The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
TO
Filters: Collection: ehsl_heal
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 401 |
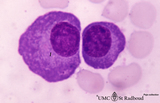 |
Plasma cells in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The two plasma cells are mature antibody-producing cells. The basophilic cytoplasm is filled up with rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER). The lighter zone (1) represents the Golgi areas. The nucleus is situated eccentrically and contains strands of condensed chromatin ... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 402 |
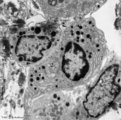 |
Plasma cells with Russell bodies (nose septum, rat) | Electron microscopy. Accumulation of few plasma cells. These mature plasma cells exhibit in their cytoplasm's dilated rough endoplasmic reticula (1) filled with electron-grey material (antibodies) as well as electron-dense granules (3) of varying sizes confirming their secretory activities. (2) indi... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 403 |
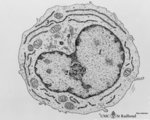 |
Plasmablast | Scheme electron microscopy. This plasmablast (up to 20 μm) shows an indented large nucleus (1) and a distinct nucleolus (2). In addition to free ribosomes long profiles of rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) (3) are being developed concomitant with Golgi packages (4). The cytoplasm is scanty with few... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 404 |
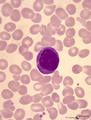 |
Plasmablast in peripheral blood smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The oval shaped cell with a slightly excentric nucleus and coarsely clumped chromatin has a basophilic blue cytoplasm in which the Golgi area usually remains unstained (white area). | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 405 |
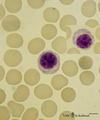 |
Plasmacytoid lymphocytes (activated B cells) in peripheral blood smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). Two different plasmacytoid lymphocytes or activated young B cells (up to 15 μm) contain a dark-stained nucleus and a slightly basophilic cytoplasm with a kind of a 'nuclear hof' indicating the Golgi area. These cells will develop into plasma cells. | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 406 |
 |
Platelets | Scheme electron microscopy. These disc-shaped anucleate cells (2-4 m) are derived from cytoplasmic fragments of the megakaryocyte. They contain few mitochondria, a canalicular system, a smooth tubular system, marginal localized microtubules, glycogen and different types of granula. A circumferential... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 407 |
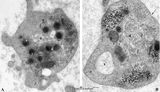 |
Platelets (peripheral blood, human) | Electron microscopy. These anucleate cells (2-4 μm) are derived from cytoplasmic fragments of a megakaryocyte and when free floating in the peripheral blood they develop thin extensions. These platelets contain among others few mitochondria (1), microtubules (2), glycogen (3), small vacuoles (4, op... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 408 |
 |
Platelets (peripheral blood, human) | Electron microscopy. These disc-shaped cells (2-4 m) without nucleus are derived from cytoplasmic fragments of the megakaryocyte. Free floating in the peripheral blood they develop thin extensions. They contain among others few mitochondria, smooth tubular systems, marginal localized microtubules, g... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 409 |
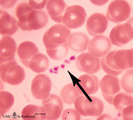 |
Platelets in peripheral blood smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The platelets or thrombocytes are small cell fragments released from megakaryocytes. The platelets (→) measure 1-3 μm in diameter. They contain fine azurophilic granules which may be dispersed throughout the cytoplasm or concentrated in the centre; in the latter c... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 410 |
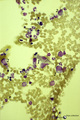 |
Pleiomorph bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). Low power view of a normal bone marrow smear. The bone marrow is pleiomorph and contains all cell types such as a large reticulum cells (1) with many granules or lysosomes (phagocytosis); myeloid cells (2); and erythroblasts (3). | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 411 |
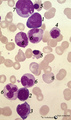 |
Pleiomorph normal bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The normal bone marrow with pleiomorphism, i.e. contains all stages of the erythroblastic differentiation series (1-5) as well as the stages of the myeloblastic series (6). (1) Basophilic erythroblast. (2),(3),(4) Polychromatic erythroblasts. (5) Orthochromatic er... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 412 |
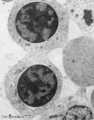 |
Polychromatic erythroblasts (bone marrow, rabbit) | Electron microscopy. Shown are two polychromatic erythroblasts or intermediate normoblasts between other erythroblasts and reticulocytes (2). Few mitochondria and polysomes are present but there is a decrease in amount of all organelles and nuclear clumping starts to take place. During this maturing... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 413 |
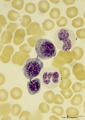 |
Polychromatic erythroblasts and neutrophilic granulocytes in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). Three polychromatic erythroblasts or normoblasts (1) and two neutrophils (2). The erythroblasts show light basophilic cytoplasm and well condensed nuclear chromatin. The lower neutrophil (more mature) has a more segmented nucleus than the upper one. | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 414 |
 |
Polycythemia in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: Hematoxylin and eosin. Low power view. Polycythemic phase. Hypercellular marrow as a result of excessive proliferation of erythroid cells (numerous dark nuclei) and of the megakaryocytic lineage (tendency to cluster). (1) fat cells in bone marrow. (2) megakaryocytes. (3) erythropoietic cell t... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 415 |
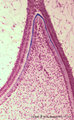 |
Predentin formation at the cuspal tip in tooth development - bell stage, human, embryo | Stain: Azan. From top to bottom: Stellate reticulum consisting of a network of ectoderm-derived cells; Cell layers of the stratum intermedium; Columnar (presecretory) ameloblasts with their upper side (nuclear area) in close contact with the stratum intermedium, and at the distal side (secretion are... | oral cavity; predentin | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 416 |
 |
Premolar permanent tooth (human, adult; low magnification of labiolingual section) | Stain: Hematoxylin and eosin. From top to bottom: Crown region with enamel-dentin boundary (there is no enamel present in decalcified specimens); dentin (blue-pink) enwraps the whole pulp chamber (light) and here the lines of dentinal tubules appear S-shaped. Neck region at the attachment of the gin... | oral cavity; pulp canal | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 417 |
 |
Presecretory ameloblast in tooth development - mammalian embryo | Scheme electronmicroscopy. The ectodermal-derived cell appears as tall columnar with fingerlike extensions (dependent on the development stages) at their distal side (secreting area = 'functional base'). These extensions are formed as the cell withdraws during the production of initial enamel. The s... | oral cavity | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 418 |
 |
Presecretory ameloblasts in tooth development - bell stage, gerbil, postnatal | Electronmicroscopy. Well-arranged epithelial formation of presecretory ameloblasts (active nuclei) with their distal secretion sides towards the thin grey basal lamina. Predentin at the bottom close to the basal lamina and comprises collagen fibers, odontoblastic extensions and dispersed calcified m... | oral cavity; predentin; matrix vesicles | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 419 |
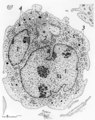 |
Pro-megakaryocyte | Scheme electron microscopy. The pro-megakaryocyte (20-80 m) develops from a basophilic megakaryoblast (up to 50 m) that originates from a committed stem cell. The large pro-megakaryocyte starts with the early synthesis of the characteristic granules of platelets. Apart from a bilobed nucleus (1) and... | Blood; Bone Marrow; Electron microscopy; Pro-megakaryocyte; Megakaryocyte | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset |
| 420 |
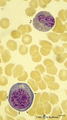 |
Proerythroblast and eosinophilic metamyelocyte in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald Giemsa (MGG). The late proerythroblast (1) has a deep blue-stained basophilic cytoplasm and so called ears (→, slight bulging) of sidewards accumulated ribosomes (in electron microscopy) in the cytoplasm. The eosinophilic metamyelocyte (2) has characteristic large, solitary brow... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 421 |
 |
Proerythroblasts in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The two proerythroblasts (1) are large cells with condensed nuclear chromatin and a deep blue-stained basophilic cytoplasm with so-called ears (→, bulging) where ribosomes (in electron microscopy) are aggregated or shifted towards the periphery of the cell. (2) smu... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 422 |
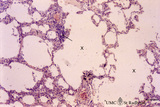 |
Progressing centrilobular lung emphysema (human, adult) | Stain: Hematoxylin and eosin. Emphysema is defined as enlargement of the air spaces (X) distal to the terminal bronchioles, with destruction of the alveolar walls. The remaining alveolar walls are thickened (1). There is an increased cellularity and locally signs of chronic inflammation (↓) are pr... | Poja Histology Collection - Respiratory System Subset | |
| 423 |
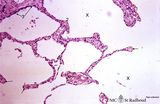 |
Progressing centrilobular lung emphysema (human, adult) | Stain: Hematoxylin and eosin. Emphysema is defined as enlargement of the airspaces (X) distal to the terminal bronchioles, with destruction of the alveolar walls. At (3) remnant of a respiratory bronchiolus. Alveolar walls are destroyed and other alveolar walls are thickened (1) and show an increas... | Alveolar tips | Poja Histology Collection - Respiratory System Subset |
| 424 |
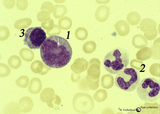 |
Promonocyte in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The promonocyte (1) has an irregular nucleus and shows the first step towards indentation (arrow). The cell has a characteristic greyish-blue cytoplasm. (2) Represents three young neutrophils. (3) A plasmacytoid lymphocyte. | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 425 |
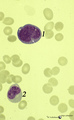 |
Promonocyte in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The young promonocyte (1) shows clear nucleoli and a distinct indentation of the nucleus (arrow). (2) Neutrophilic myelocyte. | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset |
