The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
TO
Filters: Collection: "ehsl_heal" Format: image
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 251 |
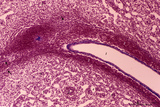 |
Spleen with central artery in lymphatic nodule (human) | Stain: Azan. A longitudinally cut central artery (1) of a lymphatic nodule or follicle, (white pulp) is invested by a distinct lymphatic sheath (PALS) composed of concentric layered T lymphocytes) (2). The red pulp consists of open venous sinusoids (4) and splenic cords (5, Billroth) with macrophage... | central artery; PALS; sinusoid ; Billroth | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 252 |
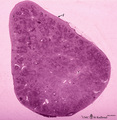 |
Survey of spleen (human) | Stain: Trichrome (Goldner). Encapsulated by a relatively thin fibroelastic capsule (1), the splenic parenchyma shows a preferable peripheral location of the red pulp (3). There are many secondary lymphatic nodules (2) as part of the white pulp, all showing a clear germinal centre. The red pulp is a ... | white pulp; red pulp | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 253 |
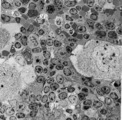 |
Survey of the border of splenic white and red pulp (rat) | Electron microscopy. Megakaryocytes (1) are commonly found in adult spleen of rodents. In this area they are located just at the border of the white pulp (WP) with a variety of lymphocytes (3). In the splenic cords (Billroth) of the red pulp (RP) erythrocytes (2) are found. | electron microscopy; white pulp; Billroth | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 254 |
 |
Scheme of blood circulation in the red pulp in the spleen | A. closed circulation B. open circulation A. The route of closed circulation proposes that blood empties from the capillaries directly into the splenic sinus. The central artery bifurcates into penicillar arterioles (1) and the blood slowly enters ensheathed capillaries, surrounded by agg... | white pulp; marginal zone; red pulp; open circulation | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 255 |
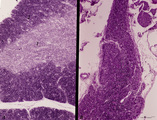 |
Accidental involution of thymus (mouse, malaria infection) | Stain: Hematoxylin & eosin. Due to the infection with malarial parasites (Plasmodium berghei in mice) a steroid-related involution of the thymus is induced in mice within 14 days. A: normal thymus with cortex (2) and medulla (1). B: There is still a quite large remnant of the original thymus tissue ... | malaria infection; thymus involution; Plasmodium berghei; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 256 |
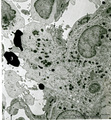 |
Border of a marginal zone in spleen (rat) | Stain: Immunoelectron microscopy (gold labeling of heparan sulfate in Lowicryl embedding, using the single chain antibody HS4C3). The zone of red pulp immediately surrounding a lymphatic nodule is called the marginal zone (perilymphoid zone) and is composed of a scaffold of basal lamina material w... | marginal zone; immuno electron microscopy; heparan sulfate; dendritic cell | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 257 |
 |
Scheme of the medullar changes in lymph node after antigen stimulation | Upon antigenic stimulation the reticular cells that line the medullar sinusoids start to phagocytise the antigens (i.e. infective agents) and change from small tiny stellate cells into swollen large cells due to phagocytosis. They detach from the medullar sinus wall. After ten days the situation has... | follicle; antigen stimulation; scheme; germinal center | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 258 |
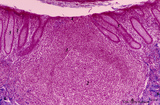 |
Appendix ('gut-associated lymphatic tissue' or GALT) (human) | A large nodule in the appendix extends through the proper lamina (1) and submucosa. The nodule is similar to that found in a lymph node with germinal centre (2) and darker-stained cap (crescent) (3) orientated towards the lumen of the gut showing a flattened dome area covered with discontinuous epit... | GALT; follicle; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 259 |
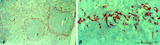 |
: Localization of ED3-positive subpopulation of macrophages in spleen (rat) | Stain: Immunohistochemistry of Vector red staining using the antibody ED3. The survey in (A) shows that the ED3-positive macrophages are found as a ring in the marginal zone border, as well as spread in the red pulp area (2). The cells are sometimes referred as marginal metallophilic macrophages. T... | metallophilic macrophages; ED3 antibody; marginal zone | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 260 |
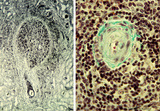 |
Spleen with central artery in lymphatic nodule (human) | Stain: A: Silver stain (Gomori). B: Trichrome (Goldner). In A: the reticular fibers (2) around the PALS (periarteriolar lymphatic sheath) and continuing in and around the marginal zone are stained black, illustrating the reticular framework of the lymphatic nodule. (1) central arteries. (4) red pulp... | central artery; PALS; white pulp; T cells | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 261 |
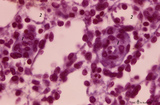 |
Macrophage-sheathed capillaries in spleen (human) | Azan. The branching of each penicillar arteriole gives rise to capillaries and a slow-down of the blood stream. In certain regions monocyte-derived macrophages leave the capillary and enter its wall where they develop into macrophages. Together with the present reticular cells these cell accumulatio... | macrophage-sheathed capillaries; penicillar arterioles; sinusoid | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 262 |
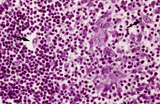 |
Medulla of thymus (human, puberty) | Stain: Hematoxylin. The light-stained medulla consists of a loosened framework of epithelial reticular cells, macrophages, thymocytes and capillaries. Accumulations of a specialized type of epithelial reticular cells (1) are localized between the thymocytes. These clusters represent precursors of fu... | thymic corpuscle (Hassalls); epithelioreticular cell (ERC); thymus medulla; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 263 |
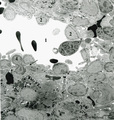 |
Splenic venous sinusoid in red pulp (rat) | Immunoelectron microscopy (gold labeling of heparan sulfate in Lowicryl embedding, using the single chain antibody HS4C3). (1) shows the open lumen of a venous sinusoid filled with few electron-dense erythrocytes and lining cells (2). (3) marks a neutrophilic granulocyte. (4) points to the diaped... | sinusoid; immuno electron microscopy; heparan sulfate | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 264 |
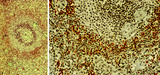 |
Secondary lymphatic nodule in the spleen (human) | Stain: Trichrome (Goldner). A: Survey of a follicle in the spleen. B: a higher magnification of a similar section shows part of a lymphatic nodule (follicle, white pulp) with cross-sections of the central artery (6). (1) germinal centre (filled with reticular cells, B-memory lymphocytes and macroph... | white pulp; PALS; germinal center; marginal zone | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 265 |
 |
Immunoperoxidase stained CD8 positive T cells in spleen (rat) | Stain: Immunoperoxidase staining using diaminobenzidin (DAB)/ hematoxylin counterstained on frozen section with anti-CD8 antibodies. A, B and C show brown-stained CD8-positive T cells or Tc cells at different enlargements. The CD8 Tc/s cells are localised predominantly in the PALS area (1), while th... | CD8 lymphocytes; immunohistochemistry; PALS | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 266 |
 |
Thymus (human, fetus) | Stain: Silver stain (Gomori). Reticular fibers are demonstrated in the interlobular septa in the thymic cortical area (2) of this lobule. In the medulla (1) the more loosened reticular framework is more distinct. The reticular fibers are produced by the epithelioreticular cells and are particular ... | thymic corpuscle (Hassalls); epithelioreticular cell (ERC); reticular fibers; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 267 |
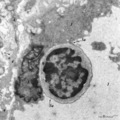 |
Thymus cortex (rat, young adult) | Electron microscopy. Type I epithelioreticular cells (4) separate connective tissue compartment (capsule, trabeculae, blood vessels) from the thymic parenchyma. At the left the capsule is bordered by a basal lamina (4a) of two projections (4) of type I epithelioreticular cells. Close to them, part o... | lymphoid tissue ; epithelioreticular cell type I; diapedesis | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 268 |
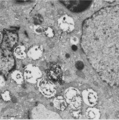 |
Thymus cortex (rat, young adult) | Electron microscopy. Two epithelioreticular cells type II or TEC2 (1) show the characteristic vacuoles (*) partly filled with granules (thymulin, lymphokines). At (--><--) small desmosomes. Apart from the mitochondria electron-dense lysosomal structures are present as well as tonofilaments (1, kera... | epithelioreticular cell II ; desmosome; MHC-II expression; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 269 |
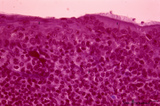 |
Detail of pharyngeal tonsils (human) | Stain: Azan. In contrast to the palatine and lingual tonsils, the epipharyngeal tonsil has a ciliated epithelium (1). Islands of multilayered squamous epithelium may interrupt it (transition zone, 2). The epithelium may be infiltrated with lymphocytes. The surface of this tonsil can be enlarged by m... | pharyngeal tonsil; GALT; squamous epithelium; ciliated epithelium | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 270 |
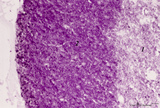 |
Thymus cortex (mouse, young adult) | Stain: Hematoxylin. Autoradiography after pulse labeling with tritiated thymidin. Most of the (black) radioactive labeling is found in the outer thymic cortex (3) where pre-T cells divide and subsequently migrate to the lighter stained medulla (1) that consists of a more loosened framework of epith... | thymus cortex; thymus medulla; thymidin labeling; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 271 |
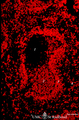 |
Localization of B cells in spleen (rat) | Stain: Immunofluorescence of Vector red using Mark-1 antibody against B cells. The T cells in the PALS (periarteriolar lymphatic sheath) remain unstained (1, dark). The red-stained B cells are packed in the germinal centre (2), the corona (3) or mantle layer that diffuses into the marginal zone and... | B lymphocytes; immunofluorescence; PALS | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 272 |
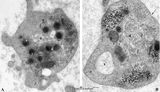 |
Platelets (peripheral blood, human) | Electron microscopy. These anucleate cells (2-4 μm) are derived from cytoplasmic fragments of a megakaryocyte and when free floating in the peripheral blood they develop thin extensions. These platelets contain among others few mitochondria (1), microtubules (2), glycogen (3), small vacuoles (4, op... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 273 |
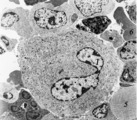 |
Megakaryocyte (bone marrow, rabbit) | Electron microscopy. A survey of a megakaryocyte demonstrates very well the differences in diameter between this giant polyploid cell (1) and the other young white blood cells (2-5). In the intermediate zone the (dark) granules (of the future platelets) are close associated with the electron-light i... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 274 |
 |
Megakaryocyte (peripheral blood, human) | Electron microscopy. A small part of a megakaryocyte (see also inset) shows two nuclear segments (1) and two areas of cytoplasm. Seen at this magnification and close to the perinuclear area, the granular population can be divided into homogeneous electron-dense (2) and electron-grey (3) granules. Th... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 275 |
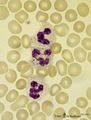 |
Neutrophilic granulocytes in peripheral blood smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The three neutrophilic granulocytes display segmented and lobulated nuclei. The lobes are connected with thin chromatin strands (→). The cytoplasm is ample filled with fine, dust-like granules and the majority are specific granules filled with enzymes such as lysoz... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset |
