The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
TO
Filters: Collection: ehsl_heal
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 601 |
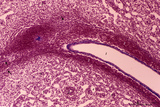 |
Spleen with central artery in lymphatic nodule (human) | Stain: Azan. A longitudinally cut central artery (1) of a lymphatic nodule or follicle, (white pulp) is invested by a distinct lymphatic sheath (PALS) composed of concentric layered T lymphocytes) (2). The red pulp consists of open venous sinusoids (4) and splenic cords (5, Billroth) with macrophage... | central artery; PALS; sinusoid ; Billroth | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 602 |
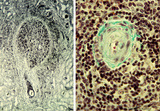 |
Spleen with central artery in lymphatic nodule (human) | Stain: A: Silver stain (Gomori). B: Trichrome (Goldner). In A: the reticular fibers (2) around the PALS (periarteriolar lymphatic sheath) and continuing in and around the marginal zone are stained black, illustrating the reticular framework of the lymphatic nodule. (1) central arteries. (4) red pulp... | central artery; PALS; white pulp; T cells | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 603 |
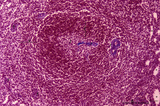 |
Spleen with central artery in secondary lymphatic nodule (human) | Stain: Azan. The white pulp consists of (1) a cross-section of the central artery, (2) the germinal centre with few branches of the central artery; the mantle zone (3) and the marginal zone (4) surrounded by a perilymphoid zone around the nodule. The perilymphoid zone is composed of concentricall... | germinal center; PALS; central artery; marginal zone | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 604 |
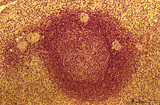 |
Spleen with secondary lymphatic nodule (human) | Stain: Hematoxylin & eosin. The splenic follicle as part of the white pulp is arranged around the cross sectioned central artery (1).The lymphatic sheath or PALS is composed of T cells (2). The darker stained mantle zone of mainly nave B lymphocytes (3) encompasses the lighter stained germinal centr... | white pulp; PALS; marginal zone; mantle layer | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 605 |
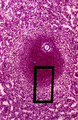 |
Spleen with secondary lymphatic nodule (human) | Stain: Azan. The white pulp of this perfused spleen consists of: at (1) a cross-section of the central artery, (2) tangential cut mantle zone and (3) the marginal zone. The red pulp contains empty venous sinusoids (4) and the perilymphoid zone (3a) is the zone of red pulp immediately surrounding ... | white pulp; germinal center; follicle; white pulp | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 606 |
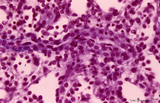 |
Splenic sheathed capillaries (human) | Stain: Azan. The blood flow in the spleen goes from splenic artery to trabecular artery to central or follicular artery (with a periarteriolar lymphatic sheath or PALS), and upon leaving the follicle the blood flows through penicillar arterioles and sheathed capillaries and terminal arterial capilla... | penicillar arterioles; red pulp; sheathed capillaries | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 607 |
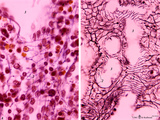 |
Splenic sinusoids (human) | Stain: A: Azan and B: Silver stain (Gomori). The splenic sinusoids are built in the form of a grid. The frame of the barrel consists of elongated endothelial cells (1) which are spirally wrapped around by reticular fibers (2). To this reticular fibers are attached many macrophages which control the... | sinusoid; reticular fibers | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 608 |
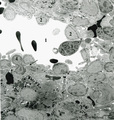 |
Splenic venous sinusoid in red pulp (rat) | Immunoelectron microscopy (gold labeling of heparan sulfate in Lowicryl embedding, using the single chain antibody HS4C3). (1) shows the open lumen of a venous sinusoid filled with few electron-dense erythrocytes and lining cells (2). (3) marks a neutrophilic granulocyte. (4) points to the diaped... | sinusoid; immuno electron microscopy; heparan sulfate | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 609 |
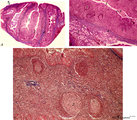 |
Survey and details of palatine tonsil ('lymphoepithelial tissues', 'gut-associated lymphatic tissue' or GALT) (human) | Stain: Azan. The survey in (A) shows that the palatine tonsil (localized in the lateral wall of the oropharynx) consists of crypts (1) and folds of the surface epithelium (stratified squamous) surrounded by accumulations of lymphoid cells organized in follicles (2). (B): the lining epithelium (5) i... | stratified squamous epithelium | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 610 |
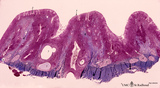 |
Survey of pharyngeal tonsil ('lymphoepithelial tissues', 'gut-associated lymphatic tissue' or GALT) (human) | Stain Azan. The solitary pharyngeal tonsil is localized in the pharyngeal fornix and belongs to the so-called Waldeyer's ring of pharyngeal lymphatic tissue. A survey shows the folded columnar epithelium (1) with faintly light-stained goblet cells with clefts (2) in between. The lamina propria co... | pharyngeal tonsil; GALT | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 611 |
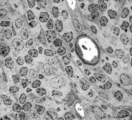 |
Survey of part of splenic lymphatic nodule (rat) | Electron microscopy. (1) shows an arteriolar branch of a central artery, and cross-sections of capillary branches (1a). Within the periarteriolar lymphatic sheath (PALS) mostly T lymphocytes (5) are present between concentric arranged reticular cells (2). Cells with larger lighter stained nuclei rep... | central artery ; electron microscopy; PALS; Antigen presenting cells (APC) | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 612 |
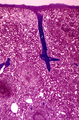 |
Survey of spleen (human) | Stain: Azan. The spleen is covered by a capsule (1) of dense connective tissue and elastic fibers. The capsule continues into the spleen as trabeculae (2) carrying blood vessels and nerve fibers. As arteries leave the trabeculae it becomes invested by a sheath of T cells forming a PALS (3) or periar... | white pulp; sinusoid; red pulp; PALS | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 613 |
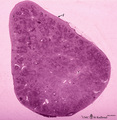 |
Survey of spleen (human) | Stain: Trichrome (Goldner). Encapsulated by a relatively thin fibroelastic capsule (1), the splenic parenchyma shows a preferable peripheral location of the red pulp (3). There are many secondary lymphatic nodules (2) as part of the white pulp, all showing a clear germinal centre. The red pulp is a ... | white pulp; red pulp | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 614 |
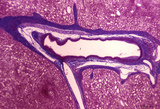 |
Survey of splenic trabecular artery (human) | Stain: Azan. The splenic artery (or lienal artery) is the blood vessel that provides oxygenated blood to the spleen. Branches of the splenic artery divide into trabecular arteries (1) which enter the white pulp as central arteries (4) that is surrounded with lymphocytes (5,periarteriolar lymphatic s... | trabecular artery; PALS; sinusoid | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 615 |
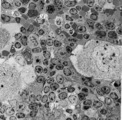 |
Survey of the border of splenic white and red pulp (rat) | Electron microscopy. Megakaryocytes (1) are commonly found in adult spleen of rodents. In this area they are located just at the border of the white pulp (WP) with a variety of lymphocytes (3). In the splenic cords (Billroth) of the red pulp (RP) erythrocytes (2) are found. | electron microscopy; white pulp; Billroth | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 616 |
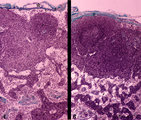 |
T cell depletion in lymph nodes (dog) | Stain: Trichrome (Goldner). Left and right: survey of lymph nodes. A: lymph node after treatment with anti-thymocyte-antiserum (ATS); B: normal, untreated lymph node ATS treatment results in a considerable depletion of the T cells in the paracortical area (2), while also the germinal centre (1) i... | T cell depletion; follicle; medulla; paracortex | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 617 |
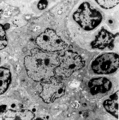 |
Thymic nurse cell (TNC) (mouse) | Electron microscopy. The thymic nurse cell (TNC) consists of an epithelial reticular cell (type II) enclosing thymocytes. The TNC exists as a sealed structure in situ, i.e. the lymphocytes within the TNC are isolated from the general thymic environment. TNC are located in the cortex, where mature ... | epithelioreticular cell type II; thymic nurse cell | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 618 |
 |
Thymus (human, fetus) | Stain: Silver stain (Gomori). Reticular fibers are demonstrated in the interlobular septa in the thymic cortical area (2) of this lobule. In the medulla (1) the more loosened reticular framework is more distinct. The reticular fibers are produced by the epithelioreticular cells and are particular ... | thymic corpuscle (Hassalls); epithelioreticular cell (ERC); reticular fibers; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 619 |
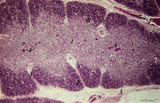 |
Thymus (human, newborn) | Stain: Hematoxylin & eosin. The thymus is a bilobed lymphoepithelial organ derived as an outgrowth from the third branchial (pharyngeal) pouch, and situated in the anterior mediastinum. Each lobe is divided into multiple lobules by fibrous septa or trabeculae (3). Each lobule consists of an outer co... | epithelioreticular cells (ERC); thymus hormones; Hassalls corpuscle ; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 620 |
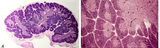 |
Thymus (human, newborn, low and higher magnification) | Stain: Hematoxylin & eosin. The infantile thymus is surrounded by connective tissue capsule (3) from where vascularized interlobular septa (or trabeculae, 3) penetrate into the lobulated organ. Each lobule consists of a darker stained cortex (2) and a lighter stained medulla (1). The medulla has a l... | Zhen; thymus cortex; thymus medulla; Hassall's corpuscle ; Lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 621 |
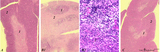 |
Thymus after cyclophosphamide treatment (rat) | Stain: Hematoxylin & eosin. A single injection with cyclophosphamide (CP, 4 70 mg/ml) induces a transient cortical involution, i.e. inhibition of the cell proliferation and maturation. A: Normal thymus with medulla (1) and cortex (2). B1: Inversion of thymic cortex and medulla 4 to 8 days after CP ... | cyclophosphamide; immunosuppression; involution; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 622 |
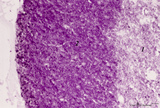 |
Thymus cortex (mouse, young adult) | Stain: Hematoxylin. Autoradiography after pulse labeling with tritiated thymidin. Most of the (black) radioactive labeling is found in the outer thymic cortex (3) where pre-T cells divide and subsequently migrate to the lighter stained medulla (1) that consists of a more loosened framework of epith... | thymus cortex; thymus medulla; thymidin labeling; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 623 |
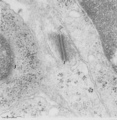 |
Thymus cortex (mouse, young adult) | Electron microscopy. (1) A well developed desmosome (1) of an epithelioreticular cells type II (TEC2). Apart from few free ribosomes, glycogen granules (2) are present in the electron-light cytoplasm. (3) part of an electron-grey thymocyte with many ribosomes. | epithelioreticular cell type II ; desmosome; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 624 |
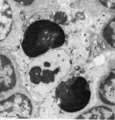 |
Thymus cortex (mouse, young adult) | Electron microscopy. Surrounded by thymocytes (2) a cortical macrophage (starry-sky macrophage) is seen and shows an electron-light nucleus (N) and a distinct nucleolus. The cell has engulfed two apoptotic thymocytes (1). The cytoplasm also contains small electron-dense lysosomes and myelin figures ... | cortical macrophage; epithelioreticular cell type II ; apoptotic thymocyte; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 625 |
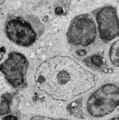 |
Thymus cortex (rat, young adult) | Electron microscopy. Within the thymic cortex a type II epithelioreticular cell or so-called (sometimes multinucleated) thymic nurse cell (TNC) shows a characteristic electron-light nucleus and nucleolus (1). The branches are squeezed between the thymocytes (2). In the cytoplasm a variety of empty a... | MHC class I and II expression; epithelioreticular cell type I and II; thymic nurse cell TNC; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
