John A. Moran Eye Center Neuro-Ophthalmology Collection: A variety of lectures, videos and images relating to topics in Neuro-Ophthalmology created by faculty at the Moran Eye Center, University of Utah, in Salt Lake City.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
Filters: Collection: "ehsl_novel_jmec"
| Title | Description | Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 126 |
 |
Blepharospasm | Example of patient with blepharospasm. Patient is led through instructions for direction of gaze and opening and closing of eyes. Patient is led through same exercises again after receiving indomethacin treatment. | Image/MovingImage |
| 127 |
 |
Fusional Vergence Amplitudes | Demonstration of fusional vergence amplitudes examination. Incluudes: a. Convergence Amplitudes b. Divergence Amplitudes c. Vertical Ampitudes | Text |
| 128 |
 |
Herpes Zoster Ophthalmicus with Third Nerve Palsy | Images showing presentation of Herpes Zoster (Zoster Ophthalmicus). | Text |
| 129 |
 |
Marcus Gunn Jaw Winking | Example of patient with Marcus Jaw Winking. Patient is led through instructions for movement of jaw (open, close, back and forth), with eyelid seen to be affected. Patient is then led through instructions for direction of gaze and pursuit. | Image/MovingImage |
| 130 |
 |
Normal Eye Movements | This is an examination of a person with normal eye movements. Notice the patient has normal excursions. He has normal pursuit and saccades (horizontally and vertically). | Text |
| 131 |
 |
Progressive Supranuclear Palsy | Progressive Supranuclear Palsy | Image/MovingImage |
| 132 |
 |
Retinal Fluorescein Angiography | This slide set provides a brief description of Retinal Fluorescein Angiography. First introduced in 1960, sodium fluorescein, a dye, is administered through an angiocatheter (3-5cc) by a nurse or technician. The dye reaches the central retinal artery after passing through the heart and lungs. | Text |
| 133 |
 |
Spontaneous Venous Pulsations | This clips shows a spontaneous venous pulsation viewed during an ocular examination. | Image/MovingImage |
| 134 |
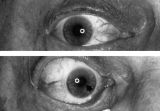 |
Aberrant Regeneration of the Right Pupil | Aberrant regeneration of the right pupil in a man with a large intracavernous sinus meningioma causing a pupil-involving, incomplete third cranial nerve palsy. His pupil is round when he gazes straight ahead (top). When he tries to rotate the eye medially, the pupil constricts, but a segment of the ... | Image |
| 135 |
 |
Before Tensilon | Example of patient with myasthenia gravis. Demonstration of baseline examination, followed by administration of 2mg of tensilon, which is a test dose. Procedure for administration of tensilon test is described, including variations. Patient is then shown after being given 4mg of tensilon, with very ... | Image/MovingImage |
| 136 |
 |
Dilation Lag | Two examples of dilation lag (Horner's syndrome). In the first example, the right pupil dilates much faster than the left pupil when the light is turned out. In the second example, the left pupil dilates much faster than the right pupil when the light is turned out. Discussion of methods of document... | Image/MovingImage |
| 137 |
 |
Duane's Retraction Syndrome Type 3 | Example of a patient with Type 3 Duane's Retraction Syndrome, as well as bilateral Duane's Syndrome. Shows limitation of abduction in both eyes and adduction in the left eye. Also shows side-view of globe retraction in abduction. | Image/MovingImage |
| 138 |
 |
Facial Myokymia Unilateral | Example of patient with facial myokymia, a disorder of the seventh nerve, probably due to brain stem involvement. Patient has multiple sclerosis. Discussion of characteristics, such as continuous, undulating, contractions in the distribution of the seventh nerve, and a spreading of these movements t... | Image/MovingImage |
| 139 |
 |
Hemifacial Spasm | Example of patients with hemifacial spasm. First patient has a sequela of Bell's palsy, and is seen to have mainly clonic movements around the eye, with occasional tonic movements around the mouth. Second patient has a cerebellopontine angle epidurmoid tumor, and is seen to have movements around the... | Image/MovingImage |
| 140 |
 |
How to Measure the RAPD | This clip demonstrates the examination technique for measuring the Relative Afferent Pupillary Defect (RAPD). Demonstration of balancing an afferent papillary defect using filters in a patient with a resolving optic neuritis and an afferent papillary defect on the left. | Image/MovingImage |
| 141 |
 |
Opsoclonus | Example of patients with opsoclonus, a saccadic abnormality. Discussion of characteristics of opsoclonus, such as involuntary, rapid, brief, random, conjugate saccades. Discussion of possible causes, including brain stem encephalitis (as in first patient), a paraneoplastic effect, tumors, and drug t... | Image/MovingImage |
| 142 |
 |
Parinaud's Syndrome | Two examples of patients with Parinaud's syndrome, a dorsal midbrain syndrome. Discussion of hallmarks of this syndrome, including convergence retraction nystagmus, vertical gaze palsies, light-near dissociation, and Collier's Sign. Discussion of age-dependent disorders associated with this syndrome... | Image/MovingImage |
| 143 |
 |
Spasm of the Near Reflex | Example of patient with spasm of the near reflex and voluntary nystagmus. Discussion of similar-looking conditions (e.g. six nerve palsy, limitation of abduction, lateral rectus muscle problems) and how to tell them apart from spasm of the near reflex by observing the myosis evoked by the near respo... | Image/MovingImage |
| 144 |
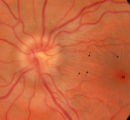 |
3-32b - Papilledema Stages | Grading Papilledema: Stage 1 Stage 1 = C shaped blurring of the nasal, superior and inferior borders. Usually the temporal margin is normal. Also notice the chorio-retinal folds (arrows) that eminate toward the macula (m) | Image |
| 145 |
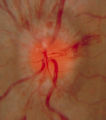 |
3-34c Papilledema Stages | Grading Papilledema: Stage 3 Stage 3 = Elevation of the entire disc with partial obscuration of the retinal vessels at the disc margin. Here the vessels are partly obscured and make the development into stage 3 easier to call. | Image |
| 146 |
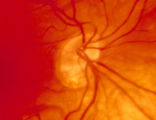 |
3-4 - Tilted Disc | Tilted discs are normal variants caused by oblique insertion of the optic nerve to the globe. They can be and frequently are mistaken for papilledema. In this case the superior edge of the disc is tilted and appears elevated. This disc exhibits a nasal inferior tilt. | Image |
| 147 |
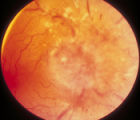 |
3-59a - Glioma | This 45-year-old man presented with vision loss in his right eye; his examination showed severe disc swelling in this eye and vision loss on visual field testing (3-59a). MRI with fat saturation and enhancement and MRI with T2 signals also confirm an enlarged optic nerve. (3-59c) Excisional biopsy o... | Image |
| 148 |
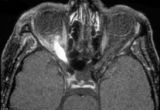 |
3-59c - Glioma | This 45-year-old man presented with vision loss in his right eye; his examination showed severe disc swelling in this eye and vision loss on visual field testing (3-59a). MRI with fat saturation and enhancement and MRI with T2 signals also confirm an enlarged optic nerve. (3-59c) Excisional biopsy o... | Image |
| 149 |
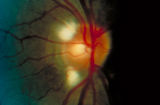 |
3-5b - Myelinated Nerve Fibers | Myelinated nerve fibers are frequently confused with papilledema. The feathery edge of the myelinated fibers that conceal the disc and vessel should provide the clue. These myelinated nerve fibers make the disc look blurred. | Image |
| 150 |
 |
3-60a - Meningioma | This 35 year old woman presented with slowly progressive loss of central acuity to 20/30. 3-60a: Her visual field shows progressive restriction over time. 3-60b: Her disc was chronically swollen, with refractile bodies on the disc surface. 3-60d: The CT axial scan showed an enlarged calcified optic... | Image |
