John A. Moran Eye Center Neuro-Ophthalmology Collection: A variety of lectures, videos and images relating to topics in Neuro-Ophthalmology created by faculty at the Moran Eye Center, University of Utah, in Salt Lake City.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
Filters: Collection: "ehsl_novel_jmec"
| Title | Description | Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 26 |
 |
Basic Neurologic Exam: Cranial Nerves | Demonstration of a cranial nerve examination. | Image/MovingImage |
| 27 |
 |
Basic Neurologic Exam: Mental Status | Demonstration of a mental status examination. | |
| 28 |
 |
Basic Neurologic Exam: Motor Examination | Demonstration of a motor examination. | Image/MovingImage |
| 29 |
 |
Basic Neurologic Exam: Sensory | Demonstration of a sensory examination. | Image/MovingImage |
| 30 |
 |
Brainstem Trauma | Image/MovingImage | |
| 31 |
 |
Cogan's Lid Twitch | Image/MovingImage | |
| 32 |
 |
Mimics of Atrophy | Text | |
| 33 |
 |
The Orbital Exam | Comprehensive demonstration of the entire orbital examination. | |
| 34 |
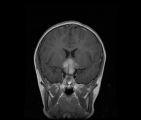 |
See-saw Nystagmus MRI 1 | MRI; See-saw Nystagmus | Image |
| 35 |
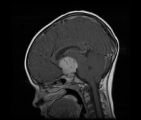 |
See-saw Nystagmus MRI 2 | MRI; See-saw Nystagmus | Image |
| 36 |
 |
Aberrant Regeneration of Third Nerve, Bilaterally (1 degree OD, 2 Digrees OS) | Example of patient with bilateral aberrancy of the third nerve. Shows lids popping up (synkinetic) with adduction. Patient had bilateral internal carotid artery aneurisms with third nerve compression. | Image/MovingImage |
| 37 |
 |
Convergence Retraction Nystagmus (Parinaud's Syndrome) | Examples of patients with convergence retraction nystagmus. Shows saccadic oscillations in patients looking upwards and following downwards moving targets. Also shows a side-view of the retracting movements of the globes. | Image/MovingImage |
| 38 |
 |
Latent Nystagmus | Example of a patient with latent nystagmus. Demonstrates a lack of oscillations in forward gaze, followed by the occlusion of each eye, showing how this generates a jerking oscillation in the non-occluded eye away from the occluded eye. | Image/MovingImage |
| 39 |
 |
Levator Disinsertion | Example of patient with levator disinsertion, a lid disorder. Patient is pregnant and wears poorly fitting contacts. Discussion of characteristics, such as lid ptosis (shown in the left eye of patient), but with full levator function. | Image/MovingImage |
| 40 |
 |
Light-near Dissociation | Example of patient with Argyll Robertson pupil with neurosyphilis. Shows a lack of pupillary response to light and some pupillary response to nearness of finger. | Image/MovingImage |
| 41 |
 |
Ocular Flutter | Two examples of patients, the first with rotary, flutter-like movements, but not ocular flutter, and the second with genuine ocular flutter. Discussion of difference between ocular flutter and nystagmus, and how to elicit ocular flutter. | Image/MovingImage |
| 42 |
 |
Paradoxical Constriction of Pupils to Darkness (Flynn Phenomenon) | Example of patients both with and without paradoxical constriction of pupils. Observed in many congenital retinal disorders, such as achromatopsia, congenital stationary night-blindness, and Leber's congenital amaurosis. Sometimes seen in optic nerve disorders, such as dominant optic atrophy. | Image/MovingImage |
| 43 |
 |
Periodic Alternating Nystagmus | Example of a patient with periodic alternating nystagmus, showing an alternation between left-beats and right-beats as the patient maintains forward gaze. Nystagmus maintain horizontal direction regardless of position of gaze. | Image/MovingImage |
| 44 |
 |
Progressive Supranuclear Palsy | Example of patient with progressive supranuclear palsy. Discussion of difference between saccadic movement in supranuclear palsy and nystagmus. Shows saccadic intrusions in forward gaze, pursuit, saccades, and doll's head maneuver. | Image/MovingImage |
| 45 |
 |
Rebound Nystagmus | Example of a patient with rebound nystagmus, where the oscillations alternate direction as the patient shifts gaze in different directions. Discussion of relationship to disease and disorders of the cerebellum, including degenerations of the cerebellum, infarction, and demyelination. | Image/MovingImage |
| 46 |
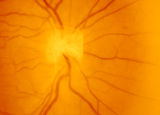 |
3-3 - Bergmeister Papilla | Image | |
| 47 |
 |
Basic Neurologic Exam: Coordination | Demonstration of a coordination examination. | Image/MovingImage |
| 48 |
 |
Basic Neurologic Exam: Station and Gait | Demonstration of a station and gait examination. | Image/MovingImage |
| 49 |
 |
Introduction to Fogging Refraction | An introduction to fogging refraction. | |
| 50 |
 |
Macula | Overview of the structure and viewing of the macula. | Text |
