The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
TO
Filters: Collection: "ehsl_heal"
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 226 |
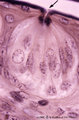 |
Taste bud of a foliate papil of the tongue (dorsal side, rabbit; high magnification) | Stain: Heidenhain's iron hematein. Taste bud with slender cells and darker stained spiky nuclei (type I cell), and cells with light stained round nuclei (type II cells). Below axons of the gustatory nerve fibers and nuclei of Schwann cells. Arrow points to narrow pore where dark stained fluffy struc... | oral cavity; foliate papillae; taste pore | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 227 |
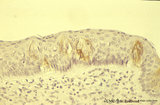 |
Taste bud of a foliate papilla of the tongue (dorsal side, human) | Stain: antikeratin-7 / immunoperoxidase and hematoxylin counterstained. Type I cells with small slender nuclei are identified by positive staining with cytokeratin 7 (monoclonal antibody OVTL12/30). | cytokeratin; oral cavity; foliate papilla; von Ebner | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 228 |
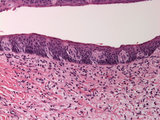 |
Taste bud | Human taste bud with underlying neural tissue. | HEAL Reviewed Collection | |
| 229 |
 |
Tooth ('free' gingiva of decalcified tooth, human, adult) | Stain: Hematoxylin and eosin. Oral side (left) with stratified squamous epithelium, at the right side part of a tooth (dentin), at the bottom side part of the alveolar bone. The epithelium shows slight parakeratosis with many narrow deep papillae of the lamina propria (oral side). On the tooth-relat... | oral cavity; junctional epithelium; alveolar bone; gingival sulcus | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 230 |
 |
Tooth ('free' gingiva of decalcified tooth, human, adult) | Stain: Hematoxylin and eosin. On top part of the gingival sulcus, at the left stratified junctional epithelium normally attached to the surface of the enamel (dissolved due to decalcification). Top left shows foci of chronic inflammatory cell infiltration, left side faint stained bundle of fibers (p... | oral cavity; acellular cementum; junctional epithelium | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 231 |
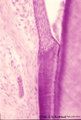 |
Tooth ('free' gingiva of decalcified tooth, human, adult) | Stain: Hematoxylin and eosin. On top the gingival sulcus; at the left stratified junctional epithelium normally attached to the surface of the enamel (dissolved due to decalcification). Below the epithelium a focus of chronic inflammatory cell infiltration, followed by a bundle of fibers of the per... | oral cavity; acellular cementum; junctional epithelium | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 232 |
 |
Tongue (macroscopy, dorsal side, human) | At the bottom (apex) of the picture the dorsal side is covered with numerous closed packed, small, conical filiform papillae. Interspersed among them are the larger fungiform papillae. Posteriorily the circumvallatae papillae are arranged in a V-shape row. Behind the V-row the area is covered with l... | oral cavity; papillae | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 233 |
 |
Tongue Papillae Scheme - tongue, human, adult | A. Scheme survey dorsal surface of tongue (human, adult). Magnification 35x. B. Scheme of filiform and fungiform papillae (tongue, human, adult). Magnification 35x. 1. foliate papillae (rudimentary in human); 2. circumvallate papillae; 3. foramen cecum; 4. palatine tonsils; 5. filiform ... | oral cavity; papillae | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 234 |
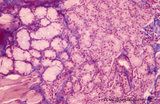 |
Tongue (lingual gland, human) | Stain: Azan. The posterior lingual gland is composed of areas with pure serous acini neighbouring pure mucous acini between the tongue muscles (at the left few striated fibers). | oral cavity; lingual gland | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 235 |
 |
Tongue (ventral part, human) | Stain: Hematoxylin and eosin. Non-keratinized squamous epithelium, followed by a small lamina propria and the intrinsic striated lingual muscles. | oral cavity; lingual muscles | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 236 |
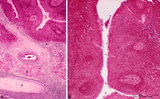 |
Tubal tonsil (human) | Stain: Azan. The tubal tonsil consists of a collection of lymphoid nodules near the auditory tube opening and forms part of the Waldeyers ring of defense in the nasopharyngeal cavity. This tonsil has fewer crypts (1), and the surface is covered by one to more layered ciliated epithelium (2). The la... | tubal tonsil; nasopharynx | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 237 |
 |
Villi of complete hydatidiform mole (human) | (A) Macroscopy aggregation (1) of abnormal villi of hydatidiform mole intermingled with blood clots (2). (B) After dissection of a complete mole grape-like aggregations of dilated chorionic villi are presented as numerous liquid-filled vesicles (1) varying in diameters (from few mm up to 1 cm) surr... | placenta; trophoblast; hydatiform mole | Poja Histology Collection - Placenta |
| 238 |
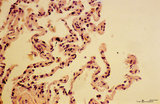 |
Trophoblast cell in lung alveolar interstitium (human, early midpregnancy) | Stain: Hematoxylin-eosin. It is well known that free circulating trophoblast cells can be found migrated into lung parenchyma during normal pregnancy. In this sample a large trophoblast cell (→) is localised within the normal alveolar interstitium. Alveolar phagocytes (*) are present in the alve... | placenta; trophoblast; lung | Poja Histology Collection - Placenta |
| 239 |
 |
Uvula (soft palate, human) | Stain: Azan. Detail of the uvula at the nasal side shows the border between the non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium (right, oral side) and pseudostratified columnar epithelium (left, nasal side). The lamina propria is composed of dense connective tissue. At the bottom part of a blood-fil... | oral cavity; lining mucosa | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 240 |
 |
Uvula (soft palate, human; low magnification) | Stain: Azan. At the right (oral side, non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium); at the left (nasal side, same epithelium). In the submucosa mainly mucous uvular glands are localized. At the bottom, striated muscle of the uvular muscle. The uvular tip is richly vascularized. | oral cavity | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 241 |
 |
Uvula (soft palate, human) | Stain: Azan. Detail of the uvula at the oral side; non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium. Note richly vascularized lamina propria. In the submucosa mainly mucous uvular glands with draining ducts. | oral cavity; lining mucosa; mucous glands | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 242 |
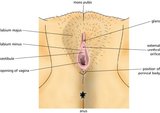 |
Vulva (Labeled) | External genitalia. Female. | Mons Pubis; Glans; External Urethral Orifice; Perineal Body; Opening of Vagina; Vestibule of Vagina; Labium Minus; Labium Majus | Royal College of Surgeons in Ireland Illustrations |
| 243 |
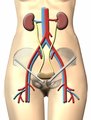 |
Urinary System | Urinary system. Kidneys. Ureter. Bladder. | Common Iliac Veins; Common Iliac Arteries | Royal College of Surgeons in Ireland Illustrations |
| 244 |
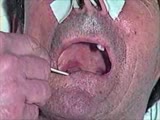 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerves 9 & 10 - Sensory & Motor: Gag Reflex | Using a tongue blade, the left side of the patient's palate is touched which results in a gag reflex with the left side of the palate elevating more then the right and the uvula deviating to the left consistent with a right CN 9 & 10 deficit. Video courtesy of Alejandro Stern, Stern Foundation. Neur... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 245 |
 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Smooth Pursuit | The patient shown has progressive supranuclear palsy. As part of this disease there is disruption of fixation by square wave jerks and impairment of smooth pursuit movements. Saccadic eye movements are also impaired. Although not shown in this video, vertical saccadic eye movements are usually the i... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 246 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Anatomy: Subdivisions of the Cerebellum (includes Spanish audio & captions) | The cerebellum has 3 functional subdivisions, which function as feedback and feed forward systems. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics and the Office of Education at the University of Nebraska M... | Coordination Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 247 |
 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Vergence | Light-near dissociation occurs when the pupils don't react to light but constrict with convergence as part of the near reflex. This is what happens in the Argyll-Robertson pupil (usually seen with neurosyphilis) where there is a pretectal lesion affecting the retinomesencephalic afferents controllin... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 248 |
 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerves 9 & 10 - Sensory & Motor: Gag Reflex (x2) | Using a tongue blade, the left side of the patient's palate is touched which results in a gag reflex with the left side of the palate elevating more then the right and the uvula deviating to the left consistent with a right CN 9 & 10 deficit. Video courtesy of Alejandro Stern, Stern Foundation. Neur... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 249 |
 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Smooth Pursuit (x2) | The patient shown has progressive supranuclear palsy. As part of this disease there is disruption of fixation by square wave jerks and impairment of smooth pursuit movements. Saccadic eye movements are also impaired. Although not shown in this video, vertical saccadic eye movements are usually the i... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 250 |
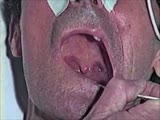 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerves 9 & 10 - Motor (x2) | When the patient says ah there is excessive nasal air escape. The palate elevates more on the left side and the uvula deviates toward the left side because the right side is weak. This patient has a deficit of the right 9th & 10th cranial nerves. Video courtesy of Alejandro Stern, Stern Foundation. ... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
