The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
TO
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 26 |
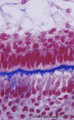 |
Ameloblasts and odontoblasts in tooth development - advanced bell stage, human, embryo | Stain: Azan. From top to bottom: Stellate reticulum consisting of a loose network of ectoderm-derived cells; Cell layers of the stratum intermedium; Columnar presecretory ameloblasts with their nuclear area close to the stratum intermedium, and at the distal side (secretion area) oriented towards pr... | oral cavity; predentin | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 27 |
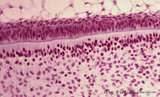 |
Ameloblasts and odontoblasts in tooth development - advanced bell stage, human, embryo | Stain: Hematoxylin and eosin. From top to bottom: Stellate reticulum consisting of a loose network of ectoderm-derived cells; Cell layers of the stratum intermedium; Palisade-arranged columnar presecretory ameloblasts at the distal side oriented towards the basal lamina enforced by deposited collage... | oral cavity | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 28 |
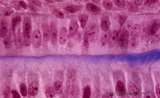 |
Ameloblasts and odontoblasts in tooth development - advanced bell stage, human, embryo; high magnification | Stain: Azan. From top to bottom: A cell layer of the stratum intermedium; Columnar presecretory ameloblasts at the distal side (secretion area) oriented towards predentin (blue); Note a gradient from left to right in the amount of deposited collagen fibers; Tall columnar odontoblasts in an epithelio... | oral cavity | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 29 |
 |
Ameloblasts and odontoblasts in tooth development - advanced bell stage, human, embryo CR 80 mm | Scheme electronmicroscopy. From top to bottom: Stellate reticulum consisting of a non-vascularized network of ectoderm-derived cells continuous with the cell layers of the stratum intermedium; Columnar presecretory ameloblasts with their upper side (nuclear area) in close contact with the stratum in... | oral cavity; predentin | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 30 |
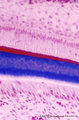 |
Ameloblasts and odontoblasts in tooth development - bell stage, human, embryo | Stain: Azan. From top to bottom: Stellate reticulum consisting of a loose network of ectoderm-derived cells; Cell layers of the stratum intermedium; Palisade-arranged tall columnar secretory ameloblasts with their nuclear area close to the stratum intermedium. The distal side of the cell is oriented... | oral cavity; predentin | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 31 |
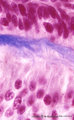 |
Ameloblasts and odontoblasts in tooth development - early bell stage, human, embryo; high magnification | Stain: Azan. From top to bottom: Presecretory ameloblasts with the distal side (secretion area) oriented towards the basal lamina intertwined with the tangential cut blue stained Korff's fibers (collagen) in predentin. Columnar odontoblasts in a epithelioid arrangement with their secretion area clos... | oral cavity; predentin; Korff's fibers | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 32 |
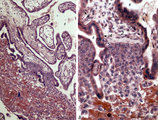 |
Anchoring villi (human placenta, early midpregnancy) | Stain: Hematoxylin -azophloxine. Survey (A) and detail (B). The maternal side at the bottom shows reddish matrix-type fibrinoid accumulations (1) (Rohr's fibrinoid layer) close to an anchoring villus (2) and the cytotrophoblastic cell columns (3). The anchoring villus is lined by cytotrophoblast... | placenta; chorionic villi; Hofbauer cell; anchoring villus; cytotrophoblast | Poja Histology Collection - Placenta |
| 33 |
 |
Anchoring villi (human placenta, early midpregnancy) | Stain: Hematoxylin -azophloxine. The maternal side at the bottom shows reddish matrix-type fibrinoid accumulations (1) (Rohr's fibrinoid layer) close to an anchoring villus (2) and a cytotrophoblastic cell column (3). The anchoring villus is lined by cytotrophoblasts (4) which are covered at th... | placenta; anchoring villus; fibrinoid; deciduas; cytotrophoblast | Poja Histology Collection - Placenta |
| 34 |
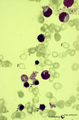 |
Anemic bone marrow smear in iron deficiency (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). Due to iron deficiency the erythrocytes (1) look empty, while also the erythroblasts (2) are relatively small and show a ruffled cell border. | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 35 |
 |
Anisocytosis of erythrocytes in peripheral blood smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). (A) shows normal human erythrocytes in a blood film, while (B) shows anisocytosis. The small cells are called microcytes. Anisocytosis is an increase in the variability of erythrocyte size beyond that which is observed in a normal healthy subject. It is a common, non... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 36 |
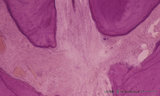 |
Apex of the tooth in osseus socket - alveolus; longitudinal section; human, adult | Stain: Hematoxylin and eosin. From top to bottom: apex region with two tips of dentin covered with cement (darker stained rim; left and right side); note at right tip a dark calcified spot (free cementicle); centrally pulp canal between the tips filled with connective tissue containing blood vessels... | oral cavity; alveolar bone; apical foramen; pulp canal | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 37 |
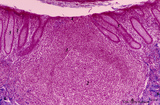 |
Appendix ('gut-associated lymphatic tissue' or GALT) (human) | A large nodule in the appendix extends through the proper lamina (1) and submucosa. The nodule is similar to that found in a lymph node with germinal centre (2) and darker-stained cap (crescent) (3) orientated towards the lumen of the gut showing a flattened dome area covered with discontinuous epit... | GALT; follicle; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 38 |
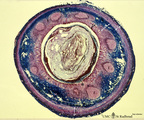 |
Appendix ('gut-associated lymphatic tissue' or GALT) (human) | Stain: Azan. Survey of vermiform appendix (see also Digestive System: Appendix) A large amount of non-encapsulated diffuse lymphatic tissue or mucosa-associated lymphatic tissue (MALT) is located in the subepithelial lamina propria/submucosa of the appendix and called gut-associated lymphatic tissue... | GALT; follicle; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 39 |
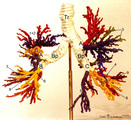 |
Arbor bronchialis, the bronchial tree (human, adult) | Resin corrosion cast of the lower trachea and bronchial tree (posterior aspect). The lobar and segmental bronchi and their main branches are coloured, different colours indicate areas supplied by different segmental bronchi. White-coloured lower trachea (Tr) divides into two principal bronchi (Bp)... | Segmental bronchi ; Macroscopy | Poja Histology Collection - Respiratory System Subset |
| 40 |
 |
Attached denticulus (pulp stone) in the tooth - longitudinal section of root; human, adult. | Stain: Hematoxylin and eosin. From left to right: dentin (purple stained) with dentin tubules; small lightly stained rim of predentin; layers of odontoblasts; irregular structured pulp stone attached to dentin; this false denticle consists of calcified layers with collagen fibers surrounding debris;... | oral cavity; denticulus; pulp stone | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 41 |
 |
Band and hyper segmented neutrophils in peripheral blood smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). (A) shows a young band neutrophil with a non-segmented nucleus. (B) shows mature neutrophils with more than 6 nuclear lobes (hyper segmented). The smear also shows anisocytosis with both microcytes and macrocytes. | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 42 |
 |
Band form of neutrophilic granulocyte | Scheme electron microscopy. From CFU-S (colony forming units-spleen) stem cells arise CFU-GM (colony forming unit-granulocyte/monocyte) stem cells. The latter divide by mitoses and differentiate via promyeloblasts and myeloblasts into neutrophilic myelocytes (the last proliferative stage). The next ... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 43 |
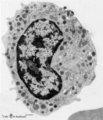 |
Band-form of neutrophilic granulocyte (peripheral blood, human) | Electron microscopy. Transition from late metamyelocyte to band form (9-12 μm). These are the earliest stages of the motile two-lobed neutrophilic granulocytes. (1) a slightly bended nucleus with a nucleolus. (2) Golgi area. Apart from a few mitochondria (3) and profiles of rough endoplasmic retic... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 44 |
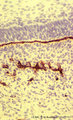 |
Basal lamina between ameloblasts and odontoblasts in tooth development - advanced bell stage, rat embryo | Stain: Anti-collagen IV immunoperoxidase and hematoxylin counterstained. From top to bottom: Stellate reticulum; Stratum intermedium; Ameloblasts at the distal side oriented towards the basal lamina intermingled with the Korffs' fibers (collagen, brown-black); Odontoblasts; Brown-black stained struc... | oral cavity; basal lamina; collagen IV | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 45 |
 |
Basophilic erythroblast and myeloid cells in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). (1) early basophilic erythroblast. (2) eosinophilic metamyelocyte. (3) neutrophilic myelocyte. (4) two band neutrophils. | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 46 |
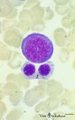 |
Basophilic erythroblast and polychromatic erythroblasts in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The basophilic erythroblast (1) shows slightly condensed chromatin and a strong basophilic (blue) cytoplasm. In the two polychromatic erythroblasts the chromatin condensation has progressed considerably, and the cytoplasm is much less basophilic. The cells are also s... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 47 |
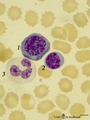 |
Basophilic erythroblast, plasmacytoid lymphocyte and neutrophilic granulocyte in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The basophilic erythroblast (1) contains a large, partly condensed but transparent nucleus with a distinct nucleolus. The cytoplasm is strong basophilic. The plasmacytoid lymphocyte (2) or activated B cell is much smaller and less basophilic. The young neutrophil (3)... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 48 |
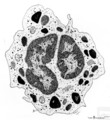 |
Basophilic granulocyte | Scheme electron microscopy. Basophils are non-phagocytic granulocytes that account for 0.5% to 1.0% of the circulating white blood cells. Their granulated cytoplasm stains with basic dyes, hence the name basophil. Electron microscopy reveals a multilobed nucleus (1); few mitochondria (2); numerous ... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 49 |
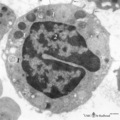 |
Basophilic granulocyte (peripheral blood, human) | Electron microscopy. The bilobed nucleus (2) is surrounded by moderate amount of organelles. The cell exhibits few short filopodia (arrows). The large coarse basophilic granules (1) (specific granules) vary in density and contain vasoactive mediators such as heparin, histamine, sulphated proteoglyca... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 50 |
 |
Basophilic granulocyte (peripheral blood, human) | Electron microscopy. The detail shows close to the nucleus characteristic developing basophilic granules (specific granules) (8-13 μm). At thin arrow (↓) a small Golgi area with a small specific granule. At (***) granules with different osmiophilic internal structures. The basophilic granules var... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset |
