The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
Filters: Collection: ehsl_heal
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 76 |
 |
Central Nervous System | The choroid plexus is found in all the ventricles of the brain. This specialization of the ependymal layer consists of tufts of capillaries embedded in connective tissue and surrounded by modified ependymal cells. The choroid plexus is the site of formation of cerebro-spinal fluid (CSF). Ependymal c... | Brain; Central Nervous System; cerebro-spinal fluid (CSF); choroid plexus; ependymal cells | UCLA Histology |
| 77 |
 |
Central Nervous System | This histochemical stain (Bodian silver stain) reveals neurofilaments. The prominent pyramidal cells have several dendrites and one axon emanating from the cell body. The dendrites taper and branch as they leave the cell body. Darkly stained nuclei of neuroglial cells, astrocytes, and neural process... | Bodian silver stain; Brain; Central Nervous System; pyramidal cell | UCLA Histology |
| 78 |
 |
Central Nervous System | Fibrous astrocytes of the cerebrum. The stellate body gives off numerous radial processes which can extend to surround a capillary. Note the long protoplasmic process marked in this section. UCLA Histology Collection. | astrocytes; Brain; Central Nervous system; cerebrum; cortex | UCLA Histology |
| 79 |
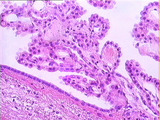 |
Central Nervous System | The choroid plexus is found in all the ventricles of the brain. This specialization of the ependymal layer consists of tufts of capillaries embedded in connective tissue and surrounded by modified ependymal cells. Compare the ependymal cells of the choroid plexus (which produce CSF) with the ependym... | Brain; Central Nervous system; cerebro-spinal fluid (CSF); choroid plexus | UCLA Histology |
| 80 |
 |
Central Nervous System | In this trichrome stained slide, the thick collagenous dura mater appears blue. The dura mater closely follows the contours of the cerebral hemispheres. This section is taken from between the left and right cerebral hemispheres. The dura mater folds down between the hemispheres, forming a two-ply di... | Brain; Central Nervous System; dura mater; falx cerebri; meninges; trichrome | UCLA Histology |
| 81 |
 |
Central Nervous System - Central Canal of the Spinal Cord | High power magnification of the central canal of the spinal cord. The central canal is continuous with the fourth ventricle superiorly and the sub-arachnoid space inferiorly. It is filled with CSF and lined by columnar ependymal cells. Note the presence of glial cells and capillaries in the surround... | Central Canal of Spinal Cord | UCLA Histology |
| 82 |
 |
Central Nervous System - Gray Matter and White Matter | This slide illustrates the difference between gray matter and white matter. The ventral horn of gray matter contains the cell bodies of motor neurons with cytoplasmic Nissl bodies (rough ER). Gray matter also contains neuropil filled with glial cells and neuronal processes. The white matter is fille... | gray matter; white matter | UCLA Histology |
| 83 |
 |
Central Nervous System - Spinal Cord | This cross section of the spinal cord shows both the white matter (myelinated axons) and the gray matter (cell bodies of neurons). The gray matter is arranged in an H pattern with both dorsal and ventral horns. The dorsal horns receive sensory information, and the ventral horns hold the motor neuron... | Gray Matter; Spinal Cord; White Matter | UCLA Histology |
| 84 |
 |
Central Nervous System - Ventral Horn Motor Neurons | Ventral horn motor neurons are large and multipolar. They have a pale staining nucleus with widely dispersed chromatin and a prominent nucleolus. Nissl bodies extend into the proximal dendrite, but the axon hillock is devoid of Nissl bodies and marks the area of the emerging axon. Note that there ar... | UCLA Histology | |
| 85 |
 |
Cervix | Very tall columnar epithelium of the cervical glands of the cervical canal. UCLA Histology Collection. | Cervix; Uterus | UCLA Histology |
| 86 |
 |
Circulatory System | In this high power view of the tunica media, identify pink elastic fibers, which appear thin and glassy. Smooth muscle appears thick and purple, and collagen fibers appear blue. Note the laminar arrangement of fibers and muscle cells. UCLA Histology Collection. | Aorta; Circulatory System; elastic artery; trichrome; tunica media | UCLA Histology |
| 87 |
 |
Circulatory System | In this aorta stained with Trichrome, identify pink elastin, blue collagen, and reddish muscle cells. Here the boundary between the tunica intima and tunica media is less distinct. However, the lumen is quite obvious. UCLA Histology Collection. | Aorta; Circulatory System; elastic artery; trichrome; tunica intima; tunica media | UCLA Histology |
| 88 |
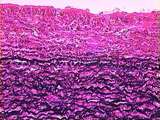 |
Circulatory System | The aortic tunica intima is largely composed of pink-stained collagen fibers. Elastin appears here as black, squiggly lines. The tunica media contains large amounts of elastin, collagen, and smooth muscle. The components of the tunica media are organized in sheet-like laminae, with holes or fenestra... | Aorta; Circulatory System; elastic artery; tunica intima; tunica media | UCLA Histology |
| 89 |
 |
Circulatory System | Image of the aorta at low power. Elastin stain demonstrating the high content of elastic fibers in the tunica media. UCLA Histology Collection. | Aorta; circulatory system | UCLA Histology |
| 90 |
 |
Circulatory System | The internal elastic membrane (IEM), a component of the tunica intima, separates the tunica intima from tunica media. The lumen of blood vessels (including the heart) is lined by simple squamous endothelium. The nuclei of the endothelium are visible here. Identify the sheet-like laminae of elastic f... | Aorta; Circulatory System; endothelium; tunica intima; tunica media | UCLA Histology |
| 91 |
 |
Circulatory System | Due to a special stain, the elastin of the tunica media is visible as dark, squiggly lines. The pink-stained areas between elastic fibers are occupied by collagen fibers and smooth muscle cells. UCLA Histology Collection. | aorta; Circulatory System; elastic artery; tunica media | UCLA Histology |
| 92 |
 |
Circulatory System | The lumen is on the far right, with no evident endothelium. The tunica intima and tunica media seem to blend together; the two are relatively small compared with more extensive tunica adventitia. Note the vasa vasorum and blue stained collagen fibers that can be identified within the tunica adventit... | Circulatory System; Hepatic cords; hepatic vein; Liver; tunica adventitia; tunica intima; tunica media; vasa vasorum | UCLA Histology |
| 93 |
 |
Circulatory System | This is slide stained for elastin (black) and collagen (pink). Identify the lumen and tunica intima. Notice the wide tunica media, which contains abundant elastic fibers. The less distinct tunica adventitia is dominated by collagen fibers. UCLA Histology Collection. | tunica intima; tunica media; Aorta; Circulatory System; elastic artery; tunica adventitia | UCLA Histology |
| 94 |
 |
Circulatory System | The tunica adventitia contains adipose tissue and the blood vessels which nourish the vessel wall: the vasa vasora. Also note the thick tunica media, rich in elastic fibers; and the innermost layer, the endothelium. UCLA Histology Collection. | tunica intima; tunica media; vasa vasora; Circulatory System; tunica adventitia | UCLA Histology |
| 95 |
 |
Circulatory System - Brachial Artery and Vein | This image shows the brachial artery (a muscular artery) at lower left, and the brachial vein at right. The staining of elastic fibers demonstrates the dark internal elastic membrane (IEM) and external elastic membrane (EEM), sandwiching the tunica media. The arterial intima appears to have sloughed... | brachial vein; tunica adventitia | UCLA Histology |
| 96 |
 |
Circulatory System - Capillary | A longitudinally sectioned capillary, showing erythrocytes in single file, a typical feature revealing the small size of capillaries. Identify the nuclei of the endothelial cells which make up the capillary wall. UCLA Histology Collection. | RBCs | UCLA Histology |
| 97 |
 |
Circulatory System - Coronary Artery | A higher magnification of a coronary artery, focusing on the tunica adventitia, which contains collagen fibers and fibroblasts. Adipocytes, vasa vasorum (containing blood cells), and nerve bundles are also present. The muscular tunica media is visible to the lower right. UCLA Histology Collection. | Circulatory System; Coronary artery; tunica adventitia | UCLA Histology |
| 98 |
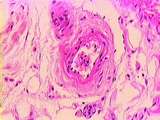 |
Circulatory System - Muscular Artery | A small muscular artery; note the extent of its tunica adventitia, almost indistinguishable from the surrounding connective tissue in which it is embedded. Identify collagen fibers and slender fibroblasts. UCLA Histology Collection. | Circulatory System; muscular artery; tunica adventitia | UCLA Histology |
| 99 |
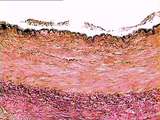 |
Circulatory System - Muscular Artery | This higher power view shows the wall of the muscular artery. The sloughed endothelium lies above the black-stained internal elastic membrane (IEM), which has a scalloped appearance due to contraction of the tunica media beneath it. The tunica media and tunica adventitia are separated by the diffuse... | muscular artery; tunica adventitia | UCLA Histology |
| 100 |
 |
Circulatory System - Muscular Artery | Muscular artery specifically stained for elastin (black). Notice the prominent internal elastic membrane which is characteristic of a muscular artery. Some of the tunica intima may have broken off into the vessel lumen. UCLA Histology Collection. | Circulatory System; Muscular artery | UCLA Histology |
