The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
TO
Filters: Collection: "ehsl_heal"
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 126 |
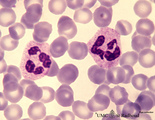 |
Neutrophilic granulocytes in peripheral blood smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The nucleus of the neutrophilic granulocytes (also called polymorphonuclear leukocyte or PMN) is segmented into three to five connected lobules. The cytoplasm displays many fine (dust-like) azurophilic granules. The majority called specific granules are filled with e... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 127 |
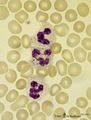 |
Neutrophilic granulocytes in peripheral blood smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The three neutrophilic granulocytes display segmented and lobulated nuclei. The lobes are connected with thin chromatin strands (→). The cytoplasm is ample filled with fine, dust-like granules and the majority are specific granules filled with enzymes such as lysoz... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 128 |
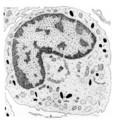 |
Neutrophilic metamyelocyte | Scheme electron microscopy. From CFU-S (colony forming units-spleen) stem cells arise CFU-GM (colony forming unit-granulocyte/monocyte) stem cells. The latter divide by mitoses and differentiate via promyeloblasts and myeloblasts into neutrophilic myelocytes (the last proliferative stage). The next ... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 129 |
 |
Neutrophilic metamyelocyte in peripheral blood smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The neutrophilic metamyelocyte is differentiating nearly to a juvenile unsegmented (band form) neutrophil, but the nuclear chromatin is only partly condensed. Hardly visible dust-like granules can be observed in the still pale bluish cytoplasm. | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 130 |
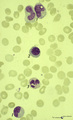 |
Neutrophilic metamyelocytes in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). (1) neutrophilic metamyelocytes. (2) polychromatic erythroblast. (3) segmented neutrophilic granulocyte. | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 131 |
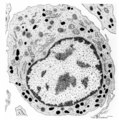 |
Neutrophilic myelocyte | Scheme electron microscopy. From CFU-S (colony forming units-spleen) stem cells arise CFU-GM (colony forming unit-granulocyte/monocyte) stem cells. The latter divide by mitoses and differentiate via promyeloblasts and myeloblasts into myelocytes (the last proliferative stage). The neutrophilic myelo... | Blood; Bone Marrow; Electron microscopy; Neutrophilic myelocyte; Neutrophilic granulocyte; Primary granule; Secondary granule; Azurophilic granule; Lysosome | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset |
| 132 |
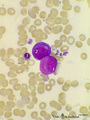 |
Neutrophilic myelocyte and basophilic erythroblast in reactive bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The neutrophilic myelocyte (1) has a nucleus (with nucleoli) located at one side of the cell. Cytoplasm contains many azurophilic granules. The early basophilic erythroblast (2) has a strong basophilic cytoplasm without granules, and a nucleus with condensed chromati... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 133 |
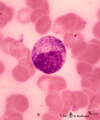 |
Neutrophilic myelocyte in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). In the neutrophilic myelocyte the nucleus is located eccentrically at one side of the cell. Nucleoli are visible as well as the primary azurophilic granules in the cytoplasm. | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 134 |
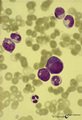 |
Neutrophilic myelocytes with strong toxic granulation in peripheral blood smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). Neutrophilic myelocytes at various differentiation stages, but all cells show strong toxic granulation. | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 135 |
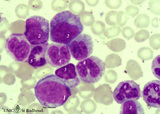 |
Neutrophilic myelopoiesis in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). A group of neutrophilic myeloid cells are clustered together. (1) late myeloblast with nucleoli and hardly any azurophilic granules. (2) promyelocytes as the largest cells of the series, with ample cytoplasm filled with many azurophilic granules. (3) myelocytes with ... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 136 |
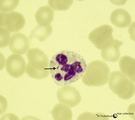 |
Normal mature neutrophilic granulocyte in peripheral blood smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). Neutrophilic granulocyte with five nuclear lobes or segments, (not hypersegmented). The arrow indicates a drumstick. Note the fine dust-like granules. | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 137 |
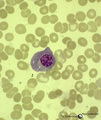 |
Normal plasma cell in peripheral blood smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The mature plasma cell has a large basophilic cytoplasma for IgG production, a clearly visible unstained (white) Golgi area, and a nucleus with well-condensed heterochromatin. Plasma cells can be found in the peripheral blood as a result of antigenic stimulation or c... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 138 |
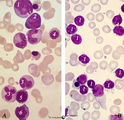 |
Normal pleiomorph and leukemic monomorph bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). In normal bone marrow smear (A) a pleimorph or heterogeneous collection of different cell types (A1-7) can be identified, while in the bone marrow smear of a leukemic patient a single type dominates (in this case lymphoid cells, B-1). | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 139 |
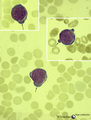 |
Normal proerythroblasts in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The three mounted proerythroblasts are easily recognized by their so called ears i.e., the blue cytoplasmic projections or extensions (arrows). The basophilic cytoplasm as well as the nucleoli point to the blast character of the cells. | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 140 |
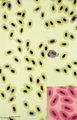 |
Nucleated erythrocytes in peripheral blood smear (bird) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). In contrast to human red blood cells mature erythrocytes of birds contain nuclei (1). (2) Indicates an eosinophilic granulocyte. Inset demonstrates chromatin pattern of the nuclei. | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 141 |
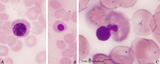 |
Nucleus expulsion in polychromatic-orthochromatic erythroblasts in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The composed pictures show three sequential stages in the final maturation stage of red blood cells. (A) polychromatic erythroblast with a condensed nucleus and an almost acidophilic cytoplasm. (B) the nucleus in the orthochromatic erythroblast is completely condense... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 142 |
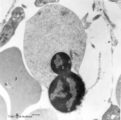 |
Orthochromatic erythroblast (bone marrow, rabbit) | Electron microscopy. The orthochromatic erythroblast (1) or late normoblast shows the early stage of extrusion of the nucleus though the latter appears not yet fully pyknotic. The cytoplasm contains few slender mitochondria (2) as well as scattered clumped polysomes. (3) Part of a reticulocyte. | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 143 |
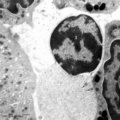 |
Orthochromatic erythroblast (bone marrow, rabbit) | Electron microscopy. The orthochromatic erythroblast or late normoblast is surrounded by young granulocytes (3) and part of a megakaryocyte (2). The cell shows the early stage of extrusion of the nucleus (1) that is already slightly pyknotic. The cytoplasm contains few small mitochondria (arrows) an... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 144 |
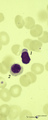 |
Orthochromatic erythroblast and lymphocyte in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The cytoplasm of this orthochromatic erythroblast (2) shows a faint polychromatic tint. The chromatin is arranged in clumps and stains deeply. (2) activated lymphocyte. | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 145 |
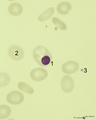 |
Orthochromatic erythroblast in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The orthochromatic erythroblast (1) has a dark condensed (pyknotic) nucleus located at one site of the cell, ready for being expulsed from the cell. (2) Erythrocyte. (3) Represents a platelet or thrombocyte. | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 146 |
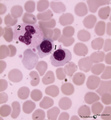 |
Orthochromatic erythroblasts in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). Two orthochromatic erythroblasts (1) with condensed nuclear chromatin and a transition of cytoplasmic stain towards the color of normal erythrocytes. (2) a segmented neutrophilic granulocyte. | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 147 |
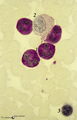 |
PAS-positively stained neutrophilic granulocytes in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: Periodic acid-Schiff reaction (PAS). Mature neutrophils (1) have fine positive granules within negatively (un)stained cytoplasm, whereas eosinophils (2) and basophils show a positive cytoplasmic reaction contrasting with the negative granules. In lymphocytes (1) PAS-positive granules are rare... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 148 |
 |
Peripheral Nervous System Review Flashcards | Eight electronic flashcard units in Macromedia Flash provide learners with drill-and-practice exercises reviewing peripheral nervous system essential terminology and associated definitions. The objective was to stimulate self-directed learning and to integrate anatomical terminology into a structure... | PNS | HEAL Reviewed Collection |
| 149 |
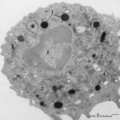 |
Peroxidase activity in neutrophilic granulocyte (peripheral blood, guinea pig) | Electron microscopy (peroxidase reaction with diaminobenzidin staining). The elongated nucleus (3) of this strongly ameboid phagocytic cell has several projections. These nuclear extensions are interconnected by thin heterochromatin strands. The cytoplasm exhibits moderate amounts of organelles, gly... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 150 |
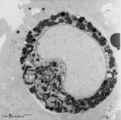 |
Peroxidase activity in neutrophilic myelocyte (postnatal liver, rat) | Electron microscopy (peroxidase reaction with diaminobenzidin staining). An early neutrophilic myelocyte with a large nucleus and well developed organelles, distinct Golgi areas (3) and granules. The Golgi areas, rough endoplasmic reticulum and nuclear membrane stain positively (species-dependent), ... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset |
