John A. Moran Eye Center Neuro-Ophthalmology Collection: A variety of lectures, videos and images relating to topics in Neuro-Ophthalmology created by faculty at the Moran Eye Center, University of Utah, in Salt Lake City.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
| Identifier | Title | Description | Subject | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 26 |
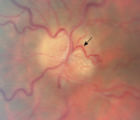 |
3-66a | 3-66a - Shunt Vessels (Post-papilledema) | The retino-choroidal collaterals seen with chronic papilledema begin with a "Hairnet" of telangiectasias that gradually winnow down to one or more large collateral tortuous draining channel. The presence of these vessels is evidence of long standing disc swelling. When the CSF pressure is lowered, t... | Shunt Vessels (Post-papilledema) |
| 27 |
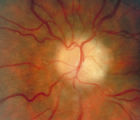 |
3-66d | 3-66d - Shunt Vessels (Post-papilledema) | The retino-choroidal collaterals seen with chronic papilledema begin with a "Hairnet" of telangiectasias that gradually winnow down to one or more large collateral tortuous draining channel. The presence of these vessels is evidence of long standing disc swelling. When the CSF pressure is lowered, t... | Shunt Vessels (Post-papilledema) |
| 28 |
 |
4-35 | 4-35 - Cupped Optic Nerve | Atrophic Glaucoma Atrophic glaucomatous discs show thinning of the neuro-retinal rim, "saucerization" (which is shallow cupping), evidence of peripapillary atrophy, and pallor of the very narrow neuroretinal rim. Notice that there is severe atrophy of the nerve fiber layer. | Cupped Optic Nerve |
| 29 |
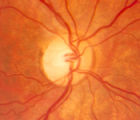 |
4-52b | 4-52b - Dominant Optic Neuropathy | A son presented with bilateral optic atrophy of unknown etiology after he failed a school visual exam. When looking for dominant optic atrophy, look at the parents. Mother was examined to find similar kind of atrophy. 4-52a mother, 4-52b son. | Dominant Optic Neuropathy |
| 30 |
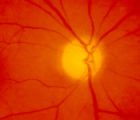 |
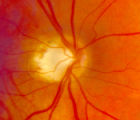
4-54a | 4-54a -Optic Neuropathy, Ischemic: Posterior | Optic Neuropathy, Ischemic; Posterior Ischemic Optic Neuropathy | |
| 31 |
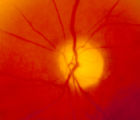 |
4-54b | 4-54b - Optic Neuropathy, Ischemic: Posterior | Optic Neuropathy, Ischemic; Posterior Ischemic Optic Neuropathy | |
| 32 |
 |
4-60a | 4-60a - Dominant Optic Neuropathy | A son presented with bilateral optic atrophy of unknown etiology after he failed a school visual exam. When looking for dominant optic atrophy, look at the parents. Mother was examined to find similar kind of atrophy. 4-60a mother, 4-60b son. | Dominant Optic Neuropathy |
| 33 |
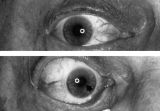 |
Figure-15 | Aberrant Regeneration of the Right Pupil | Aberrant regeneration of the right pupil in a man with a large intracavernous sinus meningioma causing a pupil-involving, incomplete third cranial nerve palsy. His pupil is round when he gazes straight ahead (top). When he tries to rotate the eye medially, the pupil constricts, but a segment of the ... | Pupil Disorders; Aberrant Regeneration; Third Nerve Palsy |
| 34 |
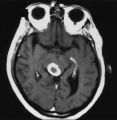 |
Figure-12 | An Enhancing Bladder Metastasis Involving the Tectum of the Midbrain | Magnetic resonance image of an enhancing bladder metastasis involving the tectum of the midbrain of a 56-year-old man who developed double vision resulting from skew deviation and divergence insufficiency. He also had a left-sided relative afferent pupillary defect measuring 1.4 log units but showed... | Physiology, Pupil; Reflex, Pupillary |
| 35 |
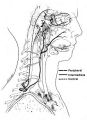 |
Figure-04 | Anatomy of the Oculosympathetic Pathway | Anatomy of the oculosympathetic pathway. (Maloney WF, Younge BR, Moyer NJ: Evaluation of the causes and accuracy of pharmacologic localization in Horner's syndrome. Am J Ophthalmol 1980;90:394-402, Ophthalmic Publishing Company with permission.) | Anatomy of the Oculosympathetic Pathway; Horner's Syndrome |
| 36 |
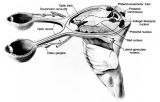 |
Figure-02 | Anatomy of the Pupillary Light Reflex Pathway | Anatomy of the pupillary light reflex pathway. (Miller NR: Walsh And Hoyt's Clinical Neuro-Ophthalmology, p 421. Vol 2, 4th ed. Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins, 1985, with permission.) | Reflex, Pupillary; Parasympathetic Pupil |
| 37 |
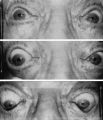 |
Figure-14 | Argyll Robertson Pupils | Argyll Robertson pupils in an elderly man treated for tabes dorsalis in 1952. His pupils are small and slightly irregular, constrict poorly in response to light stimulation (top), dilate poorly in darkness (middle), but constrict promptly in response to near stimulation (bottom). | Argyll-Robertson Pupil; Diagnosis, Pupil Disorders; Etiology, Pupil Disorders; History, Pupil Disorders; Pathology, Pupil Disorders |
| 38 |
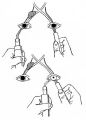 |
Figure-10 | Assessment of an Afferent Pupillary Defect When Only One Iris is Functional | Assessment of an afferent pupillary defect when only one iris is functional. In this example, a right-sided parasellar tumor is compressing both the optic and oculomotor nerves, causing an optic neuropathy and a pupil-involving third crainial nerve palsy. The pupil on the affected side has both an a... | Pupil Disorders; RAPD; Afferent Pupillary Defect |
| 39 |
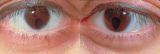 |
coloboma.jpg | Bilateral Iris Colobomas | Coloboma literally means a "gap"-and can be used to describe any fissure, hole, or gap in the eye. The term most often is used to refer to a congenital gap in the disc, retina, the choroid, and the iris. Colobomas occur because the embryonic fissure fails to fuse. Since the fissure closure begins in... | Congenital Pupillary Abnormalities; Pupil; Etiology, Pupil Disorders; Pathology, Pupil Disorders; Correctopia |
| 40 |
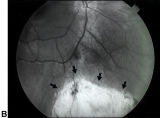 |
Figure-19B | Bilateral Iris Colobomas (B) | Bilateral iris colobomas. B. Bilateral colobomatous defects of the inferonasal retina (black arrows) are also present, as shown in the right eye. | Congenital Pupillary Abnormalities; Pupil; Etiology, Pupil Disorders; Pathology, Pupil Disorders |
| 41 |
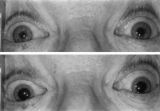 |
Figure-23 | Enhanced Mydriasis in Response to Hydroxyamphetamine | Enhanced mydriasis in response to hydroxyamphetamine in a 77-year-old woman with a long-standing, preganglionic, right-sided Horner's syndrome that occurred following cervical neck dissection for thoracic outlet syndrome 30 years earlier. Miosis of the right pupil is apparent in room light (top). Th... | Diagnostic Use, p-Hydroxyamphetamine; Pharmacology, p-Hydroxyamphetamine; Drug Effects, Pupil; Pharmacology, Amphetamines; Horner Syndrome; Testing, Pupillary Drop; Effects of Drugs on the Pupils |
| 42 |
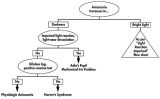 |
Figure-26 | Flow Chart for Sorting Out Anisocoria - Bright Light and Darkness | Flow chart for sorting out anisocoria based initially on how it is influenced by bright light and darkness. | Anisocoria; Adie Syndrome; Diagnostic Use, Cocaine; Constriction; Dark Adaptation; Diagnosis, Differential; Dilatation; Diagnosis, Eye Diseases; Physiopathology, Eye Diseases; Horner Syndrome; Humans; Innervation, Iris; Diagnostic Use, Methacholine Compounds; Diagnostic Use, Pilocarpine; Physiology,... |
| 43 |
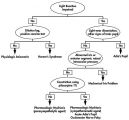 |
Figure-25 | Flow Chart for Sorting Out Anisocoria - Direct Light Reaction of the Pupil | Flow chart for sorting out anisocoria based initially on the integrity of the direct light reaction of the pupil. | Anisocoria; Adie Syndrome; Diagnostic Use, Cocaine; Constriction; Dark Adaptation; Diagnosis, Differential; Dilatation; Diagnosis, Eye Diseases; Physiopathology, Eye Diseases; Horner Syndrome; Humans; Innervation, Iris; Diagnostic Use, Methacholine Compounds; Diagnostic Use, Pilocarpine; Physiology,... |
| 44 |
 |
Figure-11 | Hand-held Equipment Used to Measure a Relative Afferent Pupillary Defect | Hand-held equipment used to measure a relative afferent pupillary defect and to record pupil sizes. Four neutral density filters (0.3, 0.6, 0.9, 1.2 log units) are conveniently carried in a soft cloth carrying pouch. A bright light source (a Finhoff model illuminator is shown here) is ideal for stim... | RAPD; Relative Afferent Pupillary Defect; Pupil; Reflex, Pupillary; Pupil Disorders; Afferent Pupillary Defect |
| 45 |
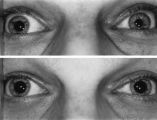 |
Figure-21 | Left-sided Dilation Lag in a Man with Horner's Syndrome | Left-sided dilation lag in a 29-year-old man with Horner's syndrome caused by a posterior mediastinal ganglioneuroma. Note that the degree of anisocoria is greater after 5 seconds in darkness (top) compared with findings after 15 seconds in darkness (bottom). | Diagnosis, Horner Syndrome; Physiopathology, Horner Syndrome; Reflex, Pupillary; Dilation Lag; Horner's Syndrome |
| 46 |
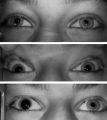 |
Figure-20 | Left-sided Horner's Syndrome with an Acquired Preganglionic Localization | Left-sided Horner's syndrome in a 12-year-old girl with an acquired preganglionic localization based on clinical and pharmacologic testing. The cause remained undetermined after extensive radiologic investigations. Left-sided ptosis and miosis are evident in room light (top), and the degree of aniso... | Etiology, Horner Syndrome; Female; Child; Drug Effects, Pupil; Horner Syndrome; Effects of Drugs on the Pupils |
| 47 |
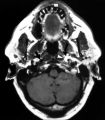 |
Figure-24 | Left-sided Internal Carotid Artery Dissection | Left-sided internal carotid artery dissection identified on T-1 weighted magnetic resonance image from a 52-year-old man who suddenly developed left-sided neck and orbital pain along with a droopy left upper eyelid while dragging a deer out of the woods during hunting season. The normal dark flow vo... | Diagnosis, Carotid Artery Diseases; Radiography, Carotid Artery Diseases; Carotid Artery, Internal; Diagnosis, Cerebral Arterial Diseases; Radiography, Cerebral Arterial Diseases; Dissection; Middle Older People; Male; Adult; Cervical Artery Dissection; Carotid Dissection |
| 48 |
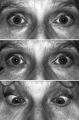 |
Figure-13 | Light-near Dissociation | Light-near dissociation in a 51-year-old woman with multiple sclerosis who experienced double vision for 1 week. Her pupils are 5 mm in diameter in room light (top), react poorly in response to direct light reaction (middle), but constrict promptly in response to near stimulation (bottom). She also ... | Nystagmus, Etiology, Pathologic; Nystagmus, Physiopathology, Pathologic; Reflex, Pupillary |
| 49 |
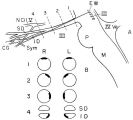 |
Figure-03 | Location of Pupillomotor Fibers | Location of pupillomotor fibers are depicted as dark regions on cross-sections of the right (R) and left (L) oculomotor nerve at various locations along its course, including its emergence from the brain stem in the interpeduncular fossa (1), the midsubarachnoid segment (2), the level of the dorsum ... | Autonomic Anatomy; Pupillomotor Fibers |
| 50 |
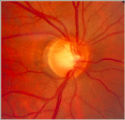 |
glaucoma notching | Notching of the Neuro-retinal Rim | The neuro-retinal rim becomes thinner; in particular the rim superotemporally and inferortemporally may develop a notch which is usually superior or inferior and rarely nasal or temporal. These notches are believed to be due to focal ischemic damage to the neuro-retinal rim. Glaucoma with Notching a... | Glaucoma |
