John A. Moran Eye Center Neuro-Ophthalmology Collection: A variety of lectures, videos and images relating to topics in Neuro-Ophthalmology created by faculty at the Moran Eye Center, University of Utah, in Salt Lake City.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
Filters: Collection: ehsl_novel_jmec
1 - 25 of 6
| Title | Description | Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
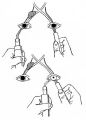 |
Assessment of an Afferent Pupillary Defect When Only One Iris is Functional | Assessment of an afferent pupillary defect when only one iris is functional. In this example, a right-sided parasellar tumor is compressing both the optic and oculomotor nerves, causing an optic neuropathy and a pupil-involving third crainial nerve palsy. The pupil on the affected side has both an a... | Image |
| 2 |
 |
How to Measure the RAPD | This clip demonstrates the examination technique for measuring the Relative Afferent Pupillary Defect (RAPD). Demonstration of balancing an afferent papillary defect using filters in a patient with a resolving optic neuritis and an afferent papillary defect on the left. | Image/MovingImage |
| 3 |
 |
Normal Light Reflex without RAPD | This clip demonstrates the examination of the Relative Afferent Pupillary Defect (RAPD.) Demonstration of gauging the size of the pupil in light, testing light reflexes, swinging flashlight test for optic nerve abnormality. | Image/MovingImage |
| 4 |
 |
RAPD Present | This clip demonstrates the technique used to determine that Relative Afferent Pupillary Defect (RAPD) is present in a patient. | Image/MovingImage |
| 5 |
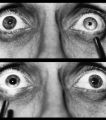 |
Right-sided Relative Afferent Pupillary Defect | Right-sided relative afferent pupillary defect in a man with optic nerve glioma. When the unaffected left eye is stimulated by light, both pupils constrict (top). When the light is then swung over to the affected right eye, both pupils dilate (bottom). This indicates that pupillomotor conduction thr... | Image |
| 6 |
 |
Hand-held Equipment Used to Measure a Relative Afferent Pupillary Defect | Hand-held equipment used to measure a relative afferent pupillary defect and to record pupil sizes. Four neutral density filters (0.3, 0.6, 0.9, 1.2 log units) are conveniently carried in a soft cloth carrying pouch. A bright light source (a Finhoff model illuminator is shown here) is ideal for stim... | Image |
1 - 25 of 6
