The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
TO
Filters: Collection: ehsl_heal
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 301 |
 |
Tongue (ventral part, human) | Stain: Hematoxylin and eosin. Non-keratinized squamous epithelium, followed by a small lamina propria and the intrinsic striated lingual muscles. | oral cavity; lingual muscles | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 302 |
 |
Tongue Papillae Scheme - tongue, human, adult | A. Scheme survey dorsal surface of tongue (human, adult). Magnification 35x. B. Scheme of filiform and fungiform papillae (tongue, human, adult). Magnification 35x. 1. foliate papillae (rudimentary in human); 2. circumvallate papillae; 3. foramen cecum; 4. palatine tonsils; 5. filiform ... | oral cavity; papillae | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 303 |
 |
Tooth ('free' gingiva of decalcified tooth, human, adult) | Stain: Hematoxylin and eosin. Oral side (left) with stratified squamous epithelium, at the right side part of a tooth (dentin), at the bottom side part of the alveolar bone. The epithelium shows slight parakeratosis with many narrow deep papillae of the lamina propria (oral side). On the tooth-relat... | oral cavity; junctional epithelium; alveolar bone; gingival sulcus | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 304 |
 |
Tooth ('free' gingiva of decalcified tooth, human, adult) | Stain: Hematoxylin and eosin. On top part of the gingival sulcus, at the left stratified junctional epithelium normally attached to the surface of the enamel (dissolved due to decalcification). Top left shows foci of chronic inflammatory cell infiltration, left side faint stained bundle of fibers (p... | oral cavity; acellular cementum; junctional epithelium | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 305 |
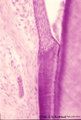 |
Tooth ('free' gingiva of decalcified tooth, human, adult) | Stain: Hematoxylin and eosin. On top the gingival sulcus; at the left stratified junctional epithelium normally attached to the surface of the enamel (dissolved due to decalcification). Below the epithelium a focus of chronic inflammatory cell infiltration, followed by a bundle of fibers of the per... | oral cavity; acellular cementum; junctional epithelium | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 306 |
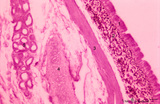 |
Trachea (cat) | Stain: Orcein and eosin. At the top pseudostratified epithelium (1) followed by a thick layer filled with dark-stained elastic fibers (2). Bundle of smooth muscle fibers (3) (note: there is an artifactual space between the elastic layer and the smooth muscle), belonging to the tunica fibro-musculo-... | Tracheal glands; Seromucous glands | Poja Histology Collection - Respiratory System Subset |
| 307 |
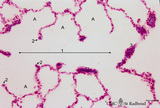 |
Transition of respiratory bronchiolus into alveolar duct in the lung (human) | Stain: Azan. The alveolar duct (1↔) exhibits an alveolated wall but at a few places (3) bronchiolar characteristics are evident such as cuboidal epithelium covering small areas of smooth muscle and connective tissue. They differ from the characteristic alveolar tips (2↓) of neighboring thin-wall... | Alveolar ducts; Alveolar tips | Poja Histology Collection - Respiratory System Subset |
| 308 |
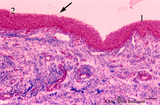 |
Transition surface of vocal cord into laryngeal surface (human, subglottis, higher magnification) | Stain:Stain: Azan. Transition (↓) from stratified squamous epithelium (1) into pseudostratified epithelium (2) in the subglottis region. Blood vessels and the cellularity of the proper lamina is evident. | Olfactory epithelium; Subglottis; Stratified epithelium; Pseudostratified epithelium | Poja Histology Collection - Respiratory System Subset |
| 309 |
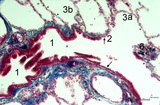 |
Transition terminal bronchiolus - respiratory bronchiolus (human) | Stain: Azan. A longitudinal section shows the transition from the lumen of a terminal bronchiolus (1) into that of a respiratory bronchiolus (2). The epithelium of the terminal bronchiolus is regularly columnar and ciliated. The respiratory bronchiolus has an irregular lining and is covered by low c... | Terminal bronchiolus; Respiratory bronchiolus; Columnar epithelium; Cuboidal epithelium; Alveolar epithelium | Poja Histology Collection - Respiratory System Subset |
| 310 |
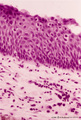 |
Transitional region of epiglottis (human, high magnification) | Stain: Hematoxylin and eosin. Transition of squamous epithelium into pseudostratified epithelium. Note diapedesis of lymphocytes (darker stained rounded cells) through the epithelial barrier (→). The proper lamina presents some lymphocyte infiltration. | Diapedesis | Poja Histology Collection - Respiratory System Subset |
| 311 |
 |
Transitional zone in the middle part of nasal vestibulum (comparable with red zone or vermilion border of lip, human) | Stain: Azan. At the right slightly cornified squamous epithelium (1) with small dermal papillae (2) and numerous blood vessels (3). To the left the transition to pseudostratified epithelium (4). In the submucosa branching seromucous nasal glands with draining ducts (5). | Stratified epithelium; Pseudostratified epithelium; Nasal glands; Seromucous glands | Poja Histology Collection - Respiratory System Subset |
| 312 |
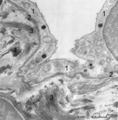 |
Type I alveolar cell in the lung (human, adult) | Electron microscopy. At the top the alveolar space is lined by type I alveolar cell (1, pneumocyte I). The cytoplasm is well provided with organelles and few electron-dense lysosomes, and pinocytotic vesicles. These pneumocyte I cells cover the interalveolar septa that contain fibroblasts and bundle... | Pneumocyte I; Interstitium | Poja Histology Collection - Respiratory System Subset |
| 313 |
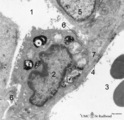 |
Type II alveolar cell in the lung (rat) | Electron microscopy. At the top the alveolar space (1) is lined by a type II alveolar cell (pneumocyte II) (2) with blunt microvilli. In the cytoplasm the characteristic electron-dense multilamellar bodies (*) and light-stained swollen mitochondria are present. The lamellar bodies are responsible fo... | Pneumocyte I; Pneumocyte II; Alveolar cell type I; Alveolar cell type II; Multilamellar bodies; Interstitial cells | Poja Histology Collection - Respiratory System Subset |
| 314 |
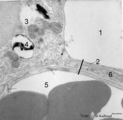 |
Type II and type I alveolar cells in the lung (human, adult) | Electron microscopy. At the top the alveolar space (1) is lined by a thin cytoplasm (2) of type I alveolar cell (pneumocyte I). At the left side part of a type II alveolar cell (3, pneumocyte II) with electron-dense remnants of two characteristic multilamellar bodies (4) as well as many organelles. ... | Pneumocyte I; Pneumocyte II; Interstitial cell; Alveolar cell type I; Alveolar cell type II | Poja Histology Collection - Respiratory System Subset |
| 315 |
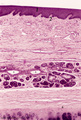 |
Upper part of nasal septum (dog, higher magnification) | Stain: Hematoxylin and eosin. Stratified squamous epithelium (1) with small papillae (2). The lamina propria contains many small and large thin-walled blood vessels also known as the venous plexus (sinusoids) of Auerbach (3, swell body). Nasal glands (4) with draining ducts (5, larger diameter) and ... | Squamous stratified epithelium; Nasal vestibulum; Venous sinusoids; Venous plexus; Swell bodies | Poja Histology Collection - Respiratory System Subset |
| 316 |
 |
Uvula (soft palate, human) | Stain: Azan. Detail of the uvula at the nasal side shows the border between the non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium (right, oral side) and pseudostratified columnar epithelium (left, nasal side). The lamina propria is composed of dense connective tissue. At the bottom part of a blood-fil... | oral cavity; lining mucosa | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 317 |
 |
Uvula (soft palate, human) | Stain: Azan. Detail of the uvula at the oral side; non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium. Note richly vascularized lamina propria. In the submucosa mainly mucous uvular glands with draining ducts. | oral cavity; lining mucosa; mucous glands | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 318 |
 |
Uvula (soft palate, human; low magnification) | Stain: Azan. At the right (oral side, non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium); at the left (nasal side, same epithelium). In the submucosa mainly mucous uvular glands are localized. At the bottom, striated muscle of the uvular muscle. The uvular tip is richly vascularized. | oral cavity | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 319 |
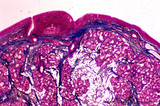 |
Ventricular fold (plica ventricularis) (human) | Stain: Azan. On top pseudostratified epithelium (1). Lamina submucosa with predominantly mucous glands (3), fat cells (4) and blood vessels. The lamina propria also contains lymphoid follicles (2) with a germinal center (immune protection). | Laryngeal glands; Ventricular fold; Seromucous glands | Poja Histology Collection - Respiratory System Subset |
| 320 |
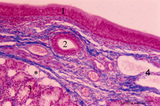 |
Ventricular fold (plica ventricularis) (human, higher magnification) | Stain: Azan. On top pseudostratified columnar, ciliated epithelium (1). Centrally below an excretory duct (2) of laryngeal seromucous gland (3) with some adipocytes (*). Blood vessels and two lymph vessels (4) are present. | Supraglottis; Ventricular fold; Laryngeal glands; Seromucous glands | Poja Histology Collection - Respiratory System Subset |
| 321 |
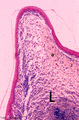 |
Vocal cord (plica vocalis) (human, glottis) | Stain: Azan. The true vocal cord consist of the vocal ligament (L) covered by stratified squamous epithelium and the striated vocal muscle (medial part of the thyreoarythenoid muscle, not depicted in this picture). At the tip of the vocal cord the stratified epithelium is distinct and the lamina pro... | Vocal ligament | Poja Histology Collection - Respiratory System Subset |
| 322 |
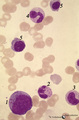 |
(Pro)myelocyte and neutrophilic granulocytes in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The promyelocyte (1) contains coarse primary, azurophilic granules in the basophilic cytoplasm. The absence of nucleoli indicates the late stage of the promyelocyte. (2) segmented neutrophilic granulocyte with toxic granulation (large irregular granules). (3) indicat... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 323 |
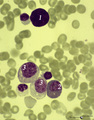 |
A bare megakaryocyte nucleus and myelocytes in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). (1) Indicates a bare large-sized polyploid nucleus of a megakaryocyte which has totally shed the cytoplasm. These cells are often seen in normal marrow and are ultimately removed by macrophages. There is no cytoplasm left, nor platelets are left around the nucleus. T... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 324 |
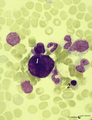 |
A bare megakaryocyte nucleus in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). (1) indicates a naked, large-sized polyploid nucleus of a megakaryocyte with visible lobes. No cytoplasm nor platelets are left around the nucleus. Most surrounding cells are of myeloid origin, except one orthochromatic erythroblast (2). | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 325 |
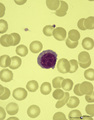 |
A plasmacytoid lymphocyte in peripheral blood smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The plasmacytoid lymphocyte is an activated B lymphocyte to be transformed into a plasma cell. The cytoplasm is more basophilic and the chromatin pattern is more clumped than in a virgin small lymphocyte. When the cell contains numerous immunoglobulin inclusions (glo... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset |
