The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
TO
Filters: Collection: "ehsl_heal"
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1401 |
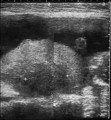 |
Ultrasound of fibroid uterus with overlying placenta | Ultrasound of fibroid uterus with overlying placenta | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction | |
| 1402 |
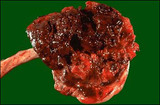 |
Abruptio placenta - Gross | This large retroplacental blood clot is known as abruptio placenta. Such abnormal hemorrhage prior to delivery can lead to sudden onset of pain in the mother. | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction | |
| 1403 |
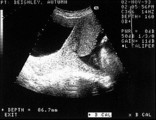 |
Partial placenta previa | The placenta partially covers the internal os. | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction | |
| 1404 |
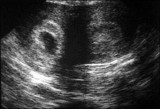 |
Ultrasound showing the two horns of a bicornuate uterus | Ultrasound showing the two horns of a bicornuate uterus | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction | |
| 1405 |
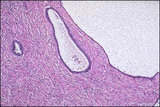 |
Serous adenofibroma | Dense, fibrous connective tissue with interspersed glandular spaces. | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction | |
| 1406 |
 |
Mature cystic teratoma | Teratomas, often called dermoid tumors, represent 25% of all benign neoplasms. The most common elements are components of stratified squamous epithelium, hence their name: dermoid tumor. | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction | |
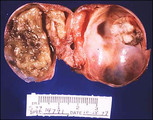
| 1407 |
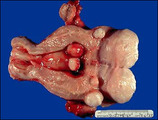 |
Fibroid uterus | Smooth muscle tumors of the uterus. Smooth muscle tumors of the uterus are often multiple. Seen here are submucosal, intramural, and subserosal leiomyomata of the uterus. | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction | |
| 1408 |
 |
Ovarian torsion of tubo-ovarian complex | Torsion of tubo-ovarian complex. In ovarian torsion the ovarian structures always torse medially. | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction | |
| 1409 |
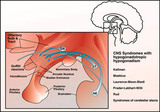 |
Kallman's syndrome | In Kallman's Syndrome of the x linked variety a cell adhesion protein which participates in the migration of GnRH neurons from the medial olfactory bulb to the hypothalamus is absent. This protein is encoded by a gene on the short arm of the X chromosome. | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction | |
| 1410 |
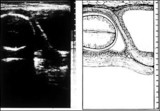 |
Low lying posterior placenta | Low lying posterior placenta | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction | |
| 1411 |
 |
Indications for intrauterine insemination | Indications for intrauterine insemination | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction | |
| 1412 |
 |
Epithelium of a follicular cyst | Low cuboidal cells are found in the lining of follicular cysts. | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction | |
| 1413 |
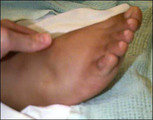 |
Edema | PIH is characterized by hypertension, edema and proteinuria. | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction | |
| 1414 |
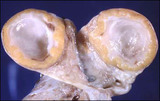 |
Corpus luteum cyst | The corpus luteum secretes progesterone which induces a secretory endometrium. It normally regresses in 14 days unless it is rescued by increasing concentrations of human chorionic gonadotropin from a pregnancy. | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction | |
| 1415 |
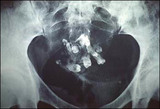 |
Tooth in the abdomen | Radiograph of ovarian teratoma with teeth. Teeth are occassionally part of the squamous components of an ovarian teratoma. | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction | |
| 1416 |
 |
Abruptio Placenta - Microscopic | Microscopically, this abruptio placenta is seen to have extensive hemorrhage at thetop of the photograph at the decidual plate, with placental villi below. | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction | |
| 1417 |
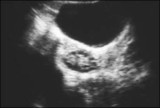 |
Polycystic ovary | Polycystic ovary-pearl necklace sign. Underlying the bladder is the ovary with a classical polycystic appearance often referred to as a pearl necklace. | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction | |
| 1418 |
 |
Turner's syndrome | Adapted with permission from Jaffe R.B.Disorders of Sexual Development. In Yen S.S.C. and Jaffe R.B. eds Reproductive Endocrinology, W. B. Saunders Co., Philadelphia, 1986, p 287. Females with a 45,XO karyotype characteristically have short stature, primary amenorrhea, streak gonads, and sexual infa... | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction | |
| 1419 |
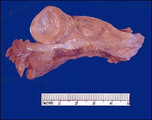 |
Follicular cyst | Benign ovarian cyst. Here is a benign cyst in an ovary. This is probably a follicular cyst. Occasionally such cysts may reach several centimeters in size and, if they rupture, can cause abdominal pain. | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction | |
| 1420 |
 |
Theca lutein cyst | Theca lutein cysts are dominated by theca interna cells. Grossly the cut surface of the ovary is often partly yellow and partly hemorrhagic. Hyperplasia of the theca interna cells is the predominant characteristic. It is believed that these cysts are the result of excessive stimulation of the theca ... | Theca Lutein Cyst | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction |
| 1421 |
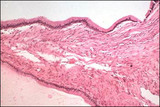 |
Serous cystadenoma | A low cuboidal epithelium is present in the serous cystadenoma. | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction | |
| 1422 |
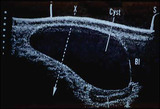 |
Cystic ovarian mass | Ovarian cyst demonstrated by ultrasound. The ovarian cyst fills the abdominal cavity in this sagittal view and is seen overlying the uterus. The bladder is represented by Bl. | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction | |
| 1423 |
 |
Fibroma | This is the cut surface of a fibroma. Such neoplasms slowly enlarge over the years. | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction | |
| 1424 |
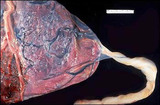 |
Velamentous Insertion of the Umbilical Cord | Seen here is a velamentous insertion of the umbilical cord in which the major umbilical vessels break up in the fetal membranes before reaching the placental disk. Such a condition is of no major consequence in utero, but could lead to a greater chance for cord trauma with bleeding during delivery. ... | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction | |
| 1425 |
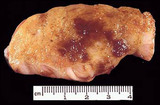 |
Endometrioma | Endometriosis. This is a section through an ovary to demonstrate several irregular hemorrhagic areas of endometriosis. Sometimes the blood is darker and gives the foci of endometriosis the gross appearance ofpowder burns. Typical locations for endometriosis include: ovaries, uterine ligaments, rect... | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction | |
| 1426 |
 |
Somatotropinoma | Somatotropinoma | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 1427 |
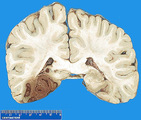 |
Recent hemorrhagic infarction | Recent hemorrhagic infarction | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 1428 |
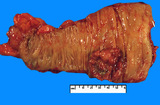 |
Adenocarcinoma, colon | Adenocarcinoma, colon | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 1429 |
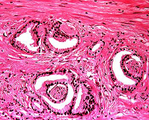 |
Adenocarcinoma, prostate | Adenocarcinoma, prostate | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 1430 |
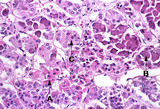 |
Anterior pituitary | Anterior pituitary | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 1431 |
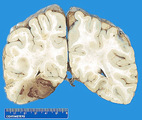 |
Recent hemorrhagic infarction 2 | Recent hemorrhagic infarction 2 | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 1432 |
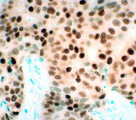 |
Infiltrating ductal carcinoma | Infiltrating ductal carcinoma | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 1433 |
 |
Adrenal gland neoplasm | Adrenal gland neoplasm | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 1434 |
 |
Medullary carcinoma | Medullary carcinoma | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 1435 |
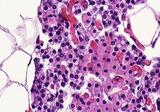 |
Normal parathyroid | Normal parathyroid | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 1436 |
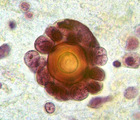 |
Psammoma body | Psammoma body | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 1437 |
 |
Lung carcinoma | Lung carcinoma | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 1438 |
 |
Carcinoma, colon | Carcinoma, colon | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 1439 |
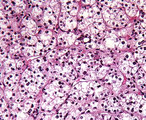 |
Adrenal cortical adenoma | Adrenal cortical adenoma | Andenoma, Adrenal Cortical | Knowledge Weavers Pathology |
| 1440 |
 |
Hyaline arteriolosclerosis | Hyaline arteriolosclerosis | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 1441 |
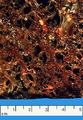 |
Idiopathic pulomonary fibrosis | Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis | Pulmonary Fibrosis | Knowledge Weavers Pathology |
| 1442 |
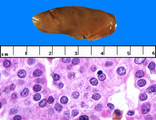 |
Parathyroid, adenoma | Parathyroid, adenoma | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 1443 |
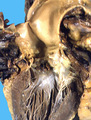 |
Endocarditis | Endocarditis | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 1444 |
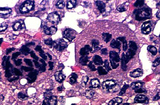 |
Giant cell carcinoma | Giant cell carcinoma | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 1445 |
 |
Metastatic prostatic carcinoma | Metastatic prostatic carcinoma | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 1446 |
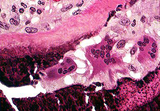 |
Renal osteodystrophy | Renal osteodystrophy | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 1447 |
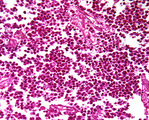 |
Testis seminoma | Testis seminoma | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 1448 |
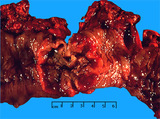 |
Adenocarcinoma, colon | Adenocarcinoma, colon | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 1449 |
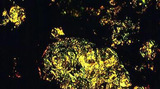 |
Medullary carcinoma | Medullary carcinoma | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 1450 |
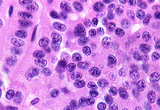 |
Islet cell carcinoma | Islet cell carcinoma | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 1451 |
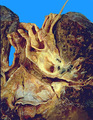 |
Bronchogenic carcinoma | Bronchogenic carcinoma | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 1452 |
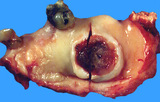 |
Hard palate carcinoma | Hard palate carcinoma | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 1453 |
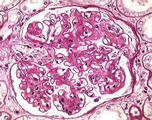 |
Diabetes mellitus | Diabetes mellitus | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 1454 |
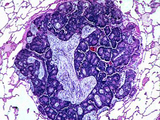 |
Metastatic colon adenocarcinoma | Metastatic colon adenocarcinoma | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 1455 |
 |
Prolactinoma | Prolactinoma | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 1456 |
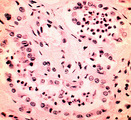 |
Acute pyelonephritis | Acute pyelonephritis | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 1457 |
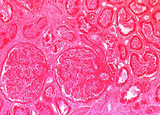 |
Kidney, acute infarction | Kidney, acute infarction | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 1458 |
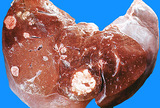 |
Metastatic lung carcinoma | Metastatic lung carcinoma | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 1459 |
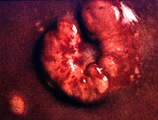 |
Renal cell carcinoma | Renal cell carcinoma | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 1460 |
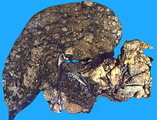 |
Pancreatic adenocarcinoma | Pancreatic adenocarcinoma | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 1461 |
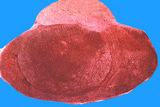 |
Pituitary microadenoma | Pituitary microadenoma | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 1462 |
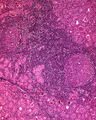 |
Chronic thyroiditis | Chronic thyroiditis | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 1463 |
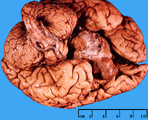 |
Pituitary adenoma | Pituitary adenoma | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 1464 |
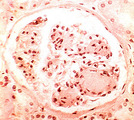 |
Nodular glomerulosclerosis | Nodular glomerulosclerosis | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 1465 |
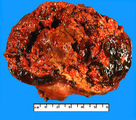 |
Anaplastic carcinoma | Anaplastic carcinoma | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 1466 |
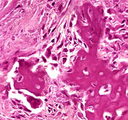 |
Osteosarcoma | Osteosarcoma | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 1467 |
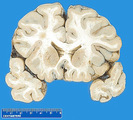 |
Normal brain | Normal brain | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 1468 |
 |
Scirrhous carcinoma, breast | Scirrhous carcinoma, breast | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 1469 |
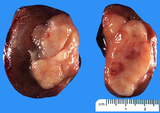 |
Seminoma | Seminoma | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 1470 |
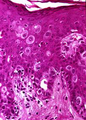 |
Paget's disease, breast | Paget's disease, breast | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 1471 |
 |
Choriocarcinoma | Choriocarcinoma | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 1472 |
 |
Hyaline membrane disease | Hyaline membrane disease | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 1473 |
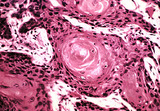 |
Squamous cell carcinoma | Squamous cell carcinoma | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 1474 |
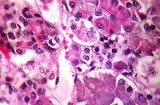 |
Anterior pituitary | Anterior pituitary | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 1475 |
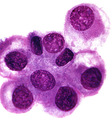 |
Metastatic adenocarcinoma | Metastatic adenocarcinoma | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 1476 |
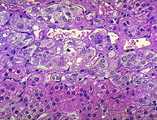 |
Normal adrenal cortex | Normal adrenal cortex | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 1477 |
 |
Carcinoma, colon | Carcinoma, colon | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 1478 |
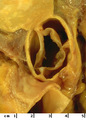 |
Aortic stenosis | Aortic stenosis | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 1479 |
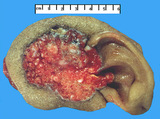 |
Basal cell carcinoma | Basal cell carcinoma | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 1480 |
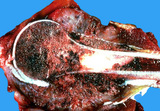 |
Osteosarcoma | Osteosarcoma | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 1481 |
 |
Split Lung Metastases | Split Lung Metastases | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 1482 |
 |
Cushing's syndrome hyperplasia | Cushing's syndrome hyperplasia | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 1483 |
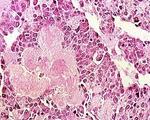 |
Medullary carcinoma | Medullary carcinoma | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 1484 |
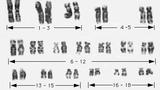 |
Philadelphia chromosome | Philadelphia chromosome | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 1485 |
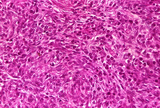 |
Thymoma | Thymoma | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 1486 |
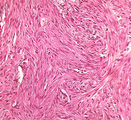 |
Fibroid uterus | Fibroid uterus | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 1487 |
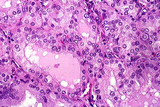 |
Grave's disease | Grave's disease | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 1488 |
 |
Adrenal adenoma | Adrenal adenoma | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 1489 |
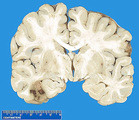 |
Temporal lobe infarction | Temporal lobe infarction | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 1490 |
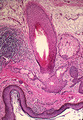 |
Ovarian dermoid cyst | Ovarian dermoid cyst | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 1491 |
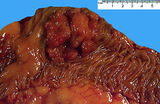 |
Carcinoma, bowel | Carcinoma, bowel | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 1492 |
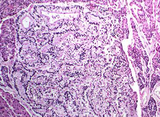 |
Hyperplasia | Hyperplasia | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 1493 |
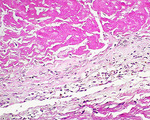 |
Fibrinous pericarditis | Fibrinous pericarditis | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 1494 |
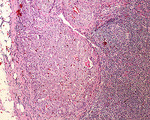 |
Metastatic carcinoma | Metastatic carcinoma | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 1495 |
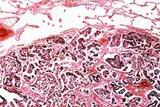 |
Metastatic adenocarcinoma | Metastatic adenocarcinoma | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 1496 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Normal Exam: Normal Gait (includes Spanish audio & captions) | The patient should be observed walking as she normally would. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics and the Office of Education at the University of Nebraska Medical Center. Viewing the video requ... | Coordination Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1497 |
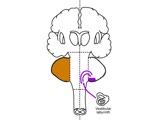 |
Coordination Exam: Anatomy: Vestibulocerebellum (x2) (includes Spanish audio & captions) | The first subdivision of the cerebellum is the vestibulocerebellum. This consists of the connections between the vestibular system and the flocculonodular lobe. Dysfunction of this system results in nystagmus, truncal instability (titubation), and truncal ataxia. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported b... | Coordination Examination; Flocculonodular Lobe; Vestibulocerebellum | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1498 |
 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerve 1 - Olfaction (x2) | This patient has difficulty identifying the smells presented. Loss of smell is anosmia. The most common cause is a cold (as in this patient) or nasal allergies. Other causes include trauma or a meningioma effecting the olfactory tracts. Anosmia is also seen in Kallman syndrome because of agenesis of... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1499 |
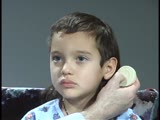 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerve 8 - Auditory Acuity, Weber & Rinne Tests | This patient has decreased hearing acuity of the right ear. The Weber test lateralizes to the right ear and bone conduction is greater than air conduction on the right. He has a conductive hearing loss. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the Univ... | Cranial Nerve Examination; Weber Test; Rinne Test | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1500 |
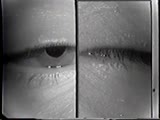 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerves 3, 4 & 6 - Inspection & Ocular Alignment | This patient with ocular myasthenia gravis has bilateral ptosis, left greater then right. There is also ocular misalignment because of weakness of the eye muscles especially of the left eye. Note the reflection of the light source doesn't fall on the same location of each eyeball. NeuroLogic Exam ha... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1501 |
 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerve 2 - Visual Fields (x2) | The patient's visual fields are being tested with gross confrontation. A right sided visual field deficit for both eyes is shown. This is a right hemianopia from a lesion behind the optic chiasm involving the left optic tract, radiation or striate cortex. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a gran... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1502 |
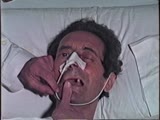 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerve 5 - Motor (x2) | The first patient shown has weakness of the pterygoids and the jaw deviates towards the side of the weakness. The second patient shown has a positive jaw jerk which indicates an upper motor lesion affecting the 5th cranial nerve. Video courtesy of Alejandro Stern, Stern Foundation. NeuroLogic Exam h... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1503 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Normal Exam: Speech - Rapid Alternating Movements (includes Spanish audio & captions) | Having the patient say lah-pah-kah can test rapid alternating movements of the tongue, lips, and palate. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics and the Office of Education at the University of Nebr... | Coordination Examination; Rapid Alternating Movements | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1504 |
 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Anatomy: Cranial Nerve 1 | Olfaction is the only sensory modality with direct access to cerebral cortex without going through the thalamus. The olfactory tracts project mainly to the uncus of the temporal lobes. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, th... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1505 |
 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerve 7 - Sensory, Taste (x2) | The patient has difficulty correctly identifying taste on the right side of the tongue indicating a lesion of the sensory limb of the 7th nerve. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics and the Offic... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1506 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Normal Exam: Station (x2) (includes Spanish audio & captions) | Have the patient stand still. Note the position of the feet and how steady the patient is with eyes open. In the demonstrated exam, the patient is asked to hop and pat at the same time. This is a good way to test upper and lower extremity coordination and balance simultaneously. NeuroLogic Exam has ... | Coordination Examination; Station | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1507 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Normal Exam: Station (includes Spanish audio & captions) | Have the patient stand still. Note the position of the feet and how steady the patient is with eyes open. In the demonstrated exam, the patient is asked to hop and pat at the same time. This is a good way to test upper and lower extremity coordination and balance simultaneously. NeuroLogic Exam has ... | Coordination Examination; Station | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1508 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Abnormal Examples: Foot - Rapid Alternating Movements (includes Spanish audio & captions) | Movements are slow and irregular with imprecise timing of agonist and antagonist muscle action. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics and the Office of Education at the University of Nebraska Medi... | Coordination Examination; Rapid Alternating Movements; Adiadochokinesis | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1509 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Normal Exam: Foot - Rapid Alternating Movements (includes Spanish audio & captions) | Patient taps her foot on the examiner's hand or on the floor. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics and the Office of Education at the University of Nebraska Medical Center. Viewing the video requ... | Coordination Examination; Rapid Alternating Movements | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1510 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Normal Exam: Tremor (includes Spanish audio & captions) | Patient's arms are held outstretched and fingers extended. Watch for postural or essential tremor. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics and the Office of Education at the University of Nebraska M... | Coordination Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1511 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Normal Exam: Normal Gait (x2) (includes Spanish audio & captions) | The patient should be observed walking as she normally would. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics and the Office of Education at the University of Nebraska Medical Center. Viewing the video requ... | Coordination Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1512 |
 |
Gait Exam: Normal Exam: Natural Gait | The patient should be able to walk with a smooth, coordinated gait. There should be normal associated movement of the upper extremities. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics and the Office of Edu... | Gait Examination; Natural Gait | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1513 |
 |
Gait Exam: Normal Exam: Tandem Gait | Have the patient walk heel-to-toe. The patient should be able to balance without falling or stepping to the side. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics and the Office of Education at the Universit... | Gait Examination; Heel-toe Gait | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1514 |
 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Vergence (x2) | Light-near dissociation occurs when the pupils don't react to light but constrict with convergence as part of the near reflex. This is what happens in the Argyll-Robertson pupil (usually seen with neurosyphilis) where there is a pretectal lesion affecting the retinomesencephalic afferents controllin... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1515 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Abnormal Examples: Check Reflex (includes Spanish audio & captions) | The patient is unable to stop flexion of the arm on sudden release so the arm may strike the chest and doesn't recoil to the initial position. This is most likely due to failure of timely triceps contraction. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at th... | Coordination Examination; Check Reflex | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1516 |
 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerve 1 - Olfaction | This patient has difficulty identifying the smells presented. Loss of smell is anosmia. The most common cause is a cold (as in this patient) or nasal allergies. Other causes include trauma or a meningioma effecting the olfactory tracts. Anosmia is also seen in Kallman syndrome because of agenesis of... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1517 |
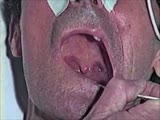 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerves 9 & 10 - Motor (x2) | When the patient says ah there is excessive nasal air escape. The palate elevates more on the left side and the uvula deviates toward the left side because the right side is weak. This patient has a deficit of the right 9th & 10th cranial nerves. Video courtesy of Alejandro Stern, Stern Foundation. ... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1518 |
 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerve 2 - Visual Acuity (x2) | This patient's visual acuity is being tested with a Rosenbaum chart. First the left eye is tested, then the right eye. He is tested with his glasses on so this represents corrected visual acuity. He has 20/70 vision in the left eye and 20/40 in the right. His decreased visual acuity is from optic ne... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1519 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Abnormal Examples: Hand - Rapid Alternating Movements (includes Spanish audio & captions) | Movements are slow and irregular with imprecise timing. Inability to perform repetitive movements in a rapid rhythmic fashion is called dysdiadochokinesia. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics an... | Coordination Examination; Dysdiadochokinesia | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1520 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Abnormal Examples: Natural Gait (includes Spanish audio & captions) | Wide-based, unsteady, irregular steps with lateral veering| ataxia is most prominent when sudden changes are needed such as turning, standing up or stopping. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics ... | Coordination Examination; Natural Gait | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1521 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Normal Exam: Hand - Rapid Alternating Movements (x2) (includes Spanish audio & captions) | Finger tapping, wrist rotation and front-to-back hand patting. Watch for the rapidity and rhythmical performance of the movements noting any right-left disparity. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediat... | Coordination Examination; Rapid Alternating Movements | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1522 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Normal Exam: Hand - Rapid Alternating Movements (includes Spanish audio & captions) | Finger tapping, wrist rotation and front-to-back hand patting. Watch for the rapidity and rhythmical performance of the movements noting any right-left disparity. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediat... | Coordination Examination; Rapid Alternating Movements | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1523 |
 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerves 9 & 10 - Motor | When the patient says ah there is excessive nasal air escape. The palate elevates more on the left side and the uvula deviates toward the left side because the right side is weak. This patient has a deficit of the right 9th & 10th cranial nerves. Video courtesy of Alejandro Stern, Stern Foundation. ... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1524 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Normal Exam: Heel-to-shin (x2) (includes Spanish audio & captions) | The patient places her heel on the opposite knee then runs the heel down the shin to the ankle and back to the knee in a smooth coordinated fashion. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics and the O... | Coordination Examination; Heel-shin Test | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1525 |
 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerves 3, 4 & 6 - Versions (x2) | The first patient shown has incomplete abduction of her left eye from a 6th nerve palsy. The second patient has a left 3rd nerve palsy resulting in ptosis, dilated pupil, limited adduction, elevation, and depression of the left eye. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Lif... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1526 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Normal Exam: Toe-to-finger (x2) (includes Spanish audio & captions) | The patient touches her toe to the examiner's finger repetitively as the examiner moves his finger to new positions. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics and the Office of Education at the Univer... | Coordination Examination; Toe-to-finger Test | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1527 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Normal Exam: Toe-to-finger (includes Spanish audio & captions) | The patient touches her toe to the examiner's finger repetitively as the examiner moves his finger to new positions. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics and the Office of Education at the Univer... | Coordination Examination; Toe-to-finger Test | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1528 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Normal Exam: Foot - Rapid Alternating Movements (x2) (includes Spanish audio & captions) | Patient taps her foot on the examiner's hand or on the floor. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics and the Office of Education at the University of Nebraska Medical Center. Viewing the video requ... | Coordination Examination; Rapid Alternating Movements | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1529 |
 |
Gait Exam: Normal Exam: Heel and Toe Walking | A good way to test balance as well as strength of the distal lower extremities is to have the patient heel and toe walk. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics and the Office of Education at the Un... | Gait Examination; Heel-toe Gait | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1530 |
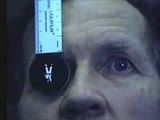 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerves 3, 4 & 6 - Ductions | Each eye is examined with the other covered (this is called ductions). The patient is unable to adduct either the left or the right eye. If you watch closely you can see nystagmus upon abduction of each eye. When both eyes are tested together (testing versions) you can see the bilateral adduction de... | Cranial Nerve Examination; Ductions | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1531 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Anatomy: Introduction (includes Spanish audio & captions) | The principle area of the brain that is examined by the coordination exam is the cerebellum. The cerebellum is important for motor learning and timing of motor activity. It fine-tunes the force of agonist and antagonist muscle activity simultaneously and sequentially across multiple joints to produc... | Coordination Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1532 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Normal Exam: Tandem Gait (x2) (includes Spanish audio & captions) | The patient is asked to walk heel-to-toe. Note steadiness. Tandem gait requires the patient to narrow the station and maintain balance over a 4-5 inch width. Patients with midline ataxias have difficulty with tandem gait. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Developme... | Coordination Examination; Tandem Gait; Heel-toe Gait | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1533 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Abnormal Examples: Toe-to-finger (includes Spanish audio & captions) | Same as finger-to-nose except for the lower extremities. For both the upper and lower extremities, it is important to always compare right versus left. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics and th... | Coordination Examination; Toe-to-finger Test | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1534 |
 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerve 5 - Motor | The first patient shown has weakness of the pterygoids and the jaw deviates towards the side of the weakness. The second patient shown has a positive jaw jerk which indicates an upper motor lesion affecting the 5th cranial nerve. Video courtesy of Alejandro Stern, Stern Foundation. NeuroLogic Exam h... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1535 |
 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerve 8 - Auditory Acuity, Weber & Rinne Tests (x2) | This patient has decreased hearing acuity of the right ear. The Weber test lateralizes to the right ear and bone conduction is greater than air conduction on the right. He has a conductive hearing loss. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the Univ... | Cranial Nerve Examination; Weber Test; Rinne Test | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1536 |
 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerves 3, 4 & 6 - Versions | The first patient shown has incomplete abduction of her left eye from a 6th nerve palsy. The second patient has a left 3rd nerve palsy resulting in ptosis, dilated pupil, limited adduction, elevation, and depression of the left eye. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Lif... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1537 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Anatomy: Subdivisions of the Cerebellum (x2) (includes Spanish audio & captions) | The cerebellum has 3 functional subdivisions, which function as feedback and feed forward systems. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics and the Office of Education at the University of Nebraska M... | Coordination Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1538 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Normal Exam: Tandem Gait (includes Spanish audio & captions) | The patient is asked to walk heel-to-toe. Note steadiness. Tandem gait requires the patient to narrow the station and maintain balance over a 4-5 inch width. Patients with midline ataxias have difficulty with tandem gait. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Developme... | Coordination Examination; Tandem Gait; Heel-toe Gait | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1539 |
 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerve 2 - Visual Fields | The patient's visual fields are being tested with gross confrontation. A right sided visual field deficit for both eyes is shown. This is a right hemianopia from a lesion behind the optic chiasm involving the left optic tract, radiation or striate cortex. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a gran... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1540 |
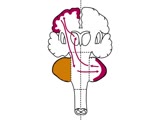 |
Coordination Exam: Anatomy: Cerebrocerebellum (x2) (includes Spanish audio & captions) | The 3rd subdivision of the cerebellum is the cerebrocerebellum. This system consists of connections from the cerebral cortex (predominantly motor) to the cerebellar hemispheres then back to the cerebral cortex. This system is important in motor planning. Dysfunction of the cerebellar hemispheres res... | Coordination Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1541 |
 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Optokinetic Nystagmus (x2) | This patient has poor optokinetic nystagmus when the tape is moved to the right or left. The patient lacks the input from the parietal-occipital gaze centers to initiate smooth pursuit movements therefore her visual tracking of the objects on the tape is inconsistent and erratic. Patients who have a... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1542 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Abnormal Examples: Speech - Rapid Alternating Movements - Dysarthria (includes Spanish audio & captions) | Impaired speech articulation of cerebellar origin is characterized by being slow, indistinct, and scanning (scanning refers to decomposition of words into monosyllabic parts and loss of normal phrasing and intonation). NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development ... | Coordination Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1543 |
 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerves 3, 4 & 6 - Inspection & Ocular Alignment (x2) | This patient with ocular myasthenia gravis has bilateral ptosis, left greater then right. There is also ocular misalignment because of weakness of the eye muscles especially of the left eye. Note the reflection of the light source doesn't fall on the same location of each eyeball. NeuroLogic Exam ha... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1544 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Normal Exam: Finger-to-nose (x2) (includes Spanish audio & captions) | The patient moves her pointer finger from her nose to the examiner's finger as the examiner moves his finger to new positions and tests accuracy at the furthest outreach of the arm. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, th... | Coordination Examination; Finger-to-nose Test | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1545 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Normal Exam: Check Reflex (includes Spanish audio & captions) | Examiner pulls on actively flexed arm then suddenly releases. The patient should be able to check or stop the arm's movement when released. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics and the Office of ... | Coordination Examination; Check Reflex | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1546 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Anatomy: Vestibulocerebellum (includes Spanish audio & captions) | The first subdivision of the cerebellum is the vestibulocerebellum. This consists of the connections between the vestibular system and the flocculonodular lobe. Dysfunction of this system results in nystagmus, truncal instability (titubation), and truncal ataxia. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported b... | Coordination Examination; Flocculonodular Lobe; Vestibulocerebellum | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1547 |
 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerve 5 - Sensory (x2) | There is a sensory deficit for both light touch and pain on the left side of the face for all divisions of the 5th nerve. Note that the deficit is first recognized just to the left of the midline and not exactly at the midline. Patients with psychogenic sensory loss often identify the sensory change... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1548 |
 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerve 5 - Sensory | There is a sensory deficit for both light touch and pain on the left side of the face for all divisions of the 5th nerve. Note that the deficit is first recognized just to the left of the midline and not exactly at the midline. Patients with psychogenic sensory loss often identify the sensory change... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1549 |
 |
Gait Exam: Abnormal Examples: Hemiplegic Gait Demonstration | The patient has unilateral weakness and spasticity with the upper extremity held in flexion and the lower extremity in extension. The foot is in extension so the leg is too long therefore, the patient will have to circumduct or swing the leg around to step forward. This type of gait is seen with a U... | Gait Examination; Hemiplegic Gait | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1550 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Abnormal Examples: Tandem Gait (x2) (includes Spanish audio & captions) | Patients with ataxia have difficulty narrowing the station in order to walk heel to toe. Tandem gait is helpful in identifying subtle or mild gait ataxia. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics and... | Coordination Examination; Tandem Gait; Heel-toe Gait | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1551 |
 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerve 2 - Visual Acuity | This patient's visual acuity is being tested with a Rosenbaum chart. First the left eye is tested, then the right eye. He is tested with his glasses on so this represents corrected visual acuity. He has 20/70 vision in the left eye and 20/40 in the right. His decreased visual acuity is from optic ne... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1552 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Abnormal Examples: Toe-to-finger (x2) (includes Spanish audio & captions) | Same as finger-to-nose except for the lower extremities. For both the upper and lower extremities, it is important to always compare right versus left. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics and th... | Coordination Examination; Toe-to-finger Test | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1553 |
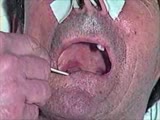 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerves 9 & 10 - Sensory & Motor: Gag Reflex | Using a tongue blade, the left side of the patient's palate is touched which results in a gag reflex with the left side of the palate elevating more then the right and the uvula deviating to the left consistent with a right CN 9 & 10 deficit. Video courtesy of Alejandro Stern, Stern Foundation. Neur... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1554 |
 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Smooth Pursuit | The patient shown has progressive supranuclear palsy. As part of this disease there is disruption of fixation by square wave jerks and impairment of smooth pursuit movements. Saccadic eye movements are also impaired. Although not shown in this video, vertical saccadic eye movements are usually the i... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1555 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Anatomy: Subdivisions of the Cerebellum (includes Spanish audio & captions) | The cerebellum has 3 functional subdivisions, which function as feedback and feed forward systems. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics and the Office of Education at the University of Nebraska M... | Coordination Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1556 |
 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Vergence | Light-near dissociation occurs when the pupils don't react to light but constrict with convergence as part of the near reflex. This is what happens in the Argyll-Robertson pupil (usually seen with neurosyphilis) where there is a pretectal lesion affecting the retinomesencephalic afferents controllin... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1557 |
 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerves 9 & 10 - Sensory & Motor: Gag Reflex (x2) | Using a tongue blade, the left side of the patient's palate is touched which results in a gag reflex with the left side of the palate elevating more then the right and the uvula deviating to the left consistent with a right CN 9 & 10 deficit. Video courtesy of Alejandro Stern, Stern Foundation. Neur... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1558 |
 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Smooth Pursuit (x2) | The patient shown has progressive supranuclear palsy. As part of this disease there is disruption of fixation by square wave jerks and impairment of smooth pursuit movements. Saccadic eye movements are also impaired. Although not shown in this video, vertical saccadic eye movements are usually the i... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1559 |
 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerves 9 & 10 - Motor (x2) | When the patient says ah there is excessive nasal air escape. The palate elevates more on the left side and the uvula deviates toward the left side because the right side is weak. This patient has a deficit of the right 9th & 10th cranial nerves. Video courtesy of Alejandro Stern, Stern Foundation. ... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1560 |
 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerves 9 & 10 - Motor | When the patient says ah there is excessive nasal air escape. The palate elevates more on the left side and the uvula deviates toward the left side because the right side is weak. This patient has a deficit of the right 9th & 10th cranial nerves. Video courtesy of Alejandro Stern, Stern Foundation. ... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1561 |
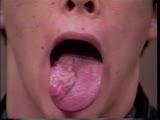 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerve 12 - Motor (x2) | Notice the atrophy and fasciculation of the right side of this patient's tongue. The tongue deviates to the right as well because of weakness of the right intrinsic tongue muscles. These findings are present because of a lesion of the right 12th cranial nerve. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1562 |
 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerve 12 - Motor | Notice the atrophy and fasciculation of the right side of this patient's tongue. The tongue deviates to the right as well because of weakness of the right intrinsic tongue muscles. These findings are present because of a lesion of the right 12th cranial nerve. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1563 |
 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerve 7 - Sensory, Taste | The patient has difficulty correctly identifying taste on the right side of the tongue indicating a lesion of the sensory limb of the 7th nerve. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics and the Offic... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1564 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Anatomy: Midline Ataxia (includes Spanish audio & captions) | Clinically, the ataxic syndromes caused by vestibulocerebellar and spinocerebellar disease are lumped together and are called midline or equilibratory (gait) ataxias. The hallmarks of these midline ataxic syndromes are truncal instability manifested by titubation (tremor of the trunk in an anterior-... | Coordination Examination; Anterior Lobe of Cerebellum; Flocculonodular Lobe | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1565 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Abnormal Examples: Speech - Rapid Alternating Movements - Dysarthria (x2) (includes Spanish audio & captions) | Impaired speech articulation of cerebellar origin is characterized by being slow, indistinct, and scanning (scanning refers to decomposition of words into monosyllabic parts and loss of normal phrasing and intonation). NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development ... | Coordination Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1566 |
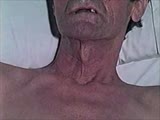 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerve 11 - Motor | When the patient contracts the muscles of the neck the left sternocleidomastoid muscle is easily seen but the right is absent. Looking at the back of the patient, the left trapezius muscle is outlined and present but the right is atrophic and hard to identify. These findings indicate a lesion of the... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1567 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Abnormal Examples: Station (x2) (includes Spanish audio & captions) | Patient's feet will be placed wider apart then usual in order to maintain balance (broad or wide-based station). Midline ataxias cause instability of station with eyes opened or closed. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, t... | Coordination Examination; Station | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1568 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Abnormal Examples: Hand - Rapid Alternating Movements (x2) (includes Spanish audio & captions) | Movements are slow and irregular with imprecise timing. Inability to perform repetitive movements in a rapid rhythmic fashion is called dysdiadochokinesia. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics an... | Coordination Examination; Dysdiadochokinesia | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1569 |
 |
Gait Exam: Abnormal Examples: Hemiplegic Gait Demonstration | The patient has unilateral weakness and spasticity with the upper extremity held in flexion and the lower extremity in extension. The foot is in extension so the leg is too long therefore, the patient will have to circumduct or swing the leg around to step forward. This type of gait is seen with a U... | Gait Examination; Hemiplegic Gait | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1570 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Abnormal Examples: Natural Gait (x2) (includes Spanish audio & captions) | Wide-based, unsteady, irregular steps with lateral veering| ataxia is most prominent when sudden changes are needed such as turning, standing up or stopping. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics ... | Coordination Examination; Natural Gait | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1571 |
 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Anatomy: Cranial Nerve 1 (x2) | Olfaction is the only sensory modality with direct access to cerebral cortex without going through the thalamus. The olfactory tracts project mainly to the uncus of the temporal lobes. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, th... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1572 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Anatomy: Introduction (x2) (includes Spanish audio & captions) | The principle area of the brain that is examined by the coordination exam is the cerebellum. The cerebellum is important for motor learning and timing of motor activity. It fine-tunes the force of agonist and antagonist muscle activity simultaneously and sequentially across multiple joints to produc... | Coordination Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1573 |
 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerves 2 & 3 - Pupillary Light Reflex (x2) | The swinging flashlight test is used to show a relative afferent pupillary defect or a Marcus Gunn pupil of the left eye. The left eye has perceived less light stimulus (a defect in the sensory or afferent pathway) then the opposite eye so the pupil dilates with the same light stimulus that caused c... | Cranial Nerve Examination; Marcus Gunn Pupil | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1574 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Abnormal Examples: Finger-to-nose (includes Spanish audio & captions) | Under (hypometria) and over (hypermetria) shooting of a target (dysmetria) and the decomposition of movement (the breakdown of the movement into its parts with impaired timing and integration of muscle activity) are seen with appendicular ataxia. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from th... | Coordination Examination; Finger-to-nose Test | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1575 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Abnormal Examples: Station (includes Spanish audio & captions) | Patient's feet will be placed wider apart then usual in order to maintain balance (broad or wide-based station). Midline ataxias cause instability of station with eyes opened or closed. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, t... | Coordination Examination; Station | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1576 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Abnormal Examples: Tandem Gait (includes Spanish audio & captions) | Patients with ataxia have difficulty narrowing the station in order to walk heel to toe. Tandem gait is helpful in identifying subtle or mild gait ataxia. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics and... | Coordination Examination; Tandem Gait; Heel-toe Gait | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1577 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Abnormal Examples: Foot - Rapid Alternating Movements (x2) (includes Spanish audio & captions) | Movements are slow and irregular with imprecise timing of agonist and antagonist muscle action. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics and the Office of Education at the University of Nebraska Medi... | Coordination Examination; Rapid Alternating Movements; Adiadochokinesis | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1578 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Abnormal Examples: Rebound (x2) (includes Spanish audio & captions) | Increased range of movement with lack of normal recoil to original position is seen in cerebellar disease. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics and the Office of Education at the University of Ne... | Coordination Examination; Rebound | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1579 |
 |
Gait Exam: Anatomy: Introduction | All levels of the neuroaxis contribute to gait although most gait abnormalities are motor in nature. In assessing gait it is important to not only watch the lower extremities but also the upper extremities for normal associated movements. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice ... | Gait Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1580 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Abnormal Examples: Rebound (includes Spanish audio & captions) | Increased range of movement with lack of normal recoil to original position is seen in cerebellar disease. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics and the Office of Education at the University of Ne... | Coordination Examination; Rebound | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1581 |
 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Anatomy: Major Oculomotor Gaze Systems (x2) | Eye movements are controlled by 4 major oculomotor gaze systems, which are tested for on the neurological exam. They are briefly outlined here: Saccadic (frontal gaze center to PPRF (paramedian pontine reticular formation) for rapid eye movements to bring new objects being viewed on to the fovea. Sm... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1582 |
 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerves 3, 4 & 6 - Ductions (x2) | Each eye is examined with the other covered (this is called ductions). The patient is unable to adduct either the left or the right eye. If you watch closely you can see nystagmus upon abduction of each eye. When both eyes are tested together (testing versions) you can see the bilateral adduction de... | Cranial Nerve Examination; Ductions | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1583 |
 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Anatomy: Major Oculomotor Gaze Systems | Eye movements are controlled by 4 major oculomotor gaze systems, which are tested for on the neurological exam. They are briefly outlined here: Saccadic (frontal gaze center to PPRF (paramedian pontine reticular formation) for rapid eye movements to bring new objects being viewed on to the fovea. Sm... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1584 |
 |
Gait Exam: Anatomy: Localizing Value | There are 7 basic pathological gaits that should be recognized by their characteristic pattern. These pathological gaits are: - Hemiplegic - Spastic diplegic - Neuropathic - Myopathic - Parkinsonian - Chorea - Ataxic These gaits have localizing value because they can indicate levels (an y axis a... | Gait Examination; Hemiplegic Gait; Spastic Diplegia; Neuropathic Gait; Myopathic Gait; Diplegic Gait | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1585 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Anatomy: Midline Ataxia (x2) (includes Spanish audio & captions) | Clinically, the ataxic syndromes caused by vestibulocerebellar and spinocerebellar disease are lumped together and are called midline or equilibratory (gait) ataxias. The hallmarks of these midline ataxic syndromes are truncal instability manifested by titubation (tremor of the trunk in an anterior-... | Coordination Examination; Anterior Lobe of Cerebellum; Flocculonodular Lobe | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1586 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Abnormal Examples: Tremor (includes Spanish audio & captions) | A cerebellar intention tremor (1st scene in this movie) arises mainly from limb girdle muscles and is maximal at the most demanding phase of the active movement. This must be distinguished from a postural tremor (fine distal 8-13 Hz)(2nd scene) or resting tremor (coarse distal 5-6 Hz pill-rolling ty... | Coordination Examination; Intention Tremor; Static Tremor; Resting Tremor | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1587 |
 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Normal Exam: Vergence (x2) | Vergence eye movements occur when the eyes move simultaneously inward (convergence) or outward (divergence) in order to maintain the image on the fovea that is close up or far away. Most often convergence is tested as part of the near triad. When a patient is asked to follow an object that is brough... | Cranial Nerve Examination; Vergence | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1588 |
 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Optokinetic Nystagmus | This patient has poor optokinetic nystagmus when the tape is moved to the right or left. The patient lacks the input from the parietal-occipital gaze centers to initiate smooth pursuit movements therefore her visual tracking of the objects on the tape is inconsistent and erratic. Patients who have a... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1589 |
 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerve 11 - Motor (x2) | When the patient contracts the muscles of the neck the left sternocleidomastoid muscle is easily seen but the right is absent. Looking at the back of the patient, the left trapezius muscle is outlined and present but the right is atrophic and hard to identify. These findings indicate a lesion of the... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1590 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Anatomy: Cerebrocerebellum (includes Spanish audio & captions) | The 3rd subdivision of the cerebellum is the cerebrocerebellum. This system consists of connections from the cerebral cortex (predominantly motor) to the cerebellar hemispheres then back to the cerebral cortex. This system is important in motor planning. Dysfunction of the cerebellar hemispheres res... | Coordination Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1591 |
 |
Gait Exam: Anatomy: Localizing Value | There are 7 basic pathological gaits that should be recognized by their characteristic pattern. These pathological gaits are: - Hemiplegic - Spastic diplegic - Neuropathic - Myopathic - Parkinsonian - Chorea - Ataxic These gaits have localizing value because they can indicate levels (an y axis a... | Gait Examination; Hemiplegic Gait; Spastic Diplegia; Neuropathic Gait; Myopathic Gait; Diplegic Gait | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1592 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Abnormal Examples: Tremor (x2) (includes Spanish audio & captions) | A cerebellar intention tremor (1st scene in this movie) arises mainly from limb girdle muscles and is maximal at the most demanding phase of the active movement. This must be distinguished from a postural tremor (fine distal 8-13 Hz)(2nd scene) or resting tremor (coarse distal 5-6 Hz pill-rolling ty... | Coordination Examination; Intention Tremor; Static Tremor; Resting Tremor | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1593 |
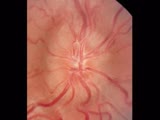 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerve 2 - Fundoscopy | The first photograph is of a fundus showing papilledema. The findings of papilledema include 1. Loss of venous pulsations 2. Swelling of the optic nerve head so there is loss of the disc margin 3. Venous engorgement 4. Disc hyperemia 5. Loss of the physiologic cup and 6. Flame shaped hemorrhages. Th... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1594 |
 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerves 2 & 3 - Pupillary Light Reflex | The swinging flashlight test is used to show a relative afferent pupillary defect or a Marcus Gunn pupil of the left eye. The left eye has perceived less light stimulus (a defect in the sensory or afferent pathway) then the opposite eye so the pupil dilates with the same light stimulus that caused c... | Cranial Nerve Examination; Marcus Gunn Pupil | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1595 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Abnormal Examples: Heel-to-shin (includes Spanish audio & captions) | The patient with ataxia of the lower extremity will have difficulty placing the heel on the knee with a side-to-side irregular over- and undershooting as the heel is advanced down the shin. Dysmetria on heel-to-shin can be seen in midline ataxia syndromes as well as cerebellar hemisphere disease so ... | Coordination Examination; Heel-shin Test | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1596 |
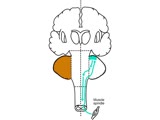 |
Coordination Exam: Anatomy: Spinocerebellum (x2) (includes Spanish audio & captions) | The 2nd subdivision of the cerebellum is the spinocerebellum. This system consists of the connections between the cutaneous and proprioceptive information coming from the spinal cord to the vermis and paravermis regions with corrective feedback predominantly to the muscles of truncal stability and g... | Coordination Examination; Anterior Lobe of Cerebellum; Spinocerebellum | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1597 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Anatomy: Spinocerebellum (includes Spanish audio & captions) | The 2nd subdivision of the cerebellum is the spinocerebellum. This system consists of the connections between the cutaneous and proprioceptive information coming from the spinal cord to the vermis and paravermis regions with corrective feedback predominantly to the muscles of truncal stability and g... | Coordination Examination; Anterior Lobe of Cerebellum; Spinocerebellum | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1598 |
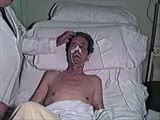 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerve 7 - Motor (x2) | The first patient has weakness of all the muscles of facial expression on the right side of the face indicating a lesion of the facial nucleus or the peripheral 7th nerve. The second patient has weakness of the lower half of his left face including the orbicularis oculi muscle but sparing the forehe... | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach | |
| 1599 |
 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerve 2 - Fundoscopy (x2) | The first photograph is of a fundus showing papilledema. The findings of papilledema include 1. Loss of venous pulsations 2. Swelling of the optic nerve head so there is loss of the disc margin 3. Venous engorgement 4. Disc hyperemia 5. Loss of the physiologic cup and 6. Flame shaped hemorrhages. Th... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1600 |
 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Normal Exam: Vergence | Vergence eye movements occur when the eyes move simultaneously inward (convergence) or outward (divergence) in order to maintain the image on the fovea that is close up or far away. Most often convergence is tested as part of the near triad. When a patient is asked to follow an object that is brough... | Cranial Nerve Examination; Vergence | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
