The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
Filters: Collection: ehsl_heal
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 101 |
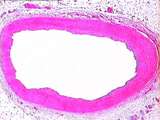 |
Circulatory System - Muscular Artery | The tunica adventitia of this muscular artery is thicker than that of elastic arteries; it contains collagen, adipose tissue, vasa vasorum, and nerve bundles. The tunica media contains abundant smooth muscle cells, and less elastin than an elastic artery. UCLA Histology Collection. | Circulatory System; muscular artery; tunica adventitia | UCLA Histology |
| 102 |
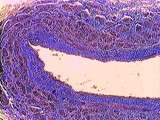 |
Circulatory System - Vein | In this Trichrome stained large vein, identify the tunica intima, tunica media, and the thick tunica advetitia. The tunica adventitia primarily contains collagen (blue) and dark-red smooth muscle cells. Note the collapsed lumen, caused by the lack of elasticity in venous walls. UCLA Histology Collec... | Circulatory System; Trichrome; tunica adventitia | UCLA Histology |
| 103 |
 |
Circulatory System - Veins | Walls of large veins have the same three tunics described for arteries, but the tunics are less distinct, and the elastic and muscular components are less developed. Note the lumen, tunica intima, tunica media, and tunica adventitia. The tunica adventitia is the thickest of the three coats, containi... | Circulatory System; tunica adventitia | UCLA Histology |
| 104 |
 |
Connective Tissue | This low power view of the monkey heel shows epidermis, dermal connective tissue, a sweat gland, and the insertion of the Achilles tendon into the dark-pink heel bone. Fatty tissue can be seen in the bone marrow cavity. UCLA Histology Collection. | Connective Tissue; epidermis; tendon | UCLA Histology |
| 105 |
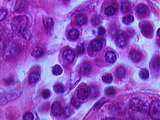 |
Connective Tissue | At a higher power these plasma cells can be seen to have a basophilic cytoplasm, and an acentric nucleus with peripherally located clumps of heterochromatin. UCLA Histology Collection. | Breast; Connective Tissue | UCLA Histology |
| 106 |
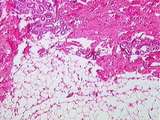 |
Connective Tissue | In the dermis of the skin, adipocytes (fat cells) are also present. These cells appear empty because the organic solvents used in tissue preparation dissolve away fat. Sweat glands are also found deep within the dermis. UCLA Histology Collection. | connective tissue; Skin; Sweat glands | UCLA Histology |
| 107 |
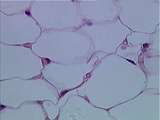 |
Connective Tissue | Adipose (fat) cells. Note that the nuclei are pushed to the periphery of the cell by the large central accumulation of lipid. UCLA Histology Collection. | Connective Tissue | UCLA Histology |
| 108 |
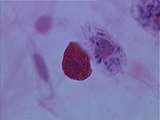 |
Connective Tissue | At a higher power can be seen the difference between a mast cell and a macrophage. Note the red cytoplasmic granules of the mast cell, and the phagocytized trypan blue dye in the macrophage. UCLA Histology Collection. | Connective Tissue; macrophage; mast cell; White Blood Cells | UCLA Histology |
| 109 |
 |
Connective Tissue | This whole mount of loose connective tissue shows bundles of reddish collagen fibers, dark elastic fibers, and macrophages. These macrophages have phagocytized trypan blue dye. UCLA Histology Collection. | Connective Tissue; macrophage | UCLA Histology |
| 110 |
 |
Connective Tissue | This is a slice of lymph node stained with silver to show reticular fibers. The larger bundles are collagen. UCLA Histology Collection. | Connective Tissue; Lymph Node | UCLA Histology |
| 111 |
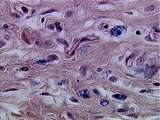 |
Connective Tissue | In this section of the abdominal wall can be seen collagen, macrophages, and slender fibroblasts within the connective tissue. UCLA Histology Collection. | Connective Tissue; macrophage | UCLA Histology |
| 112 |
 |
Connective Tissue | The lining of the gallbladder is a tall simple columnar epithelium. The underlying loose connective tissue is characterized by a large number of cells relative to collagen fibers. Look for plasma cells here. UCLA Histology Collection. | Connective Tissue; Gall bladder; Liver | UCLA Histology |
| 113 |
 |
Connective Tissue | In this slide mast cells, fibroblasts, and macrophages are evident. UCLA Histology Collection. | Connective Tissue; fibroblasts; macrophage; mast cell; White Blood Cells | UCLA Histology |
| 114 |
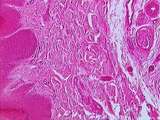 |
Connective Tissue | At a higher power of the heel, the stratified squamous epidermis, the collagen-rich dense irregular CT of the dermis, and the sweat glands can be easily distinguished. UCLA Histology Collection. | connective tissue; epidermis; sweat glands | UCLA Histology |
| 115 |
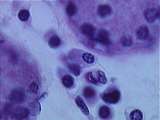 |
Connective Tissue | Plasma cells can also be found in the lacrimal gland of the eye. Note the classic clock face nucleus produced by clumps of heterochromatin. UCLA Histology Collection. | Connective Tissue; Eye; lacrimal gland | UCLA Histology |
| 116 |
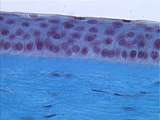 |
Connective Tissue | At a higher power of the corneal stroma, the flattened fibroblast nuclei and collagen bundles are easily seen. UCLA Histology Collection. | Connective Tissue; cornea; Eye | UCLA Histology |
| 117 |
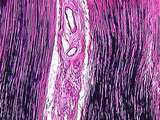 |
Connective Tissue | This ligament consists of dense regular connective tissue with large amounts of dark-stained elastic fibers and pinkish collagen. UCLA Histology Collection. | Connective Tissue; ligament | UCLA Histology |
| 118 |
 |
Connective Tissue | This higher power view of the heel shows dermis and tendon. Note the flattened fibroblast nuclei and the pink-staining collagen bundles of the tendon. Compare the dense irregular dermal CT with the dense regular CT of the tendon. UCLA Histology Collection. | collagen; Connective Tissue; Tendon | UCLA Histology |
| 119 |
 |
Connective Tissue | Plasma cells can also be found in the lacrimal gland of the eye. Note the classic clock face nucleus produced by clumps of heterochromatin. UCLA Histology Collection. | Connective Tissue; Eye; lacrimal gland | UCLA Histology |
| 120 |
 |
Connective Tissue - Mesenchyme | Embryonic connective tissue is called mesenchyme. Mesenchymal cells are embryonic fibroblasts. You are not required to identify developing tooth. UCLA Histology Collection. | mesenchyme | UCLA Histology |
| 121 |
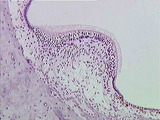 |
Ear | At this higher magnification, one can differentiate the hair & supporting cells, the gelatinous cupula, and the dark cells which mark the transition of the membranous labyrinth into the crista ampullaris. Bone is also evident. Movement of the endolymph against the cupula causes bending of hair cell ... | Crista Ampullaris; Ear | UCLA Histology |
| 122 |
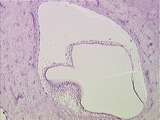 |
Ear | This image shows the bony labyrinth filled with perilymph, containing the membranous labyrinth filled with endolymph. Within the ampulla of each semicircular canal is the crista ampullaris, which is a specialization of the membranous labyrinth. UCLA Histology Collection. | Crista Ampullaris; Ear | UCLA Histology |
| 123 |
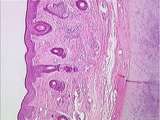 |
Ear | The thin skin of the external ear canal with hair follicles. Note the presence of the cartilage of the auricle. UCLA Histology Collection. | Ear; External Ear Canal | UCLA Histology |
| 124 |
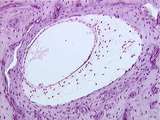 |
Ear | This image shows a semicircular canal in cross-section. It clearly differentiates the bony labyrinth filled with perilymph from the membranous labyrinth filled with endolymph. Here, bone is stained light purple. UCLA Histology Collection. | Ear; Semi-Circular Canal | UCLA Histology |
| 125 |
 |
Ear | This image shows one section through the coiled cochlear canal. The scala vestibuli and scala tympani are filled with perilymph, and the scala media is filled with endolymph. Also visible is a section of the spiral ganglion and the large acoustic nerve. The cochlea is encased in bone. UCLA Histology... | Cochlea; Ear | UCLA Histology |
