The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
TO
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 226 |
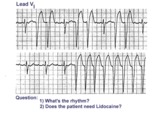 |
Atrial flutter with variable AV block and rate-dependent LBBB | The basic rhythm is atrial flutter with variable AV block. When 2:1 conduction ratios occur there is a rate-dependent LBBB. Don't be fooled by the wide QRS tachycardia on the bottom strip. It's not ventricular tachycardia, but atrial flutter with 2:1 conduction and LBBB. Lidocaine is not needed ... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 227 |
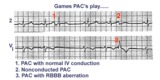 |
three fates of PAC's | As illustrated, PAC's can have three fates: PAC-1enters the ventricles and encounters no conduction delays, therefore causing a narrow QRS; PAC-2 occurs a little earlier and can't get through the AV junction, therefore beingnonconducted; PAC-3 seen inlead V1 makes it into the ventricles but encounte... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 228 |
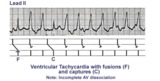 |
Ventricular tachycardia with AV dissociation, captures, and fusions | Approximately 50 percent of ventricular tachycardias are associated with AV dissociation. In these cases atrial impulses can enter the ventricles and either fuse with a ventricular ectopic beat or completely capture the ventricles. This ladder diagram illustrates these events. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 229 |
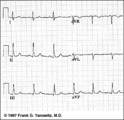 |
Frontal plane QRS axis = +75 degrees | Since there is no isoelectric lead in this ECG, the two closest leads are I and aVL. If I were isoelectric, the axis would be +90 degrees; if aVL were isoelectric, the axis would be +60 degrees. A nice compromize is +75 degrees. (The two closest leads are always 30 degrees apart.) | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 230 |
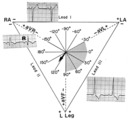 |
Right axis deviation: QRS axis = +130 degrees | Lead aVR is almost isoelectric; lead I is mostly negative, and lead III is very positive. The QRS axis, therefore, is +130 degrees. Note that the slightly more positive AVR moves the axis slightly beyond +120 degrees; i.e., closer to the + pole of the aVR lead. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 231 |
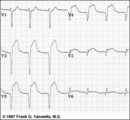 |
Extensive anterior/anterolateral MI: precordial leads | Extensive anterior/anterolateral MI: precordial leads | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 232 |
 |
LVH: strain pattern + left atrial enlargement | LVH: strain pattern + left atrial enlargement | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 233 |
 |
Ventricular asystole - marquette | Ventricular asystole - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 234 |
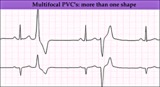 |
Multifocal PVC's - marquette | Multifocal PVC's - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 235 |
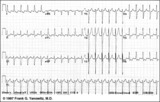 |
Atrial flutter with 2:1 AV conduction | In this example of atrial flutter with 2:1 AV conduction the flutter waves are very hard to see. Atrial flutter with 2:1 block must be considered, however, because the heart rate is about 150 bpm. A careful look at V1 shows the two flutter waves for each QRS complex complex. One flutter wave imme... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 236 |
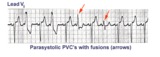 |
Ventricular parasystole | In ventricular parasystole, non-fixed coupled PVC's occur at a common inter-ectopic interval. Fusion beats, indicated by arrows, are often seen. Fusions occur when the sinus impulse entering the ventricles find the ventricles already partially depolarized by the parasystolic focus. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 237 |
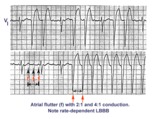 |
Atrial flutter with 2:1 and 4:1 conduction and rate dependent LBBB | In this example of atrial flutter with variable AV conduction, the faster rates are associated with rate-related LBBB. Don't confuse this for ventricular tachycardia. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 238 |
 |
Propionyl CoA carboxylase reaction | Propionyl CoA is metabolized by a process that first converts it to D-methylmalonyl CoA. The reaction is catalyzed by propionyl CoA carboxylase,and requires energy in the form of ATP. | Biosynthesis | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids |
| 239 |
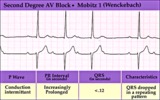 |
2nd degree AV block, type I (Wenckebach) | 2nd degree AV block, type I (Wenckebach) | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 240 |
 |
Diagram: stages of acute Q-wave MI | Diagram: stages of acute Q-wave MI | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 241 |
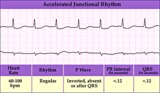 |
Accelerated junctional rhythm | Accelerated junctional rhythm | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 242 |
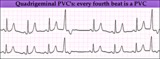 |
PVC's - marquette | PVC's - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 243 |
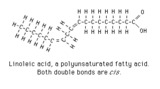 |
Linoleic acid structure | Linoleic acid is a typical polyunsaturated fatty acid. | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids | |
| 244 |
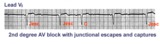 |
2nd degree AV block with junctional escapes and captures | Second degree AV block is present; conducted beats are identified by those QRS's that terminate shorter cycles than the junctional escape cycle; i.e., the 3rd and probably the 4th QRS's are captures; the other QRS's are junctional escapes. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 245 |
 |
Atrial fibrillation with moderate ventricular response - Marquette | Atrial fibrillation with moderate ventricular response - Marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 246 |
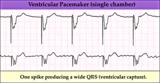 |
Ventricular pacing in atrial fibrillation - marquette | Ventricular pacing in atrial fibrillation - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 247 |
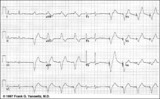 |
Ventricular pacemaker: demand mode functioning | Ventricular pacemaker: demand mode functioning | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 248 |
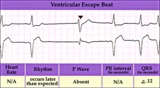 |
Ventricular escape beat - marquette | Ventricular escape beat - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 249 |
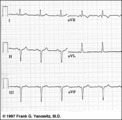 |
LAFB: frontal plane leads | LAFB: frontal plane leads | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 250 |
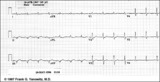 |
Old infero-posterior MI | Old infero-posterior MI | Knowledge Weavers ECG |
