The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
TO
Filters: Collection: "ehsl_heal"
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 51 |
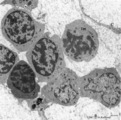 |
Erythroblasts (bone marrow, rabbit) | Electron microscopy. (1) shows basophilic erythroblasts or early normoblasts with clumped heterochromatin in the nucleus and numerous polysomes. (1m) points to a mitotic figure of a basophilic erythroblast. A late polychromatic erythroblast or intermediate normoblast (2) marks a maturing stage in wh... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 52 |
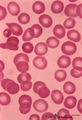 |
Erythrocytes in peripheral blood smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). Normal erythrocytes in a blood smear of peripheral blood. The mature human erythrocytes do not have nuclei. Their normal diameter is about 7.5 μm. Macrocytes have a diameter >9 μm, while microcytes are smaller than 6 μm. The thickness of an erythrocyte in the cent... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 53 |
 |
Erythron in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The erythron or erythroblastic island consists of a large reticulum cell (1) surrounded by erythroblastic cell types (2) at varoius stages of differentiation. The nucleus of the reticulum cell (histiocyte) usually contains a noticeable nucleolus. At distance, some my... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 54 |
 |
Erythron in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). In the center of the slide an erythron that consists of a reticular cell (1) surrounded by erythroblasts (2) at various maturational stages. | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 55 |
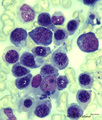 |
Erythron or erythropoietic island in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa. The picture shows a reticular cell (1) surrounded by almost exclusively erythroblasts at different stages of development and maturation (2). The cells marked with (*) are myeloid cell types. The reticular cell has phagocytized nuclear debris of expulsed nuclei (→). The r... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 56 |
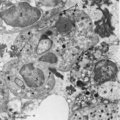 |
Fibrin phagocytosis by neutrophils (peripheral blood, mouse) | Electron microscopy. At site of tissue damage motile neutrophils are among the first to be involved actively in phagocytosis. In between a cluster of neutrophilic granulocytes fibrin depositions (1) are present. At (1→) fibrin accumulations are close attached to the surface of a neutrophil indicat... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 57 |
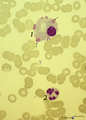 |
Flaming plasma cell in peripheral blood smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The so-called flaming plasma cell (1) is characterized by fiery fringes, which are formed by pseudopodic cytoplasmic projections (arrows) that stain with carmin red. These peripheral cytoplasmic spots contain numerous dilated endoplasmic reticulum cisterns, which are... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 58 |
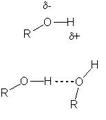 |
General Description of Hydrogen Bonding in Alcohols | This image depicts the basic interaction between the oxygen in one alcohol with the hydrogen of an adjccent alcohol. The oxygen is shown with a partial negative charge (as shown by the negative lowercase delta), and the hydrogen of the adjacent alcohol has the corresponding partial postive charge (p... | HEAL Open Review Collection | |
| 59 |
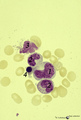 |
Giant neutrophilic metamyelocyte in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). (1) Giant neutrophilic metamyelocyte. (2) Normal neutrophilic metamyelocytes. (3) Smudged eosinophilic granulocyte. (4) Orthochromatic erythroblast. | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 60 |
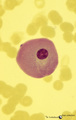 |
Giant plasma cell in peripheral blood smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). A giant plasma cell with diffusely spread immunoglobulins in the cytoplasm. The Golgi area remains unstained (white area). | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 61 |
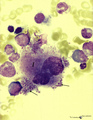 |
Granular megakaryocyte producing platelets in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The centrally located megakaryocyte (1) has a huge nucleus (polyploidy) and an extended cytoplasm from which platelets are released at the periphery (arrows). | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 62 |
 |
Granuloma in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: (A) Hematoxylin and eosin. (B) Silver stain. Granuloma composed of giant cells, epithelioid cells, lymphocytes and reticular fibers (B). Granulomas in the bone marrow may be found in various inflammatory reactions as well as hematological and non-hematological malignancies and as a reaction t... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 63 |
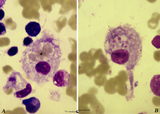 |
Hemophagocytosis by reticular cells in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). (A) shows a reticular cell that has phagocytosed several erythrocytes (*). The cell is surrounded by darkly stained expulsed nuclei. In (B) a similar cell has phagocyized blood platelets (arrows). | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 64 |
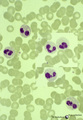 |
Heterozygotic Pelger-Hut's nuclear anomaly of neutrophilic granulocytes in peripheral blood smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The majority of neutrophils has bilobed nuclei, the lobes being rounder than normal and the chromatin is more condensed. About 30% of the cells appear as band forms (imitating shift to the left). A characteristic 'pince-nez' shape is common. Note the fine dust-like g... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 65 |
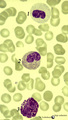 |
Homozygotic Pelger-Huet's nuclear anomaly of granulocytes in peripheral blood smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). In this case of homozygotic Pelger-Hut anomaly the neutrophil (1) as well as the eosinophil (2) have non-lobed nuclei with condensed chromatin. Characteristic fine dust-like granules are present in the neutrophil, while the eosinophil has separate recognizable coarse... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 66 |
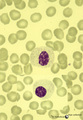 |
Homozygotic Pelger-Hut's nuclear anomaly of neutrophilic granulocytes in peripheral blood smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The neutrophils in this patient with homozygotic Pelger-Hut's anomaly have non-lobed nuclei. The chromatin is condensed and fine dust-like granules are present. | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 67 |
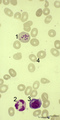 |
Howell-Jolly bodies in reticulocytes in peripheral blood smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The Howell-Jolly-bodies (1) in the reticulocyte are remnants of the nucleus (nuclear chromatin granules) of an erythroblast during anomalous development due to vitamin B12 deficiency, folic acid deficiency or in megaloblastic and hemolytic anemias. (2) Neutrophil wit... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 68 |
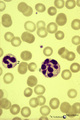 |
Hypersegmented neutrophil in peripheral blood smear of a hyperthermic patient (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). In hyperthermic patients the neutrophils (1) show hypersegmentation of the nuclear lobe (>5) and a pyknotic appearance. The nucleus appears like a bunch of grapes. (2) immature band neutrophil (juvenile unsegmented neutrophil). Hypersegmentation may also occur in meg... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 69 |
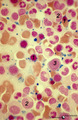 |
Iron (Perls) staining of sideroblasts in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: Perl's stain for iron (Prussian blue). The intense blue stained hemosiderin in the erythroblasts (1) is visible as siderotic granules (pathologic siderosomes). These pathologic siderosomes are sometimes distributed in a circle around the nucleus (ringed sideroblasts). The myeloid cell types (... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 70 |
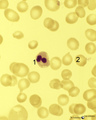 |
Karyorrhexis of polychromatic erythroblast in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The nucleus of the polychromatic erythroblast (1) shows abnormal karyorrhexis due to vitamin B12 deficiency or folic acid deficiency. Normochromic normocyte (2, normal erythrocyte), poikilocytosis and oval macrocytes are seen. | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 71 |
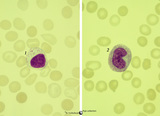 |
Large lymphocyte and monocyte in peripheral blood smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The large lymphocyte (1) has a slightly condensed nucleus and the cytoplasm contains some fine azurophilic granules, and is therefore sometimes called large granular lymphocyte (LGL) or killer cell. The monocyte (2) is generally larger than the lymphocyte with a roun... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 72 |
 |
Large lymphocyte and small plasmacytoid lymphocyte in peripheral blood smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). (1) large lymphocyte with a transparent light cytoplasm in which few fine granules are visible. (2) (inset) smaller plasmacytoid lymphocyte (activated young B cell) with light basophilic cytoplasm. | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 73 |
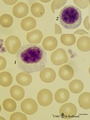
 |
Large lymphocyte in peripheral blood smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The large lymphocyte has a dense chromatin structure and a large transparent cytoplasm with some granules (→). (On the contrary a monocyte exposes a more transparent nucleus and a slightly greyish cytoplasm). | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 74 |
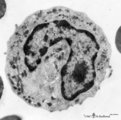 |
Late band-form of neutrophilic granulocyte (peripheral blood, human) | Electron microscopy. Band forms (9-12 μm) are the earliest stages of the motile two-lobed granulocytes. The horseshoe shaped nucleus (3) is irregularly and indicates progressing lobulation. The neutrophil contains many granules of varying sizes and densities. On base of routine electron microscopy ... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 75 |
 |
Leukocyte Alkaline Phosphatase (LAP/NAP score) in peripheral blood smear (human) | Stain: Alkaline phosphatase staining (Ackerman). In mature neutrophils granules contain alkaline phosphatase. In eosinophils no alkaline phosphatase activity is present. A considerable number of brown stained neutrophils can be indicative for a patient with infection (leukemoid reaction, A). Image i... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset |
