John A. Moran Eye Center Neuro-Ophthalmology Collection: A variety of lectures, videos and images relating to topics in Neuro-Ophthalmology created by faculty at the Moran Eye Center, University of Utah, in Salt Lake City.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
Filters: Collection: "ehsl_novel_jmec"
| Title | Description | Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 51 |
 |
Exophthalmometry | Demonstration of exophthalmometry examination. | Text |
| 52 |
 |
Gaze Palsy with Facial Weakness from Pontine AVM | Example of a patient with torsional nystagmus in both eyes and pendular nystagmus in the left eye. Patient is led through instructions for direction of gaze. | Image/MovingImage |
| 53 |
 |
Intermittent Square Wave Jerks | Patient with intermittent square wave jerks (no audio) | Image/MovingImage |
| 54 |
 |
Introduction to Headache, Migraine and Secondary Headaches | Video lecture covering an introduction to headache, migraine, and secondary headaches by Kathleen Digre, MD. | |
| 55 |
 |
Leber's Hereditary Optic Neuropathy | Images and visual fields from a boy with acute visual loss. | Text |
| 56 |
 |
Normal Optic Disc | Overview of the structure and function of the normal optic disc. | Text |
| 57 |
 |
Optic Disc Pallor Pseudo and Real | Discussion of the causes of optic disc pallor. | Text |
| 58 |
 |
Papilledema 2013 | Discussion of papilledema, the swelling due to increased pressure. | Text |
| 59 |
 |
Pupil Exam | Demonstration of pupil examination. | Text |
| 60 |
 |
Retinitis Pigmentosa Disease of Rods | Discussion of retinitis pigmentosa which is a retinal/choroidal degeneration caused by various genetic defects. | Text |
| 61 |
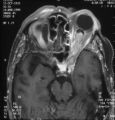 |
Shunt Vessel Meningioma - MRI | Meningiomas block venous egress and open potential venous channels known as retinochoroidal (optociliary) collateral vein. This meningioma extends from the back of the globe through the optic canal. | Image |
| 62 |
 |
Stages of Papilledema | Text | |
| 63 |
 |
Stereoacuity Testing | Demonstration of examination for stereoacuity. | Text |
| 64 |
 |
Superior Oblique Myokymia | Close-up video of a patient with superior oblique myokymia (no audio.) | Image/MovingImage |
| 65 |
 |
Tilted Discs | Short PowerPoint discussion of tilted discs with illustrations and images. | |
| 66 |
 |
Ultrasonography Techniques | This video describes and demonstrates the various techniques for examination of the eye using ultrasonography, including A-scan, B-scan and immersion. | Image/MovingImage |
| 67 |
 |
Wall-Eyed Bilateral Internuclear Ophthalmoplegia (WEBINO) | Example of patient with Wall-Eyed Bilateral Internuclear Ophthalmoplegia. Patient is led through instructions for direction and distance of gaze. | Image/MovingImage |
| 68 |
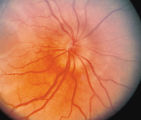 |
3-33b - Papilledema Stages | Grading Papilledema: Stage 2 = Elevation of the disc margin 360 degrees. Since the blood vessels at the disc margin are not swollen or obscured, this disc could be mistaken for pseudo-papilledema. | Image |
| 69 |
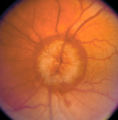 |
3-36a - Papilledema Stages | Grading Papilledema: Stage 5 Stage 5 = Dome-shaped appearance with all vessels being obscured. (Sometimes called "champagne cork" swelling--because of its dome shape.) | Image |
| 70 |
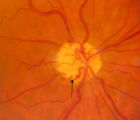 |
3-64a - Shunt Vessels (CRVO) | This man with a chronic CRVO and retino-choroidal collaterals developed AION and his collaterals disappeared. CRVO with retinochoroidal collaterals is almost always associated with multiple peripheral dot and blot hemorrhages as well as nerve fiber layer infarcts of various ages. Notice the retino-c... | Image |
| 71 |
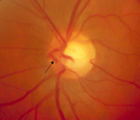 |
3-65 - Shunt Vessels (Glaucoma) | Chronic end-stage glaucoma produces high pressure that interferes with venous drainage from the disc and broad smooth venous collaterals drain the disc centrifugally to the disc margin where they drain. | Image |
| 72 |
 |
4-35 - Cupped Optic Nerve | Atrophic Glaucoma Atrophic glaucomatous discs show thinning of the neuro-retinal rim, "saucerization" (which is shallow cupping), evidence of peripapillary atrophy, and pallor of the very narrow neuroretinal rim. Notice that there is severe atrophy of the nerve fiber layer. | Image |
| 73 |
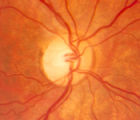 |
4-52b - Dominant Optic Neuropathy | A son presented with bilateral optic atrophy of unknown etiology after he failed a school visual exam. When looking for dominant optic atrophy, look at the parents. Mother was examined to find similar kind of atrophy. 4-52a mother, 4-52b son. | Image |
| 74 |
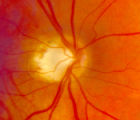 |
4-60a - Dominant Optic Neuropathy | A son presented with bilateral optic atrophy of unknown etiology after he failed a school visual exam. When looking for dominant optic atrophy, look at the parents. Mother was examined to find similar kind of atrophy. 4-60a mother, 4-60b son. | Image |
| 75 |
 |
Anterior Ischemic Optic Neuropathy | PPT describing Anterior Ischemic Optic Neuropathy (AION). Covers clinical signs, such as monocular vision loss, swollen nerve, and visual field defects, as well as risk factors. | Text |
