John A. Moran Eye Center Neuro-Ophthalmology Collection: A variety of lectures, videos and images relating to topics in Neuro-Ophthalmology created by faculty at the Moran Eye Center, University of Utah, in Salt Lake City.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
| Title | Description | Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
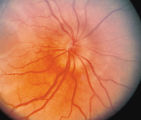 |
3-33b - Papilledema Stages | Grading Papilledema: Stage 2 = Elevation of the disc margin 360 degrees. Since the blood vessels at the disc margin are not swollen or obscured, this disc could be mistaken for pseudo-papilledema. | Image |
| 2 |
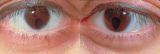 |
Bilateral Iris Colobomas | Coloboma literally means a "gap"-and can be used to describe any fissure, hole, or gap in the eye. The term most often is used to refer to a congenital gap in the disc, retina, the choroid, and the iris. Colobomas occur because the embryonic fissure fails to fuse. Since the fissure closure begins in... | Image |
| 3 |
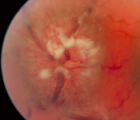 |
3-35a - Papilledema Stages | Grading Papilledema: Stage 4 Stage 4 = Complete obliteration of the cup and complete obscuration of at least some vessels on the surface of the disc. There may be small dilated capillaries on the disc that resemble telangiectasia. It is not the NFL infarcts or hemorrhages but the obscuration of the ... | Image |
| 4 |
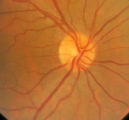 |
3-31b - Papilledema Stages | Grading Papilledema: Stage 0 GRADING PAPILLEDEMA GRADING PAPILLEDEMA We grade papilledema in order to tell us how severe it is. The most sensible grading scheme has been provided by Lars Frisén. STAGE 0: This woman had documented increased intracranial pressure of 340 mm water. Very little if any ... | Image |
| 5 |
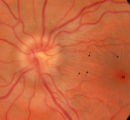 |
3-32b - Papilledema Stages | Grading Papilledema: Stage 1 Stage 1 = C shaped blurring of the nasal, superior and inferior borders. Usually the temporal margin is normal. Also notice the chorio-retinal folds (arrows) that eminate toward the macula (m) | Image |
| 6 |
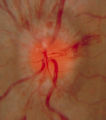 |
3-34c Papilledema Stages | Grading Papilledema: Stage 3 Stage 3 = Elevation of the entire disc with partial obscuration of the retinal vessels at the disc margin. Here the vessels are partly obscured and make the development into stage 3 easier to call. | Image |
| 7 |
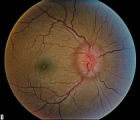 |
Stage 2 - Papilledema | Image | |
| 8 |
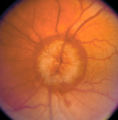 |
3-36a - Papilledema Stages | Grading Papilledema: Stage 5 Stage 5 = Dome-shaped appearance with all vessels being obscured. (Sometimes called "champagne cork" swelling--because of its dome shape.) | Image |
| 9 |
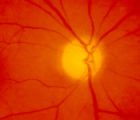 |
4-54a -Optic Neuropathy, Ischemic: Posterior | Image | |
| 10 |
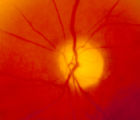 |
4-54b - Optic Neuropathy, Ischemic: Posterior | Image | |
| 11 |
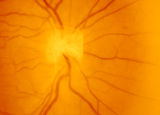 |
3-3 - Bergmeister Papilla | Image | |
| 12 |
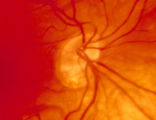 |
3-4 - Tilted Disc | Tilted discs are normal variants caused by oblique insertion of the optic nerve to the globe. They can be and frequently are mistaken for papilledema. In this case the superior edge of the disc is tilted and appears elevated. This disc exhibits a nasal inferior tilt. | Image |
| 13 |
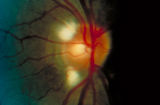 |
3-5b - Myelinated Nerve Fibers | Myelinated nerve fibers are frequently confused with papilledema. The feathery edge of the myelinated fibers that conceal the disc and vessel should provide the clue. These myelinated nerve fibers make the disc look blurred. | Image |
| 14 |
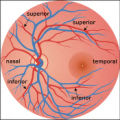 |
2-37a - Vascular Features | When looking at the disc, the central retinal artery and vein should be visible. The central retinal artery is usually slightly narrower than the vein. When the central retinal artery goes though the lamina cribrosa, the artery becomes smaller because of diminution of the muscular layer and loss of ... | Image |
| 15 |
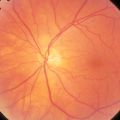 |
2-37b - Vascular Features | When looking at the disc, the central retinal artery and vein should be visible. The central retinal artery is usually slightly narrower than the vein. When the central retinal artery goes though the lamina cribrosa, the artery becomes smaller because of diminution of the muscular layer and loss of ... | Image |
| 16 |
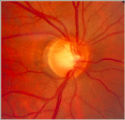 |
Notching of the Neuro-retinal Rim | The neuro-retinal rim becomes thinner; in particular the rim superotemporally and inferortemporally may develop a notch which is usually superior or inferior and rarely nasal or temporal. These notches are believed to be due to focal ischemic damage to the neuro-retinal rim. Glaucoma with Notching a... | Image |
| 17 |
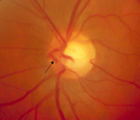 |
3-65 - Shunt Vessels (Glaucoma) | Chronic end-stage glaucoma produces high pressure that interferes with venous drainage from the disc and broad smooth venous collaterals drain the disc centrifugally to the disc margin where they drain. | Image |
| 18 |
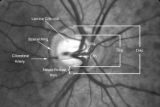 |
2-4a - Disc Anatomy | The optic disc appearance is determined by: the size of the eye, the size of the scleral canal, how the nerve is inserted into the globe, the appearance of the lamina cribrosa, where myelination stops, and what is left behind in normal development. Even though this is a disc with a very large cup, i... | Image |
| 19 |
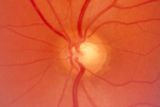 |
2-53a - Venous Pulsations | On the disc, look for spontaneous venous pulsations. Spontaneous venous pulsations can be seen in the large trunks of veins at the level of the disc margin. They are normally present and seen in 37-90% of normals -- depending on the experience of the examiner and the shape of the disc. The spontaneo... | Image |
| 20 |
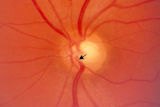 |
2-53b - Venous Pulsations | On the disc, look for spontaneous venous pulsations. Spontaneous venous pulsations can be seen in the large trunks of veins at the level of the disc margin. They are normally present and seen in 37-90% of normals -- depending on the experience of the examiner and the shape of the disc. The spontaneo... | Image |
| 21 |
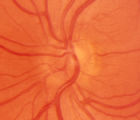 |
2-6a - Little Red Discs | Image | |
| 22 |
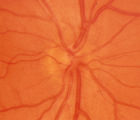 |
2-6b - Little Red Discs | Image | |
| 23 |
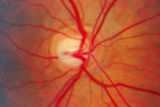 |
2-7a - Disc Anatomy | The optic disc appearance is determined by: the size of the eye, the size of the scleral canal, how the nerve is inserted into the globe, the appearance of the lamina cribrosa, where myelination stops, and what is left behind in normal development. Even though this is a disc with a very large cup, i... | Image |
| 24 |
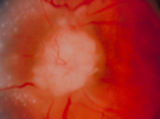 |
3-56a - Sarcoid | Image | |
| 25 |
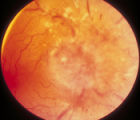 |
3-59a - Glioma | This 45-year-old man presented with vision loss in his right eye; his examination showed severe disc swelling in this eye and vision loss on visual field testing (3-59a). MRI with fat saturation and enhancement and MRI with T2 signals also confirm an enlarged optic nerve. (3-59c) Excisional biopsy o... | Image |
