The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
TO
Filters: Collection: ehsl_heal
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 576 |
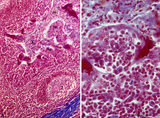 |
Palatine tonsil ('lymphoepithelial tissues', 'gut-associated lymphatic tissue' or GALT) (human) | Stain: Azan. A low magnification in A shows the thick blue connective septum (1) with a secondary lymphatic nodule (2). (3) is a cross-section of a crypt filled with detached squamous epithelium (3a) mixed up with keratinized material (red) and a huge amount of lymphocytes (3b). A higher magnificati... | follicle; germinal center; mantle layer; stratified squamous epithelium | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 577 |
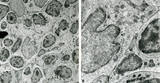 |
Part of lymphatic nodule in spleen (rat) | Electron microscopy. The left image (A) reveals part of a white pulp area stuffed with a dendritic cell (1) between a majority of different types of lymphocytes (2, 3). The right image shows a larger magnification of the same area with the dendritic cell (1) sandwiched in between the enclosing lymp... | dendritic cell; electron microscopy; white pulp | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 578 |
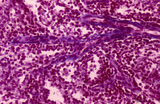 |
Penicillar arterioles in spleen (human) | Stain: Azan. The central or follicular artery in the follicle of the spleen splits into many arterioles. These arterioles spread as so-called penicillar arterioles (1) shown here. They are still surrounded by a very thin perilymphatic sheath (PALS) that disappears as the arteries in a brush-like pat... | penicillar arterioles; red pulp | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 579 |
 |
Phagocytosis in small splenic blood vessel (mouse) | Electron microscopy. Stain: Peroxidase reaction with diaminobenzidin staining. A diversity of red blood cells is black-stained due to the staining of hemoglobin by oxidized benzidin. Circulating lymphocytes (2) in the lumen (*) remain unstained. An oblong monocyte (1) developing into a macrophage h... | electron microscopy; phagocytosis | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 580 |
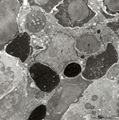 |
Phagocytosis in splenic red pulp (mouse) | Electron microscopy. Stain: Peroxidase reaction with diaminobenzidin staining. A diversity of red blood cells in the red pulp can be discerned due to the DAB staining of hemoglobin by oxidized benzidin (dark and light staining). The macrophage (1) shows peroxidase activity along the nuclear membran... | electron microscopy; phagocytosis | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 581 |
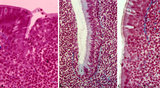 |
Pharyngeal tonsil ('gut-associated lymphatic tissue' or GALT) (human) | Stain: Azan. The combination demonstrates stages of infiltration (=diapedesis) of lymphocytes in the epithelium of the pharyngeal tonsil. The pharyngeal tonsil or adenoid is located in the nasopharyngeal roof. The agglomerations of lymphocytes (4) are covered by (1) pseudostratified ciliated epithel... | pharyngeal tonsil ; GALT; diapedesis; pseudostratified ciliated epithelium | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 582 |
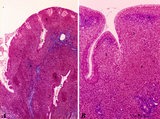 |
Pharyngeal tonsil ('lymphoepithelial tissues', 'gut-associated lymphatic tissue' or GALT) (human) | Stain Azan. The solitary pharyngeal tonsil is localized in the pharyngeal fornix and belongs to the so-called Waldeyer's ring of pharyngeal lymphatic tissue. A: The roof of the nasopharynx is covered by a columnar epithelium with faintly light-stained goblet cells (1) and part of a fold shows cle... | pharyngeal tonsil; GALT; pseudostratified columnar epithelium | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 583 |
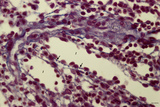 |
Red pulp of spleen with perfused venous sinusoids (human) | Stain: Azan. Cross-sectioned venous sinusoids with splenic cord (1). The wall of a sinusoid is composed of elongated rod-like endothelial cells that are orientated parallel to each other in the long axis of the sinusoid. There is a discontinuous pale-stained basement membrane (difficult to observe i... | sinusoid ; red pulp; splenic cord; central arteriole | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 584 |
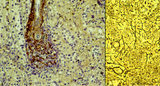 |
Red pulp of spleen with venous sinusoids (monkey, human) | Stain: A: Silver stain (Movat) (monkey); B: Silver stain (Gomori) (human). (A): The darkly stained fibres are conspicuous in the PALS (1) area arranged in parallel rows. The blood vessels continue in the surrounding splenic sinusoids (4). The wall of the sinusoid is built as a grid, the space is su... | sinusoid; reticular fibres | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 585 |
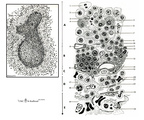 |
Scheme electron microscopy of the border of secondary nodule/red pulp in spleen | The left figure POJA-L974 shows a scheme of histological impression of a survey of a secondary splenic follicle or nodule. The rectangle is enlarged in the right figure POJA-L976B and shows the following elements: A. germinal centre; B. mantle zone; C. dendritic cell area; D. marginal zone; E. ... | white pulp; marginal zone; red pulp; antigen presenting cell (APC) | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 586 |
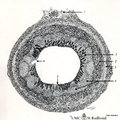 |
Scheme of appendix ('gut-associated lymphatic tissue' or GALT) (human) | Survey vermiform appendix (see also Digestive System: Appendix) A large amount of non-encapsulated diffuse lymphatic tissue or mucosa-associated lymphatic tissue (MALT) is located in the subepithelial lamina propria (e.g. respiratory passages, genitourinary tract). The gut-associated lymphatic tis... | GALT; follicle; scheme; germinal center | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 587 |
 |
Scheme of blood circulation in the red pulp in the spleen | A. closed circulation B. open circulation A. The route of closed circulation proposes that blood empties from the capillaries directly into the splenic sinus. The central artery bifurcates into penicillar arterioles (1) and the blood slowly enters ensheathed capillaries, surrounded by agg... | white pulp; marginal zone; red pulp; open circulation | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 588 |
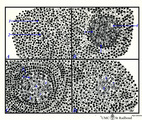 |
Scheme of development of germinal centre in lymphatic nodule (human) | A. primary nodule (or follicle) with mainly nave B lymphocytes and some memory cells, but no germinal centre; B. proliferation of lymphoblasts by mitosis (3,-->) and development of capillaries (*) in the centre of the follicle; C. so-called secondary nodule with lighter stained germinal centre wit... | follicle; antigen stimulation; scheme; germinal center | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 589 |
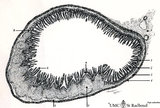 |
Scheme of ileum with Peyers patches (gut-associated lymphatic tissue or GALT) (dog) | Survey ileum (see also Digestive System: Ileum) A large amount of non-encapsulated diffuse lymphatic tissue or mucosa-associated lymphatic tissue (MALT) is located in the subepithelial lamina propria (e.g. respiratory passages, genitourinary tract). The gut-associated lymphatic tissues (GALT) are ... | GALT; follicle; scheme; germinal center | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 590 |
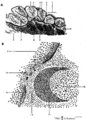 |
Scheme of lingual tonsil ('lymphoepithelial tissue') | Lingual tonsil (consisting of the accumulation of folliculi linguales). The root of the tongue contains invaginations or crypts or narrow caverns (3). In these crypts the ducts of the mucous glands (8) end up. The crypts are lined by multilayered, non-keratinizing squamous epithelium (2) and are sur... | lingual tonsil; scheme; germinal center; follicle | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 591 |
 |
Scheme of lymph node (human) | Lymph node: A. survey; B. detail subcapsular (or marginal) sinus 1. adipose tissue; 2. capsule; 3. afferent lymph vessel with valves (B); 4. subcapsular (or marginal) sinus; 5. germinal centre of a secondary lymphatic nodule (or follicle); 6. crescent or mantle zone indicated by cap of per... | cortex; scheme; paracortex; germinal center | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 592 |
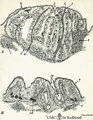 |
Scheme of palatine and pharyngeal tonsils ('lymphoepithelial tissues') (human) | The palatine tonsils are covered by the multilayered, non-keratinizing squamous epithelium of the oral cavity (A-1). In contrast to the palatine and lingual tonsils, the epipharyngeal tonsil has a multilayered ciliated epithelium (respiratory-like epithelium, B-9). The Waldeyer's tonsillar ring i... | germinal center; scheme; follicle | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 593 |
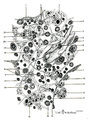 |
Scheme of reticular tissue in lymph node | Lymph node stroma does not contain stromal cells but instead the reticular meshwork is build by reticular cell types, macrophages and lymphoid cells and myeloid cells. Route (A) in the scheme represents morphological differentiation path from B lymphocytes to plasma cells. 1 endothelial ce... | reticular tissue; scheme; follicle; germinal center | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 594 |
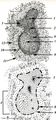 |
Scheme of secondary lymphatic nodule in spleen (human) | A. histological impression of a follicle or nodule B. outline of impression 1. pulpa artery; 2. central artery ; 3. lymphatic sheath; 4. lymphatic nodule; 5. thymus-dependent area (periarteriolar lymphatic sheath or PALS), composed of Th subset lymphocytes; 6. mantle zone with mainly nave B l... | white pulp; marginal zone; antigen presenting cell (APC) | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 595 |
 |
Scheme of the medullar changes in lymph node after antigen stimulation | Upon antigenic stimulation the reticular cells that line the medullar sinusoids start to phagocytise the antigens (i.e. infective agents) and change from small tiny stellate cells into swollen large cells due to phagocytosis. They detach from the medullar sinus wall. After ten days the situation has... | follicle; antigen stimulation; scheme; germinal center | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 596 |
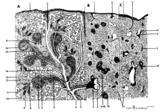 |
Scheme of the spleen (human) | Spleen: A. general diagram; B. adult; C. senium 1. capsule of dense irregular connective tissue with few elastic and smooth muscle fibers (it varies with the species); 2. trabecula (septum); 3. trabecular artery derived from the splenic artery; 4. trabecular vein; 5. when the pulpa artery ... | white pulp; red pulp | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 597 |
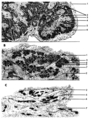 |
Scheme of the thymus during ageing (human) | Physiological changes in the course of human ageing lead to almost complete degeneration of the thymus (age involution). Both cortex and medulla become depleted of lymphocytes, and the distinction between both layers gradually becomes less. The remaining reticular meshwork of connective tissue is gr... | thymus involution; thymus development; thymus age; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 598 |
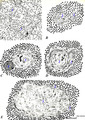 |
Scheme of the thymus medulla (human) | A-B: medullar epithelioreticular cells; C-D-E: development stages of thymic corpuscles (or Hassall bodies) (1): branching (-->) epithelioreticular cells in the medulla forming a meshwork (cytoreticulum) that normally is populated by thymocytes; (2): specialized epithelioreticular cells (2) often... | thymic corpuscle; Hassall ; epithelioreticular cells ; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 599 |
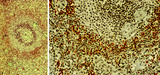 |
Secondary lymphatic nodule in the spleen (human) | Stain: Trichrome (Goldner). A: Survey of a follicle in the spleen. B: a higher magnification of a similar section shows part of a lymphatic nodule (follicle, white pulp) with cross-sections of the central artery (6). (1) germinal centre (filled with reticular cells, B-memory lymphocytes and macroph... | white pulp; PALS; germinal center; marginal zone | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 600 |
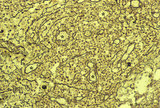 |
Section of lymph node (human) | Stain: Silver stain (Gomori). Due to the argyrophilia the reticular fibers are black-stained. They are derived from the fibrous capsule and penetrate into the deep cortex (i.e. paracortical area) and are embedded among other fibers such as collagen type III, IV. Note the postcapillary venules (*) ... | high endothelial venule (HEV); paracortex; argyrophilia; paracortex | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
