John A. Moran Eye Center Neuro-Ophthalmology Collection: A variety of lectures, videos and images relating to topics in Neuro-Ophthalmology created by faculty at the Moran Eye Center, University of Utah, in Salt Lake City.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
| Title | Description | Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 51 |
 |
Before Tensilon | Example of patient with myasthenia gravis. Demonstration of baseline examination, followed by administration of 2mg of tensilon, which is a test dose. Procedure for administration of tensilon test is described, including variations. Patient is then shown after being given 4mg of tensilon, with very ... | Image/MovingImage |
| 52 |
 |
Bilateral Asynchronous Blepharospasm with Facial and Cervical Dystonia | Bilateral Asynchronous Blepharospasm with Facial and Cervical Dystonia. | Image/MovingImage |
| 53 |
 |
Bilateral Facial Myokymia | Example of a patient with a brain stem glioma. Shows bilateral facial myokymia. | Image/MovingImage |
| 54 |
 |
Bilateral Internuclear Ophthalmoplegia | Example of patient with bilateral internuclear ophthalmoplegia. Patient is led through instructions for direction and distance of gaze. | Image/MovingImage |
| 55 |
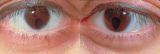 |
Bilateral Iris Colobomas | Coloboma literally means a "gap"-and can be used to describe any fissure, hole, or gap in the eye. The term most often is used to refer to a congenital gap in the disc, retina, the choroid, and the iris. Colobomas occur because the embryonic fissure fails to fuse. Since the fissure closure begins in... | Image |
| 56 |
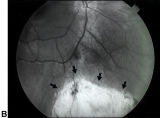 |
Bilateral Iris Colobomas (B) | Bilateral iris colobomas. B. Bilateral colobomatous defects of the inferonasal retina (black arrows) are also present, as shown in the right eye. | Image |
| 57 |
 |
Bilateral Ptosis | Video of patient with bilateral ptosis. | Image/MovingImage |
| 58 |
 |
Binocular Pendular Nystagmus | Example of a patient with binocular pendular nystagmus. Patient has somewhat dissociated nystagmus, with nystagmus seen more prominently in the left eye. Patient shows an occasional jerk nystagmus to the right in the right eye. Left eye oscillations are mostly pendular. | Image/MovingImage |
| 59 |
 |
Blepharospasm | Example of patient with blepharospasm. Patient is led through instructions for direction of gaze and opening and closing of eyes. Patient is led through same exercises again after receiving indomethacin treatment. | Image/MovingImage |
| 60 |
 |
Blepharospasm with Apraxia of the Eye | Image/MovingImage | |
| 61 |
 |
Brainstem Trauma | Image/MovingImage | |
| 62 |
 |
Brun's Nystagmus | Observation of patient with Brun's Nystagmus. Shows patient gazing to the right and the nystagmus beating in the direction of the gaze. | Image/MovingImage |
| 63 |
 |
Central Retinal Artery Occlusion | Video of central retinal artery occlusion. | Image/MovingImage |
| 64 |
 |
Cogan's Lid Twitch | Example of a patient with Cogan's lid twitch, with discussion of how to detect it in an exam. | Image/MovingImage |
| 65 |
 |
Cogan's Lid Twitch | Image/MovingImage | |
| 66 |
 |
Color Vision Testing | Demonstration of color vision examination. | Text |
| 67 |
 |
Cone Dystrophy | PPT covering Cone Dystrophy - An inherited degeneration that presents between 10 - 30 years of age. Symptoms are decreased visual acuity, poor color vision, and sometimes light sensitivity. | Text |
| 68 |
 |
Congenital Nystagmus | Example of patients with congenital nystagmus. First patient's nystagmus are mostly jerk and not pendular. Second patient's nystagmus are mostly pendular. Both patients show a uniform horizontal oscillation. Second patient also shows differences in frequency of oscillations depending on gaze, includ... | Image/MovingImage |
| 69 |
 |
Congenital Nystagmus | Patient with congenital nystagmus (no audio) | Image/MovingImage |
| 70 |
 |
Congenital Ocular Motor Apraxia | Two examples of congenital ocular motor apraxia. Patients have trouble initiating saccades, and compensate with head movement. Discussion of how to distinguish this condition from simply not seeing well. | Image/MovingImage |
| 71 |
 |
Convergence Retraction Nystagmus (Parinaud's Syndrome) | Examples of patients with convergence retraction nystagmus. Shows saccadic oscillations in patients looking upwards and following downwards moving targets. Also shows a side-view of the retracting movements of the globes. | Image/MovingImage |
| 72 |
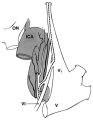 |
The Course of the Postganglionic Segment of the Oculosympathetic Fibers from the Internal Carotid Artery | The course of the postganglionic segment of the oculosympathetic fibers from the internal carotid artery (ICA) to the orbit is depicted as a dotted line. Note that they briefly join the abducens nerve (cranial nerve VI) before joining the nasociliary branch of the of the ophthalmic division of the t... | Image |
| 73 |
 |
CPEO | Patient with Chronic Progressive External Ophthalmoplegia (CPEO) | Image/MovingImage |
| 74 |
 |
Cyclic Oculomotor Palsy | Example of patient with cyclic oculomotor palsy. | Image/MovingImage |
| 75 |
 |
Dilation Lag | Two examples of dilation lag (Horner's syndrome). In the first example, the right pupil dilates much faster than the left pupil when the light is turned out. In the second example, the left pupil dilates much faster than the right pupil when the light is turned out. Discussion of methods of document... | Image/MovingImage |
