The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
TO
Filters: Collection: "ehsl_heal"
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
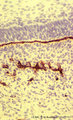 |
Basal lamina between ameloblasts and odontoblasts in tooth development - advanced bell stage, rat embryo | Stain: Anti-collagen IV immunoperoxidase and hematoxylin counterstained. From top to bottom: Stellate reticulum; Stratum intermedium; Ameloblasts at the distal side oriented towards the basal lamina intermingled with the Korffs' fibers (collagen, brown-black); Odontoblasts; Brown-black stained struc... | oral cavity; basal lamina; collagen IV | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 2 |
 |
Connective Tissue | This higher power view of the heel shows dermis and tendon. Note the flattened fibroblast nuclei and the pink-staining collagen bundles of the tendon. Compare the dense irregular dermal CT with the dense regular CT of the tendon. UCLA Histology Collection. | collagen; Connective Tissue; Tendon | UCLA Histology |
| 3 |
 |
Circulatory System | This is slide stained for elastin (black) and collagen (pink). Identify the lumen and tunica intima. Notice the wide tunica media, which contains abundant elastic fibers. The less distinct tunica adventitia is dominated by collagen fibers. UCLA Histology Collection. | tunica intima; tunica media; Aorta; Circulatory System; elastic artery; tunica adventitia | UCLA Histology |
| 4 |
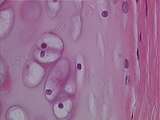 |
Cartilage - Hyaline Cartilage | Hyaline cartilage matrix appears glassy; the collagen is too finely dispersed to be seen easily. Theses chondrocytes have shrunk during tissue preparation, producing an empty space or lacuna, hence only the nuclei are evident. The perichondrium is made up of coarse bundles of collagen in which fibro... | Hyaline Cartilage; Perichondrium | UCLA Histology |
| 5 |
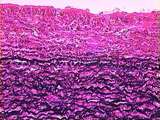 |
Circulatory System | The aortic tunica intima is largely composed of pink-stained collagen fibers. Elastin appears here as black, squiggly lines. The tunica media contains large amounts of elastin, collagen, and smooth muscle. The components of the tunica media are organized in sheet-like laminae, with holes or fenestra... | Aorta; Circulatory System; elastic artery; tunica intima; tunica media | UCLA Histology |
| 6 |
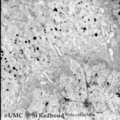 |
Dentinogenesis in tooth development - bell stage, gerbil, postnatal | Electronmicroscopy. At the bottom side of the predentin partly cross-sectioned odontoblasts with some organelles and many vesicular structures, the dark ones containing hydroxyapatite. Close to the odontoblasts a high concentration of secreted collagen fibers. Further away numerous matrix vesicles (... | oral cavity; predentin; matrix vesicles | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 7 |
 |
Acellular cementum in the tooth (longitudinal segment of coronal half of root; high magnification; human, adult) | Stain: Hematoxylin and eosin. From left to right: periodontal ligament with collagen fibers; flattened cementoblasts followed by a thin seam of pink cementoid; darker stained acellular cementum, the so-called acellular extrinsic fiber cementum as collagen fibers protrude from the periodontal ligamen... | oral cavity; acellular cementum; Sharpey's fibers; incremental lines | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 8 |
 |
Ameloblasts and odontoblasts in tooth development - advanced bell stage, human, embryo CR 80 mm | Scheme electronmicroscopy. From top to bottom: Stellate reticulum consisting of a non-vascularized network of ectoderm-derived cells continuous with the cell layers of the stratum intermedium; Columnar presecretory ameloblasts with their upper side (nuclear area) in close contact with the stratum in... | oral cavity; predentin | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 9 |
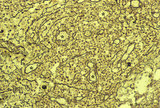 |
Section of lymph node (human) | Stain: Silver stain (Gomori). Due to the argyrophilia the reticular fibers are black-stained. They are derived from the fibrous capsule and penetrate into the deep cortex (i.e. paracortical area) and are embedded among other fibers such as collagen type III, IV. Note the postcapillary venules (*) ... | high endothelial venule (HEV); paracortex; argyrophilia; paracortex | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 10 |
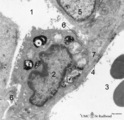 |
Type II alveolar cell in the lung (rat) | Electron microscopy. At the top the alveolar space (1) is lined by a type II alveolar cell (pneumocyte II) (2) with blunt microvilli. In the cytoplasm the characteristic electron-dense multilamellar bodies (*) and light-stained swollen mitochondria are present. The lamellar bodies are responsible fo... | Pneumocyte I; Pneumocyte II; Alveolar cell type I; Alveolar cell type II; Multilamellar bodies; Interstitial cells | Poja Histology Collection - Respiratory System Subset |
| 11 |
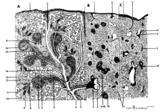 |
Scheme of the spleen (human) | Spleen: A. general diagram; B. adult; C. senium 1. capsule of dense irregular connective tissue with few elastic and smooth muscle fibers (it varies with the species); 2. trabecula (septum); 3. trabecular artery derived from the splenic artery; 4. trabecular vein; 5. when the pulpa artery ... | white pulp; red pulp | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 12 |
 |
Bone - Haversian System | Concentric layers of collagen (the remnant of decalcified bone) surround the Haversian canal. Osteocyte nuclei can be seen within lacunae. UCLA Histology Collection. | Haversian canal | UCLA Histology |
| 13 |
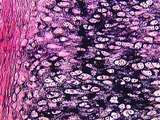 |
Cartilage | At a higher power, the black elastic fiber deposits are clearly seen. Pinkish collagen is also a component of the matrix. Also note chondrocytes and perichondrium. UCLA Histology Collection. | chondrocytes; Elastic Cartilage; perichondrium | UCLA Histology |
| 14 |
 |
Connective Tissue | This whole mount of loose connective tissue shows bundles of reddish collagen fibers, dark elastic fibers, and macrophages. These macrophages have phagocytized trypan blue dye. UCLA Histology Collection. | Connective Tissue; macrophage | UCLA Histology |
| 15 |
 |
Connective Tissue | This is a slice of lymph node stained with silver to show reticular fibers. The larger bundles are collagen. UCLA Histology Collection. | Connective Tissue; Lymph Node | UCLA Histology |
| 16 |
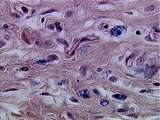 |
Connective Tissue | In this section of the abdominal wall can be seen collagen, macrophages, and slender fibroblasts within the connective tissue. UCLA Histology Collection. | Connective Tissue; macrophage | UCLA Histology |
| 17 |
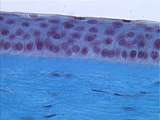 |
Connective Tissue | At a higher power of the corneal stroma, the flattened fibroblast nuclei and collagen bundles are easily seen. UCLA Histology Collection. | Connective Tissue; cornea; Eye | UCLA Histology |
| 18 |
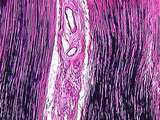 |
Connective Tissue | This ligament consists of dense regular connective tissue with large amounts of dark-stained elastic fibers and pinkish collagen. UCLA Histology Collection. | Connective Tissue; ligament | UCLA Histology |
| 19 |
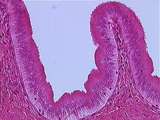 |
Glands of GI Tract | Higher magnification of the gallbladder mucosa illustrating the tall cells of the simple columnar epithelium and collagen fibers within the lamina propria. UCLA Histology Collection. | Gall bladder; gastrointestinal tract | UCLA Histology |
| 20 |
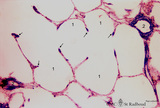 |
Alveolar sac in the lung (human) | Stain: Azan. Characteristic alveolar tips (arrows) of neighbouring thin-walled alveoli (1). The tips contain elastin masked by collagen (blue-stained). At (2) small pulmonary arteries. | Alveolar tips | Poja Histology Collection - Respiratory System Subset |
| 21 |
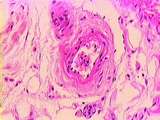 |
Circulatory System - Muscular Artery | A small muscular artery; note the extent of its tunica adventitia, almost indistinguishable from the surrounding connective tissue in which it is embedded. Identify collagen fibers and slender fibroblasts. UCLA Histology Collection. | Circulatory System; muscular artery; tunica adventitia | UCLA Histology |
| 22 |
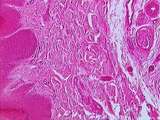 |
Connective Tissue | At a higher power of the heel, the stratified squamous epidermis, the collagen-rich dense irregular CT of the dermis, and the sweat glands can be easily distinguished. UCLA Histology Collection. | connective tissue; epidermis; sweat glands | UCLA Histology |
| 23 |
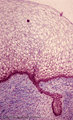 |
Early cap stage in tooth development - human, embryo | Stain: Azan. From top to bottom: stratified ectoderm with ingrowth of the dental lamina; knob-like end of the dental lamina; and collagen fibers of lamina propria are blue. | oral cavity; tooth development; dental lamina | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 24 |
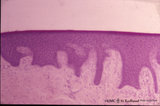 |
Gingiva - 'free' gingiva of decalcified alveolar bone, human | Stain: Hematoxylin and eosin. Thick layer of stratified squamous epithelium with parakeratosis (reddish) and broad papillae of the lamina propria. At the left, dense collagen tissue (projections of the the periodontal ligament). | oral cavity | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 25 |
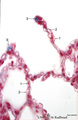 |
Lung alveoli (human) | Stain: Azan. Alveoli (diameter about 200 m) are formed by thin walls of epithelial cells (1) such as type I alveolar cells and (blue stained) fine collagen (3) and elastin intermingled with dilated capillaries (2). | Poja Histology Collection - Respiratory System Subset |
