The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
TO
Filters: Collection: "ehsl_heal"
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 126 |
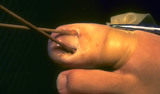 |
Ingrown nail | Small cotton-tip swabs saturated with pheno are used to destroy the nail matrix. Times of application range from 10 seconds to 3 minutes, depending on the author. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 127 |
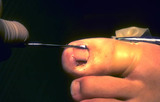 |
Ingrown nail | I use a curette to scrape back in the cul-de-sac beneath the proximal nail fold to physically remove all of the nail matrix I can. | Surgical Methods | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology |
| 128 |
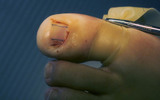 |
Ingrown nail | The portion of the nail plate that is to be removed is marked. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 129 |
 |
Ingrown nail | A broad band tourniquet is applied to the digit. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 130 |
 |
Ingrown nail | Appearance of ingrown nail. The nail plate is dystrophic, and in this case has induced significant foreign body reaction and secondary infection. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 131 |
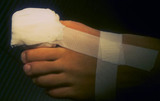 |
Ingrown nail | After cleaning the blood from the toe with hydrogen peroxide and removing the tourniquet, I apply a bulky dressing to absorb the blood, as it may bleed for up to about an hour if the foot is dependent. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 132 |
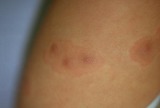 |
Insect bite reaction | This represents an exaggerated insect bite reaction with her other striking erythema surrounding the papules. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 133 |
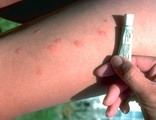 |
Insect Bites | Itchy insect bites can be treated with a topical steroid; I prefer to use an ultra-potent topical steroid, such as Temovate, twice daily to the inflamed lesions. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 134 |
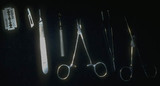 |
Instruments for skin lesion removal | The standard set of instruments that is necessary for removal of skin lesions. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 135 |
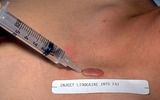 |
Keloid | Before injecting the keloid with the corticosteroid, I recommend injecting local anesthetic into the underlying fat, and waiting about five minutes for the anesthetic to take effect. The anesthetic should not be injected into the keloid as this reduces the amount of space into which one can inject t... | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 136 |
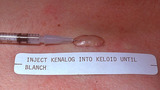 |
Keloid | Once the keloid is anesthetized, the corticosteroid should be injected directly into the middle of the keloid until the keloid blanches. I find it easiest to advancethe needle to the tip of the keloid, and then as I withdraw the needle I inject into the canal that I have created with the needle. I d... | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 137 |
 |
Keloid | Keloids can be injected with a Depo form of injectable steroid and/or silicone gel sheet. The corticosteroid reduces the production of all components of the keloid, which include ground substance, collagen, and elastin. The silicone gel is thought to act by increasing the temperature of the skin and... | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 138 |
 |
Keloid | Keloid. Keloids tend to form on areas where there is a significant amount of tension on the wound, and also in certain families, and in certain races, particularly those who are more darkly pigmented. A keloid is defined as scar tissue that extends beyond the boundaries of the original injury.(Summa... | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 139 |
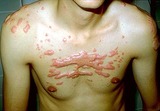 |
Keloids | Keloids. These are composed of excessive amounts of collagen, elastin, and ground substance. They occur generally on the upper chest and back, and also over areas of stretch such as the elbows and knees. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 140 |
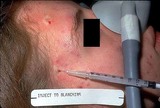 |
Kenalog | The solution should be injected directly into the lesion until there is slight blanching, which indicates saturation with the solution. You must warn the patient beforehand that there is some risk of atrophy of the skin and sometimes the underlying fat, and it can take 6 to 12 months for that to fil... | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 141 |
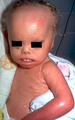 |
Lamellar ichthyosis | Lamellar ichthyosis. The abnormal stratum corneum has produced what appears as very thick scale on the skin, and with an abnormal barrier layer these patients commonly get secondary staphylococcal and yeast infections. Note that there are other associated ectodermal problems such as the teeth, hair,... | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 142 |
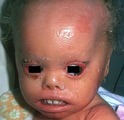 |
Lamellar ichthyosis | Lamellar ichthyosis. The abnormal stratum corneum has produced what appears as very thick scale on the skin, and with an abnormal barrier layer these patients commonly get secondary staphylococcal and yeast infections. Note that there are other associated ectodermal problems such as the teeth, hair,... | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 143 |
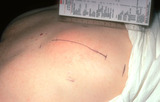 |
Layered closure | Large lesions can be removed using the layered closure. This was a large lipoma on the back of a patient, and I removed this in my office. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 144 |
 |
Leg amputation wound | This is a breakdown of the wound in the leg amputation of an elderly woman who is diabetic. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 145 |
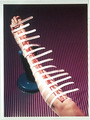 |
Leg measurement | This demonstrates measurement of the leg before custom support hose is made. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 146 |
 |
Lichen simplex chronicus | After repeated scratching, the epidermis thickens and darkens as shown here; this is called lichenification. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 147 |
 |
Lipoma and layered closure | This shows the lipoma and the results of the layered closure. This was located on the back. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 148 |
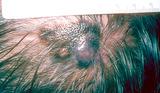 |
Melanoma | Melanoma in the scalp of a patient approximately 65-years-old. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 149 |
 |
Micrograph of the base of hair follicle | An electron micrograph of the base of hair follicle. The epidermal papilla, shown at the bottom center, controls the growth rate of the hair follicle. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 150 |
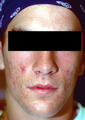 |
Mild acne vulgaris | Mild acne vulgaris. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology |
