The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
TO
Filters: Collection: "ehsl_heal"
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 26 |
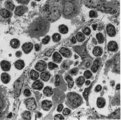 |
: Lymph node (rat) | Electron microscopy. A low magnification of a part of the medulla showing medullary cords surrounded by labyrinthine medullary sinus (*). In this picture the medullar cord runs from left bottom corner to right top corner, and is lined by flat reticular cell types. Within the cord one finds a star-sh... | medulla; electron microscopy; sinusoid | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 27 |
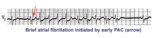 |
A PAC initiates paroxysmal atrial fibrillation | The arrow indicates slight alteration of the ST-T wave by a PAC. The PAC, in turn, falls during the vulnerable period of atrial repolarization and initiates atrial fibrillation. Similar but more catastrophic events happen in the ventricles when PVC's occur during the vulnerable period, i.e. R-on-T... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 28 |
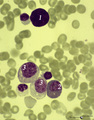 |
A bare megakaryocyte nucleus and myelocytes in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). (1) Indicates a bare large-sized polyploid nucleus of a megakaryocyte which has totally shed the cytoplasm. These cells are often seen in normal marrow and are ultimately removed by macrophages. There is no cytoplasm left, nor platelets are left around the nucleus. T... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 29 |
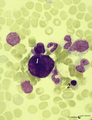 |
A bare megakaryocyte nucleus in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). (1) indicates a naked, large-sized polyploid nucleus of a megakaryocyte with visible lobes. No cytoplasm nor platelets are left around the nucleus. Most surrounding cells are of myeloid origin, except one orthochromatic erythroblast (2). | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 30 |
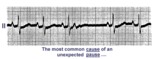 |
A nonconducted PAC causes an unexpected pause | Unexpected pauses in rhythm have several causes, the most frequent being a nonconducted PAC. In this example the nonconducted PAC is seen in the ST segment of the pause. Note the change in the ST-T compared to the other ST-T waves. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 31 |
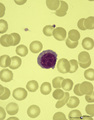 |
A plasmacytoid lymphocyte in peripheral blood smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The plasmacytoid lymphocyte is an activated B lymphocyte to be transformed into a plasma cell. The cytoplasm is more basophilic and the chromatin pattern is more clumped than in a virgin small lymphocyte. When the cell contains numerous immunoglobulin inclusions (glo... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 32 |
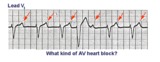 |
A very subtle 1st degree AV block | Where are the P waves??? They are hiding in the T waves as indicated by the arrows. How do we know? The PVC unmasked the sinus P wave, and now it is seen in the pause following the PVC. The PR interval is, therefore, about 500 ms. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 33 |
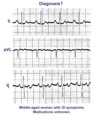 |
A very subtle atrial tachycardia with 2:1 block | Although at first glance this looks like normal sinus rhythm at 95 bpm. On closer look, there are 2 P waves for every QRS; the atrial rate is 190 bpm. Note the hidden P in the T waves. This rhythm is likely due to digitalis intoxication, as are the GI symptoms. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 34 |
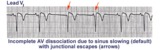 |
AV dissociation by default | If the sinus node slows too much a junctional escape pacemaker may take over as indicated by arrows. AV dissociation is incomplete, since the sinus node speeds up and recaptures the entricles. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 35 |
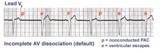 |
AV dissociation by default | The nonconducted PAC's set up a long pause which is terminated by ventricular escapes; note the wider QRS morphology of the escape beats indicating their ventricular origin. Incomplete AV dissociation occurs during the escape beats, since the atria are still under the control of the sinus node. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 36 |
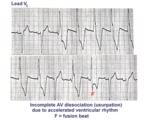 |
AV dissociation by usurpation | Normal sinus rhythm is interrupted by an accelerated ventricular rhythm whose rate is slightly faster than the sinus rhythm. Fusion QRS complexes occur whenever the sinus impulse enters the ventricles at the same time the ectopic ventricular focus initiates its depolarization. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 37 |
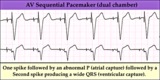 |
AV sequential pacemaker - marquette | (Summary) | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 38 |
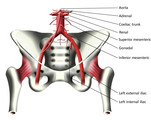 |
Abdominal Aorta and Arteries of the Pelvis (Labeled) | Abdominal aorta and pelvic arteries. | Adrenal Artery; Coeliac Trunk; Gonadal Artery; Left External Iliac Artery; Left Internal Iliac Artery | Royal College of Surgeons in Ireland Illustrations |
| 39 |
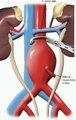 |
Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm (Labeled) | Left renal vein and inferior mesenteric artery adjacent to aortic aneurysm. | Royal College of Surgeons in Ireland Illustrations | |
| 40 |
 |
Abdominal Incision Line for Malecot Catheter Insertion | Abdominal incision for Malecot catheterization. | Malecot Catheter | Royal College of Surgeons in Ireland Illustrations |
| 41 |
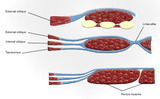 |
Abdominal Muscles (Labeled) | Abdominal muscles including external oblique, internal oblique, linea alba, transversus, and rectus muscles. | External Oblique Muscle; Internal Oblique Muscle; Transversus Abdominis; Linea Alba | Royal College of Surgeons in Ireland Illustrations |
| 42 |
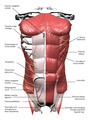 |
Abdominal Muscles (Labeled) | Abdominal muscles and adjacent structures. | Superior Epigastric Vessels; External Oblique Muscle; Rectus Sheath; Linea Alba; External Oblique Aponeurosis; Superficial Inguinal Ring; Deep Inguinal Ring; Transversalis Fascia; Medial Umbilical Ligament; Iliohypogastric Nerve | Royal College of Surgeons in Ireland Illustrations |
| 43 |
 |
Abducens nerve | Abducens nerve. Yellow nerve added to digitized image from graphic output. Photograph. Multimedia. | Abducens nerve; Central nervous system; Cranial nerves; Anatomy | Slice of Life |
| 44 |
 |
Abducens nerve, intracranial portion passing through tegmentum | Abducens nerve, intracranial portion passing through tegmentum. Transverse plane. Photograph. Multimedia. | Abducens nerve; Tegmentum mesencephali; Pons; Central nervous system; Anatomy | Slice of Life |
| 45 |
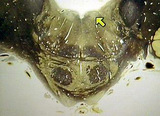 |
Abducens nucleus | Abducens nucleus. Transverse plane. Photograph. Multimedia. | Slice of Life | |
| 46 |
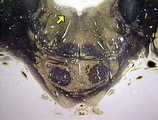 |
Abducens nucleus VI | Abducens nucleus VI. Pons. Transverse plane. Photograph. Multimedia. | Abducens nerve; Pons; Cranial nerves; Central nervous system; Anatomy | Slice of Life |
| 47 |
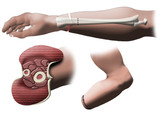 |
Above the Wrist Amputation of Hand - Forearm Cross Section | Above the wrist amputation of hand. | Amputation of Hand | Royal College of Surgeons in Ireland Illustrations |
| 48 |
 |
Abruptio Placenta - Microscopic | Microscopically, this abruptio placenta is seen to have extensive hemorrhage at thetop of the photograph at the decidual plate, with placental villi below. | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction | |
| 49 |
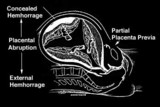 |
Abruptio placenta | Abruptio placenta | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction | |
| 50 |
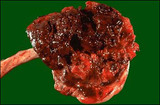 |
Abruptio placenta - Gross | This large retroplacental blood clot is known as abruptio placenta. Such abnormal hemorrhage prior to delivery can lead to sudden onset of pain in the mother. | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction |
