to disease and disorders of the cerebellum, including degenerations of the cerebellum, infarction, and demyelination. | Image/MovingImage |
| 36 |
 |
Brun's Nystagmus | Observation of patient with Brun's Nystagmus. Shows patient gazing to the right and the nystagmus beating in the direction of the gaze. | Image/MovingImage |
| 37 |
 |
Periodic Alternating Nystagmus | Example of a patient with periodic alternating nystagmus, showing an alternation between left-beats and right-beats as the patient maintains forward gaze. Nystagmus maintain horizontal direction regardless of position of gaze. | Image/MovingImage |
| 38 |
 |
Retraction Nystagmus | Patient with retraction nystagmus (no audio) | Image/MovingImage |
| 39 |
 |
Monocular Pendular Nystagmus | Example of a patient with monocular pendular nystagmus, with discussion of situations in which this condition is seen: acquired disorder of the visual-sensory pathway, and acquired disorder of the brain stem (e.g. multiple sclerosis). | Image/MovingImage |
| 40 |
 |
See-saw Nystagmus | Example of a patient with see-saw nystagmus, showing how one eye elevates as the other depresses, with the elevating eye intorting as the depressing eye extorts. Shows vertical oscillations with pendular waveforms. Suggests a large structural lesion in the pericellar region (associated with bi-tempo... | Image/MovingImage |
| 41 |
 |
Congenital Nystagmus | Example of patients with congenital nystagmus. First patient's nystagmus are mostly jerk and not pendular. Second patient's nystagmus are mostly pendular. Both patients show a uniform horizontal oscillation. Second patient also shows differences in frequency of oscillations depending on gaze, includ... | Image/MovingImage |
| 42 |
 |
Congenital Nystagmus | Patient with congenital nystagmus (no audio) | Image/MovingImage |
| 43 |
 |
Spasmus Nutans | Example of patient with spasmus nutans. Discussion of characteristics of this disorder, such as dissociated or monocular nystagmus, abnormal head position, and to-and-fro head oscillation. Sometimes an eccentric gaze is seen as well (as in patient). Patient has a monocular horizontal nystagmus in th... | Image/MovingImage |
| 44 |
 |
Rotary Nystagmus | Example of a patient with rotary nystagmus, showing occasional counterclockwise rotary movements of both eyes. Seen more in intrinsic disorders of the brainstem. | Image/MovingImage |
| 45 |
 |
Spasmus Nutans | Example of patient with spasmus nutans. | Image/MovingImage |
| 46 |
 |
Rotary Downbeat | Patient with rotary downbeat nystagmus (no audio) | Image/MovingImage |
| 47 |
 |
Ocular Flutter | Two examples of patients, the first with rotary, flutter-like movements, but not ocular flutter, and the second with genuine ocular flutter. Discussion of difference between ocular flutter and nystagmus, and how to elicit ocular flutter. | Image/MovingImage |
| 48 |
 |
Flutter in Downgaze | Examination of patient with flutter in downgaze (no audio) | Image/MovingImage |
| 49 |
 |
Square Wave Jerks | Example of patient with square wave jerks. Discussion of difference between square wave jerks (saccadic oscillations) and horizontal nystagmus. | Image/MovingImage |
| 50 |
 |
Intermittent Square Wave Jerks | Patient with intermittent square wave jerks (no audio) | Image/MovingImage |
