The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
TO
Filters: Collection: "ehsl_heal"
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2001 |
 |
Periodontal ligament with epithelial rests of Malassez - longitudinal section of root of tooth; human, adult | Stain: Hematoxylin and eosin. From left to right: connective tissue of periodontal ligament with epithelial rests of Malassez as the persistent remnants of the epithelium of Hertwig's epithelial root sheath. The three islets close to the cemental zone are slightly darker stained (note cluster of nuc... | oral cavity; cementoblasts; Sharpey's fibers; acellular cementum | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 2002 |
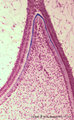 |
Predentin formation at the cuspal tip in tooth development - bell stage, human, embryo | Stain: Azan. From top to bottom: Stellate reticulum consisting of a network of ectoderm-derived cells; Cell layers of the stratum intermedium; Columnar (presecretory) ameloblasts with their upper side (nuclear area) in close contact with the stratum intermedium, and at the distal side (secretion are... | oral cavity; predentin | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 2003 |
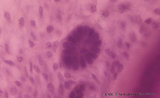 |
Periodontal ligament with epithelial rest of Malassez - longitudinal section of root of tooth, higher magnification; human, adult | Stain: Hematoxylin and eosin. Centrally within the connective tissue of the periodontal ligament a distinct darker stained epithelial islet with nuclei is present (epithelial rest of Malassez as a remnant of Hertwig's epithelial root sheath; in adults it might produce dental cyst). At the right side... | oral cavity; cementoblasts; epithelial rest of Malassez; cementoid | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 2004 |
 |
Presecretory ameloblasts in tooth development - bell stage, gerbil, postnatal | Electronmicroscopy. Well-arranged epithelial formation of presecretory ameloblasts (active nuclei) with their distal secretion sides towards the thin grey basal lamina. Predentin at the bottom close to the basal lamina and comprises collagen fibers, odontoblastic extensions and dispersed calcified m... | oral cavity; predentin; matrix vesicles | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 2005 |
 |
Presecretory ameloblast in tooth development - mammalian embryo | Scheme electronmicroscopy. The ectodermal-derived cell appears as tall columnar with fingerlike extensions (dependent on the development stages) at their distal side (secreting area = 'functional base'). These extensions are formed as the cell withdraws during the production of initial enamel. The s... | oral cavity | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 2006 |
 |
Pulpo-dentinal complex - segment of a tooth; human, adult | Stain: Hematoxylin and eosin. At the pulp-dentin border the peripheral pulp appears to be a specialized odontogenic region composed of odontoblasts, a cell-free zone and a cell-rich zone. From left to right: dentin (note striation due to dentinal tubules); (uncalcified) light stained predentin. At t... | oral cavity; Tomes' Fibers; dentinal tubules; predentin | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 2007 |
 |
Pulpo-dentinal complex of the tooth (human, adult). | Stain: Hematoxylin and eosin. At the pulpo-dentinal border the peripheral pulp appears to be a specialized odontogenic region composed of odontoblasts, a cell-free zone and a cell-rich zone; from left to right: Dentin (note striation due to dentinal tubules). (Uncalcified) Light stained predentin. A... | oral cavity; Tomes' Fibers; dentinal tubules; predentin | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 2008 |
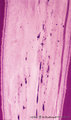 |
Pulp stones in root of tooth - longitudinal section, human, adult | Stain: Hematoxylin and eosin. Left and right side dark stained dentin with a small light rim of predentin. Centrally pulp stones represent as free lying irregular calcifications. They are found diffusely distributed as spots or as thin strands following blood vessels and bundles of collagen fibers i... | oral cavity; pulp stone; diffuse calcifications | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 2009 |
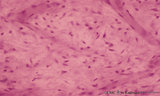 |
Pulp chamber of tooth - human, adult | Stain: Hematoxylin and eosin. Pulpal connective tissue is a special type of tissue (stromal tissue) with so-called stellate-shaped pulpal fibroblastic cells that produce growth factors, extracellular matrix including thin collageneous proteins. Blood vessels are small and thin-walled; macrophages an... | oral cavity; pulp chamber; pulp fibroblast | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 2010 |
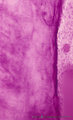 |
Pulpo-dentinal complex in longitudinal section of tooth - damaged dentin, human, adult | Stain: Hematoxylin and eosin. If odontoblastic processes are damaged, (e.g., erosion, caries, etc.), the entire cell will degenerate, though it may be able to produce dentin. From left to right: - irregular course of dentinal tubules; - light stained (damaged) area contain no tubules; - pulp connect... | oral cavity | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 2011 |
 |
Pulpo-dentinal complex in longitudinal section of tooth - secondary dentin, human, adult | Stain: Hematoxylin and eosin. From left to right: - dentinal tubules as fine striation in dentin; - vertical course of incremental lines (von Ebner); - a darker stained broad zone of secondary dentin; - pulp chamber with crowding of odontoblasts close to secondary, newly formed dentin; - connective ... | oral cavity; secondary dentin | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 2012 |
 |
Pulp canal of tooth - longitudinal section; human, adult | Stain: Hematoxylin and eosin. Centrally three thick nerve bundles. In between blood vessel filled with erythrocytes. At the right side longitudinal course of slender thin-walled blood vessels (arterioles) which pass into thin-walled capillaries with a wide lumen. | oral cavity; pulp canal | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 2013 |
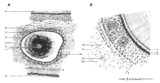 |
Scheme of cross sectional tooth in alveolar bone - cat | A. Survey of tooth (in alveolar bone) magnification x 30 objective. B. Peripheral part of tooth (in alveolar bone) magnification x 300 objective. 1. radicular pulp; 2. odontoblast layer; 3. dentin (radial arranged dentinal tubules); 4. Tomes' granular layer; 5. cementum; 6. fibers of period... | oral cavity; alveolar bone | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 2014 |
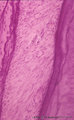 |
Root of tooth within osseous socket - cross-section; human, adult | Stain: Hematoxylin and eosin. From left to right: bundle bone of alveolus; oblique fibers of periodontal ligament with blood vessels (broad layer); flattened cementoblasts settled on a thin light rim of cementoid; darker stained acellular cementum, the so-called acellular extrinsic fiber cementum a... | oral cavity; acellular cementum | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 2015 |
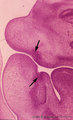 |
Sagittal section through tooth buds in jaws during tooth development - human, embryo, 6 weeks; low magnification | Stain: hematoxylin and eosin. At the top the upper jaw (maxilla) opposite the lower jaw (mandible). At the right side part of the tongue in the oral cavity. Arrows point to epithelial proliferations (future tooth bud formation) that are surrounded by condensation of mesenchymal cells (neural crest m... | oral cavity; tooth bud; tooth development | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 2016 |
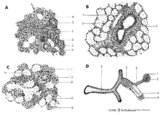 |
Scheme of compound glands in the oral cavity - human, adult | A. parotid gland (serous gland) magnification x 350 objective. B. sublingual gland (mucous part) magnification x 350 objective. C. sublingual gland (mixed part) magnification x 350 objective. D. simplified scheme of compound serous/mucous gland. 1. myoepithelial cell; 2. serous acinus; 3. stri... | oral cavity | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 2017 |
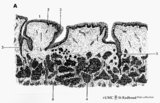 |
Scheme of circumvallate papillae of the tongue (human, adult) | 1. (circum)vallate papilla; 2. non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium; 3. taste bud; 4. serous gland (von Ebner); 5. draining duct (of serous gland); 6. lingual muscle | oral cavity; von Ebner; circumvallate papillae | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 2018 |
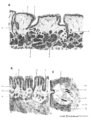 |
Scheme of tongue papillae and foliate papillae | A. Circumvallate papillae (tongue, human, adult) magnification x 35 objective. B. Foliate papillae (tongue, rabbit) magnification x 85 objective. C. Taste bud in foliate papilla (tongue, rabbit) magnification x 750 objective. 1. (circum)vallate papilla; 2. non-keratinized stratified squamous epit... | oral cavity; von Ebner; circumvallate papillae; foliate papillae | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 2019 |
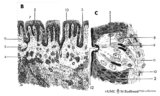 |
Scheme of tongue papillae and taste buds | B. Scheme of foliate papillae of the tongue (rabbit) magnification x 85 objective. C. Scheme of taste bud in foliate papilla of the tongue (rabbit). 2. non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium; 3. taste bud; 4. serous gland (von Ebner); 5. draining duct (of serous gland); 7. foliate papil... | oral cavity; von Ebner; foliate papillae | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 2020 |
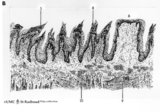 |
Scheme of filiform and fungiform papillae of the tongue - human, adult | 5. filiform papillae; 6. fungiform papillae; 8. locally cornification on top of filiform papillae; 9. lingual muscle; 10. lingual glands | oral cavity; papillae | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 2021 |
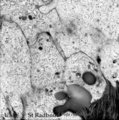 |
Secretory ameloblasts in tooth development - bell stage, gerbil, postnatal | Electronmicroscopy. Cross-sectioned distal sides of ameloblasts (secretion areas or Tomes' processes) with numerous organelles. The dark stained vesicles represent secretory granules contain among others amelogenin. At the right bottom corner intercellular spaces are filled with dark-stained organi... | oral cavity; enamel prisms | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 2022 |
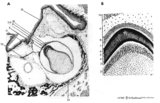 |
Scheme of tooth development (human) | A. Survey of tooth germ (bell stage, embryo) magnification x 35 objective. B. Formation of enamel and dentin (bell stage, embryo) magnification x 350 objective. 1. pulp organ; 2. odontoblasts; 3. mantle predentin; 4. dentin; 5. enamel; 6. initial enamel; 7. inner dental epithelium (ameloblasts);... | oral cavity; dental lamina; bell stage | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 2023 |
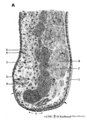 |
Scheme survey lip - human, adult | 1. red (transitional) zone; 2. keratinized stratified squamous epithelium (outer side); 3. non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium (inner side); 4. hair shaft; 5. hair follicle; 6. sebaceous gland; 7. cross-section of circumoral muscle; 8. labial glands with draining ducts; ... | oral cavity | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 2024 |
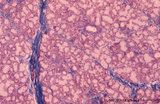 |
Sublingual gland (human) | Stain: Azan. The sublingual gland is a mixed gland and mucous cells are dominating (muco-serous acini). Intralobular ducts are present. Note one thick blue interlobular septum and few thinner intralobular ones. | oral cavity; seromucous gland | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 2025 |
 |
Scheme survey uvula - soft palate, human, adult | 1. nasal side - pseudostratified columnar ciliated epithelium (respiratory epithelium); 2. oral side - non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium; 3. mixed glands (pharyngeal glands); 4. uvular muscle; 5. mucous palatine glands | oral cavity | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 2026 |
 |
Scheme survey dorsal surface of tongue - human, adult | 1. foliate papillae (rudimentary in human); 2. circumvallate papillae; 3. foramen cecum; 4. palatine tonsils; 5. filiform papillae; 6. fungiform papillae; 7. epiglottis; 11. lingual tonsils | oral cavity | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 2027 |
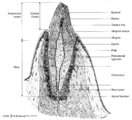 |
Scheme survey tooth (longitudinal section; human; canine) | Canine tooth in osseous alveolus. | oral cavity; pulp canal | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 2028 |
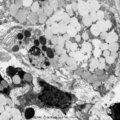 |
Submandibular gland (gerbil) | Electronmicroscopy. Upper two mucous cells of a seromucous acinus contain secretion droplets of different densities (light grey). Note partly fused mucous droplets. In the middle a serous cell cell with darkly stained granules. At the bottom a dense stained intercalated cell without granules. The ba... | oral cavity; seromucous gland | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 2029 |
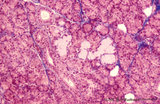 |
Submandibular gland (human) | Stain: Azan. The submandibular gland consists of mixed glands, i.e., the serous cells outnumber the mucous cells (seromucous acini). Locally crescent-shaped groups of serous cells (demi-lunes of Giannuzzi) are localized close to mucous cells to form an acinus.Intralobular ducts (left half) and thin ... | oral cavity; seromucous gland | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 2030 |
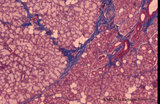 |
Sublingual gland (human) | Stain: Azan. The sublingual gland is a mixed gland and characteristic in human is the presence of large areas of serous cells neighboring areas with mucous cells. Inter- and intra-lobular ducts are present. Note inter- and intra-lobular septa (blue) and scattered fat cells (white). | oral cavity; seromucous gland | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 2031 |
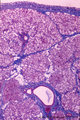 |
Submandibular gland (human) | Stain: Azan. Survey: on top capsule of dense connective tissue (blue) with septa dividing parenchyma of serous cells into lobules. At the bottom a large interlobular duct. Note white fat cells (adipocytes). | oral cavity; seromucous gland | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 2032 |
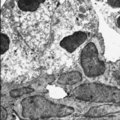 |
Submandibular gland (rat) | Electronmicroscopy. Darkly stained cells around the lumen of an intercalated duct and close to the lightly stained (partly degranulated) serous cells. | oral cavity; seromucous gland; intercalated duct | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 2033 |
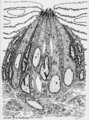 |
Taste bud of the tongue | Scheme electronmicroscopy. Generally a taste bud is composed of about 20 to 70 spindle-shaped epithelial cells. Slender type I cell ('Dark' cell) and oval shaped type II cell ('Light' cell) with a pale, round nucleus with their apices end in microvilli in the taste pore. The number of type I cells i... | oral cavity; foliate papillae; taste pore; electronmicroscopy | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 2034 |
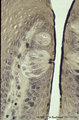 |
Taste buds of foliate papillae of the tongue (dorsal side, rabbit) | Stain: Heidenhain's iron hematein. Taste buds within the lining (non-keratinized) epithelium of the groove. Note the pore in the left taste bud, with darkly stained fluffy apical microvilli. The lightly stained gustatory nerve fibers (nuclei of Schwann cells) approach the left taste buds. The taste ... | oral cavity; foliate papillae; taste pore | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 2035 |
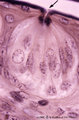 |
Taste bud of a foliate papil of the tongue (dorsal side, rabbit; high magnification) | Stain: Heidenhain's iron hematein. Taste bud with slender cells and darker stained spiky nuclei (type I cell), and cells with light stained round nuclei (type II cells). Below axons of the gustatory nerve fibers and nuclei of Schwann cells. Arrow points to narrow pore where dark stained fluffy struc... | oral cavity; foliate papillae; taste pore | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 2036 |
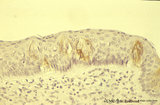 |
Taste bud of a foliate papilla of the tongue (dorsal side, human) | Stain: antikeratin-7 / immunoperoxidase and hematoxylin counterstained. Type I cells with small slender nuclei are identified by positive staining with cytokeratin 7 (monoclonal antibody OVTL12/30). | cytokeratin; oral cavity; foliate papilla; von Ebner | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 2037 |
 |
Tooth ('free' gingiva of decalcified tooth, human, adult) | Stain: Hematoxylin and eosin. Oral side (left) with stratified squamous epithelium, at the right side part of a tooth (dentin), at the bottom side part of the alveolar bone. The epithelium shows slight parakeratosis with many narrow deep papillae of the lamina propria (oral side). On the tooth-relat... | oral cavity; junctional epithelium; alveolar bone; gingival sulcus | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 2038 |
 |
Tooth ('free' gingiva of decalcified tooth, human, adult) | Stain: Hematoxylin and eosin. On top part of the gingival sulcus, at the left stratified junctional epithelium normally attached to the surface of the enamel (dissolved due to decalcification). Top left shows foci of chronic inflammatory cell infiltration, left side faint stained bundle of fibers (p... | oral cavity; acellular cementum; junctional epithelium | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 2039 |
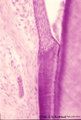 |
Tooth ('free' gingiva of decalcified tooth, human, adult) | Stain: Hematoxylin and eosin. On top the gingival sulcus; at the left stratified junctional epithelium normally attached to the surface of the enamel (dissolved due to decalcification). Below the epithelium a focus of chronic inflammatory cell infiltration, followed by a bundle of fibers of the per... | oral cavity; acellular cementum; junctional epithelium | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 2040 |
 |
Tongue (macroscopy, dorsal side, human) | At the bottom (apex) of the picture the dorsal side is covered with numerous closed packed, small, conical filiform papillae. Interspersed among them are the larger fungiform papillae. Posteriorily the circumvallatae papillae are arranged in a V-shape row. Behind the V-row the area is covered with l... | oral cavity; papillae | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 2041 |
 |
Tongue Papillae Scheme - tongue, human, adult | A. Scheme survey dorsal surface of tongue (human, adult). Magnification 35x. B. Scheme of filiform and fungiform papillae (tongue, human, adult). Magnification 35x. 1. foliate papillae (rudimentary in human); 2. circumvallate papillae; 3. foramen cecum; 4. palatine tonsils; 5. filiform ... | oral cavity; papillae | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 2042 |
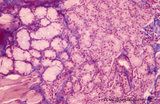 |
Tongue (lingual gland, human) | Stain: Azan. The posterior lingual gland is composed of areas with pure serous acini neighbouring pure mucous acini between the tongue muscles (at the left few striated fibers). | oral cavity; lingual gland | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 2043 |
 |
Tongue (ventral part, human) | Stain: Hematoxylin and eosin. Non-keratinized squamous epithelium, followed by a small lamina propria and the intrinsic striated lingual muscles. | oral cavity; lingual muscles | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 2044 |
 |
Uvula (soft palate, human) | Stain: Azan. Detail of the uvula at the nasal side shows the border between the non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium (right, oral side) and pseudostratified columnar epithelium (left, nasal side). The lamina propria is composed of dense connective tissue. At the bottom part of a blood-fil... | oral cavity; lining mucosa | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 2045 |
 |
Uvula (soft palate, human; low magnification) | Stain: Azan. At the right (oral side, non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium); at the left (nasal side, same epithelium). In the submucosa mainly mucous uvular glands are localized. At the bottom, striated muscle of the uvular muscle. The uvular tip is richly vascularized. | oral cavity | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 2046 |
 |
Uvula (soft palate, human) | Stain: Azan. Detail of the uvula at the oral side; non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium. Note richly vascularized lamina propria. In the submucosa mainly mucous uvular glands with draining ducts. | oral cavity; lining mucosa; mucous glands | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 2047 |
 |
Acellular cementum in the tooth (longitudinal segment of coronal half of root; high magnification; human, adult) | Stain: Hematoxylin and eosin. From left to right: periodontal ligament with collagen fibers; flattened cementoblasts followed by a thin seam of pink cementoid; darker stained acellular cementum, the so-called acellular extrinsic fiber cementum as collagen fibers protrude from the periodontal ligamen... | oral cavity; acellular cementum; Sharpey's fibers; incremental lines | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 2048 |
 |
Acellular cementum in the tooth (longitudinal segment of coronal half of root; human, adult) | Stain: Hematoxylin and eosin. From left to right: periodontal ligament with blood vessels; flattened cementoblasts followed by a thin seam of pink cementoid; darker stained acellular cementum, the so-called acellular extrinsic fiber cementum as collagen fibres protrude from the periodontal ligament ... | oral cavity; acellular cementum; Sharpey's fibers; incremental lines | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 2049 |
 |
Ameloblasts and odontoblasts in tooth development - advanced bell stage, human, embryo CR 80 mm | Scheme electronmicroscopy. From top to bottom: Stellate reticulum consisting of a non-vascularized network of ectoderm-derived cells continuous with the cell layers of the stratum intermedium; Columnar presecretory ameloblasts with their upper side (nuclear area) in close contact with the stratum in... | oral cavity; predentin | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 2050 |
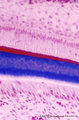 |
Ameloblasts and odontoblasts in tooth development - bell stage, human, embryo | Stain: Azan. From top to bottom: Stellate reticulum consisting of a loose network of ectoderm-derived cells; Cell layers of the stratum intermedium; Palisade-arranged tall columnar secretory ameloblasts with their nuclear area close to the stratum intermedium. The distal side of the cell is oriented... | oral cavity; predentin | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 2051 |
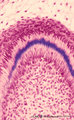 |
Advanced bell stage with ameloblasts and odontoblasts in tooth development - human embryo | Stain: Azan. From top to bottom: Stellate reticulum consisting of a non-vascularized network of ectoderm-derived cells; Cell layers of the stratum intermedium; Columnar (presecretory) ameloblasts with their upper side (nuclear area) in close contact with the stratum intermedium, and at the distal si... | oral cavity; predentin | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 2052 |
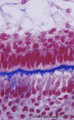 |
Ameloblasts and odontoblasts in tooth development - advanced bell stage, human, embryo | Stain: Azan. From top to bottom: Stellate reticulum consisting of a loose network of ectoderm-derived cells; Cell layers of the stratum intermedium; Columnar presecretory ameloblasts with their nuclear area close to the stratum intermedium, and at the distal side (secretion area) oriented towards pr... | oral cavity; predentin | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 2053 |
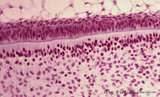 |
Ameloblasts and odontoblasts in tooth development - advanced bell stage, human, embryo | Stain: Hematoxylin and eosin. From top to bottom: Stellate reticulum consisting of a loose network of ectoderm-derived cells; Cell layers of the stratum intermedium; Palisade-arranged columnar presecretory ameloblasts at the distal side oriented towards the basal lamina enforced by deposited collage... | oral cavity | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 2054 |
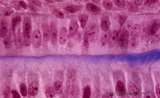 |
Ameloblasts and odontoblasts in tooth development - advanced bell stage, human, embryo; high magnification | Stain: Azan. From top to bottom: A cell layer of the stratum intermedium; Columnar presecretory ameloblasts at the distal side (secretion area) oriented towards predentin (blue); Note a gradient from left to right in the amount of deposited collagen fibers; Tall columnar odontoblasts in an epithelio... | oral cavity | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 2055 |
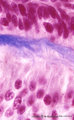 |
Ameloblasts and odontoblasts in tooth development - early bell stage, human, embryo; high magnification | Stain: Azan. From top to bottom: Presecretory ameloblasts with the distal side (secretion area) oriented towards the basal lamina intertwined with the tangential cut blue stained Korff's fibers (collagen) in predentin. Columnar odontoblasts in a epithelioid arrangement with their secretion area clos... | oral cavity; predentin; Korff's fibers | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 2056 |
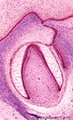 |
Bell stage of the tooth development - human, embryo; low magnification | Stain: Azan. From top to bottom: Stratified ectoderm with a distinct basal layer (red line) of cuboid cells; Dental lamina giving rise to the bell stage (left) and to the primordium of permanent tooth (right); Odontogenic organ (future deciduous tooth) surrounded by fibrous tooth follicle; Out... | oral cavity; dental lamina; predentin | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 2057 |
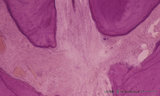 |
Apex of the tooth in osseus socket - alveolus; longitudinal section; human, adult | Stain: Hematoxylin and eosin. From top to bottom: apex region with two tips of dentin covered with cement (darker stained rim; left and right side); note at right tip a dark calcified spot (free cementicle); centrally pulp canal between the tips filled with connective tissue containing blood vessels... | oral cavity; alveolar bone; apical foramen; pulp canal | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 2058 |
 |
Attached denticulus (pulp stone) in the tooth - longitudinal section of root; human, adult. | Stain: Hematoxylin and eosin. From left to right: dentin (purple stained) with dentin tubules; small lightly stained rim of predentin; layers of odontoblasts; irregular structured pulp stone attached to dentin; this false denticle consists of calcified layers with collagen fibers surrounding debris;... | oral cavity; denticulus; pulp stone | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 2059 |
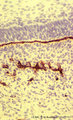 |
Basal lamina between ameloblasts and odontoblasts in tooth development - advanced bell stage, rat embryo | Stain: Anti-collagen IV immunoperoxidase and hematoxylin counterstained. From top to bottom: Stellate reticulum; Stratum intermedium; Ameloblasts at the distal side oriented towards the basal lamina intermingled with the Korffs' fibers (collagen, brown-black); Odontoblasts; Brown-black stained struc... | oral cavity; basal lamina; collagen IV | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 2060 |
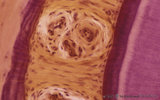 |
Cross section of tooth in alveolar bone - cat | Stain: Picric acid and hematoxylin. From left to right: alveolar bone covered with a woven type bone (bundle bone) tissue (stained darkly purple); yellow stained periodontal ligament with heavy collagen fibers (horizontal fibers) and blood vessels; bone-related part with Sharpey's fibers followed by... | oral cavity; alveolar bone | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 2061 |
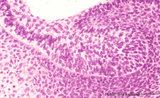 |
Bud stage outgrowth in tooth development - tooth germ, human, embryo | Stain: hematoxylin. At the top stratified ectoderm continuous with the former epithelial tooth bud that abuts toward the underlying neural crest-derived mesenchymal cells. A basal lamina delimits the palisade-arranged epithelial cells from the surrounding dense aggregate of mesenchymal cells. | oral cavity; tooth bud; tooth development | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 2062 |
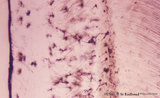 |
Cellular cementum of the tooth - longitudinal section of root; human, adult. Thin ground section. | Stain: Hematoxylin and eosin. From left to right: remnants of fibers in periodontal ligament (dark band); cementum wih dark lacunae with projecting canaliculi, originally occupied by cementocytes and their processes (broad area); dentinocemental junction; and superficial dentin with S-shaped course ... | oral cavity; cementocytes | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 2063 |
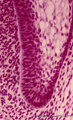 |
Cervical loop in tooth development - late cap stage, human, embryo | Stain: Azan. From left to right: Dental papilla; Thin basement membrane; Columnar inner dental epithelium (presecretory ameloblasts); Stellate reticulum; Cuboidal outer dental epithelium; Fibrous tooth follicle; Note the transition from inner to outer dental epithelium (cervical loop). | oral cavity; cervical loop | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 2064 |
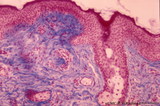 |
Lip (human), external skin surface | Stain: Azan. Keratinized squamous epithelium with one hair follicle associated with sebaceous gland. Richly vascularized connective tissue. Note the thin red cornified layer on the surface. | oral cavity | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 2065 |
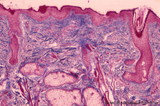 |
Lip (human), skin surface. | Stain: Azan. Keratinized squamous epithelium with hair follicles; submucosa with sebaceous glands, and extensions of skeletal muscle cells (orbicularis oris). | oral cavity | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 2066 |
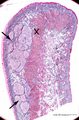 |
Survey of lip (human) | Stain: Azan. Arrows: labial glands in submucosa (mucous inner surface with non-keratinized epithelium). X: orbicularis oris muscle. Right side = skin surface (keratinized epithelium). Top = transitional zone (red zone) with slightly keratinized epithelium. | oral cavity; red zone; labial glands | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 2067 |
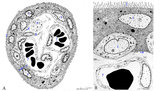 |
Scheme of electron microscopy of tertiary villus (human placenta, midpregnancy) | (See also POJA-L1227). (A) Survey and (B) detail of a tertiary placental villus lined by the multinucleated syncytiotrophoblast cell (1) (STC). The apex shows protrusions and extensive microvilli of varying sizes (brushborder, 2). Nuclei are sectioned at different levels and the cytoplasm contains a... | placenta; tertiary villi; placental barrier; electron microscopy | Poja Histology Collection - Placenta |
| 2068 |
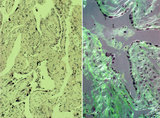 |
Spiral artery in endometrium (human, midpregnancy) | Stain: Hematoxylin-eosin. (A) cross-sections of spiral arteries in endometrium. (B) semi-polarized section of part of a spiral artery. Dark-stained large trophoblast cells (3), partly replacing the cuboidal hypertrophic (B2) endothelial cells. (4) smooth muscle cells. (L) lumen of vessel with cell... | placenta; spiral artery; endometrium; trophoblast | Poja Histology Collection - Placenta |
| 2069 |
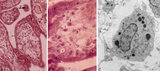 |
Tertiary villi (human placenta, midpregnancy) | (A) Lower and (B) higher magnification. Stain: Hematoxylin - azophloxine. (C) electron microscopy of Hofbauer cell. (A, B) show tertiary villi and intervillous spaces. Squeezed between villi fibrinoid clots (1). The large arrow (2) points to either a detached, free circulating large STC (syncyt... | placenta; chorionic villi; Hofbauer cell; fibrinoid; syncytiotrophoblast | Poja Histology Collection - Placenta |
| 2070 |
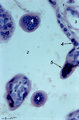 |
Tertiary villi (human placenta, full-term, cross-section) | Stain: Hematoxylin ? azophloxine. A few tertiary villi (1) within the intervillous space (2) contains capillary (3) and embryonic connective tissue (*). It remains covered by the postmitotic multinucleated syncytiotrophoblast cell (STC, 4). Distinct nuclear accumulation in the STC indicates the so-c... | placenta; tertiary villi; syncytiotrophoblast | Poja Histology Collection - Placenta |
| 2071 |
 |
Villi of complete hydatidiform mole (human) | (A) Macroscopy aggregation (1) of abnormal villi of hydatidiform mole intermingled with blood clots (2). (B) After dissection of a complete mole grape-like aggregations of dilated chorionic villi are presented as numerous liquid-filled vesicles (1) varying in diameters (from few mm up to 1 cm) surr... | placenta; trophoblast; hydatiform mole | Poja Histology Collection - Placenta |
| 2072 |
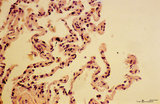 |
Trophoblast cell in lung alveolar interstitium (human, early midpregnancy) | Stain: Hematoxylin-eosin. It is well known that free circulating trophoblast cells can be found migrated into lung parenchyma during normal pregnancy. In this sample a large trophoblast cell (→) is localised within the normal alveolar interstitium. Alveolar phagocytes (*) are present in the alve... | placenta; trophoblast; lung | Poja Histology Collection - Placenta |
| 2073 |
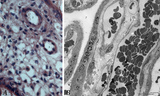 |
Tertiary villi (human placenta, late midpregnancy) | : (A) Left: stain: Hematoxylin - azophloxine. (B) Right: electron microscopy (low magnification). At the left (A) multinucleated syncytiotrophoblast cells (STCs, 1) and vaguely cytotrophoblast cells (CTCs, 2) cover the loose fetal stroma (4). A large and a small arteriole (3) are embedded with stro... | placenta; tertiary villi; placental barrier; Hofbauer cell; vasculosyncytial membrane; syncytiotrophoblast | Poja Histology Collection - Placenta |
| 2074 |
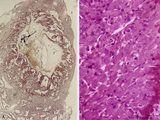 |
Survey of implanted blastocyst (human, ca. 3 weeks-old embryo) and detail of advanced stage of decidua cells (human, mid pregnancy) | Stain: Hematoxylin-eosin (A, left) and Azan (B, right). (A) Left: section through a slightly damaged implantation site shows at (1) the uterine lumen and (2) the decidua capsularis while at (3) several uterine glands are visible. At arrow (4) the amniotic cavity, (5) points to embryonic shield and... | placenta; uterus; syncytiotrophoblast; implantation; blastocyst | Poja Histology Collection - Placenta |
| 2075 |
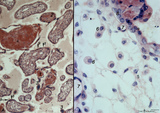 |
Tertiary villi (human placenta, midpregnancy) | Stain: Hematoxylin - azophloxine. (A) Left a variety of tertiary villi and reddish-stained fibrinoid depositions (1). At (2): the embryonic connective tissue starts to fibrinize. Note syncytiotrophoblast knots (3) or sprouts of several villi .These knots might represent aggregations of degenerati... | placenta; fibrinoid; cytotrophoblast; syncytiotrophoblast | Poja Histology Collection - Placenta |
| 2076 |
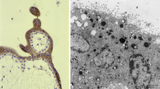 |
Syncytiotrophoblast cells of tertiary villi (human placenta, midpregnancy) | (A) Left: stain: Immunoperoxidase staining with diaminobenzidin (DAB) and human anti-chorionic gonadotrophin antibody (hCG-DAKO 231), counterstained with hematoxylin. (B) Right: electron microscopy. (A) At the left the exclusive reactivity (dark brown) in the cytoplasma of the multinucleated syn... | Syncytiotrophoblast; placenta ; chorionic villi; HCG; immunohistochemistry; electron microscopy | Poja Histology Collection - Placenta |
| 2077 |
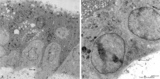 |
Electron microscopy of tertiary villus (human placenta, early pregnancy) | At the left (A), part of a tertiary (terminal) villus with the multinucleated syncytiotrophoblast cell (1) (STC) at the top. The apex shows protrusions and extensive microvilli of varying sizes (brushborder). Nuclei (1a) are sectioned at different levels and the cytoplasm contains abundant organelle... | placenta; chorionic villi; placental barrier; syncytiotrophoblast; electron microscopy | Poja Histology Collection - Placenta |
| 2078 |
 |
Electron microscopy of syncytiotrophoblast cells in tertiary villus (human placenta, midpregnancy) | The left photograph (A) shows the apical cytoplasm of a syncytiotrophoblast cell (STC, nucleus). The free cell surface displays small protrusions and a characteristic pattern of differently shaped microvilli; pinocytotic invaginations and a single macropinocytotic vacuole. Note the apical localized ... | placenta; tertiary villi; syncytiotrophoblast; electron microscopy | Poja Histology Collection - Placenta |
| 2079 |
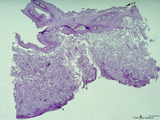 |
Survey of the chorionic plate and intervillous space (human placenta, full-term) | Stain: Perjodic acid-Schiff reaction (PAS). At the top the chorionic plate (1) with cross-sections of umbilical vessels (2) At (3) the folded amnion covering the chorionic plate. Ramifications of thicker stem villi demonstrate free-floating terminal villi (tertiary). At several places reddish-st... | placenta; tertiary villi; decidua; chorionic plate | Poja Histology Collection - Placenta |
| 2080 |
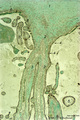 |
Stem villus (human placenta, midpregnancy) | Stain: Trichrome (Goldner). At the top the fetal site with part of the chorionic plate (1) with a thick stem villus (2) ramifying in two smaller villi with large blood vessels (3). The chorionic plate consists of a thick fibrous connective layer (green). Towards the intervillous space it is covere... | placenta; chorionic villi; stem villus; chorion plate | Poja Histology Collection - Placenta |
| 2081 |
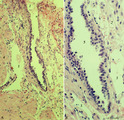 |
Spiral artery in endometrium (human, midpregnancy) | Stain: Hematoxylin-eosin. (A) Emerging into partly damaged intervillous space (1), filled with hemorrhage and fibrin (2). (3) uterine vein and (4) smooth muscle cell bundles at the endometrial-myometrial junction. (B) Lumen with hypertrophic endothelium at higher magnification (5). Note as an unu... | placenta; trophoblast; spiral artery; endometrium | Poja Histology Collection - Placenta |
| 2082 |
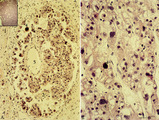 |
Choriocarcinoma (human) | Stain: Hematoxylin-eosin. (A) Inset: Survey tumor. Within the uterus (1) a choriocarcinoma forms solitary or multiple nodules composed of hemorrhagic necrotic areas (2) surrounded by neoplastic cells. It resembles an early implanted blastocyst with aggregations of mononuclear lighter-stained cyt... | choriocarcinoma; placenta; uterus; cytotrophoblast; GTD (gestational trophoblastic disease) | Poja Histology Collection - Placenta |
| 2083 |
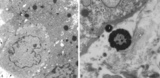 |
Electron microscopy of tertiary villus (human placenta, midpregnancy) | In the left photograph (A) is shown part of a tertiary villus with the organelle-rich cytoplasm of a syncytiotrophoblast cell (STC, 1). Below a single electron-light linked cytotrophoblast cell (CTC or Langhans cell, 2) covered by the STC. A higher magnification of another CTC (right photograph) sh... | placenta; tertiary villi; syncytiotrophoblast; electron microscopy; placental barrier | Poja Histology Collection - Placenta |
| 2084 |
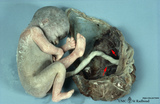 |
Normal term placenta with umbilical cord attached to the fetus (human) | The macroscopy shows the expelled placenta as a discoidal mass with a circular outline about 15-20 cm in the ruptured amnionitic and chorionic sacs. Amnion and smooth chorion (chorion leave) are fused and continuous with the margins of the placenta. The fetal surface (inner surface) is covered by... | placenta; amnion; chorion; umbilical cord; fetus | Poja Histology Collection - Placenta |
| 2085 |
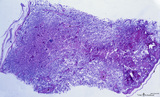 |
Survey of the intervillous space with villi (human placenta, full-term) | Stain: Perjodic Acid Schiff reaction (PAS). At the right and left side the chorionic plate (1) with few cross-sectioned umbilical vessels (2), at (3) a detached amnion. Cross-sections of thick stem villi (4) at the fetal side ramify into terminal villi (tertiary) that are found stuffed (due to fix... | placenta; stem villus; syncytiotrophoblast; amnion | Poja Histology Collection - Placenta |
| 2086 |
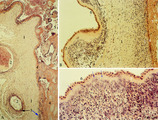 |
Chorioamnionitis (human) | Histologically chorioamnionitis describes the progression of the inflammatory process. Bacteria firstly colonized the chorioamniotic surface. In first two days polymorphonuclear granulocytes (PMN) migrate to the chorion (chorionitis) marginate and adhere to the bottom of the chorionic plate (stage 1... | chorioamnionitis; placenta; trophoblast | Poja Histology Collection - Placenta |
| 2087 |
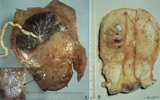 |
Partial hydatidiform mole and invasive mole (human) | (A) Macroscopy: The partial mole (1) occupies a large part of the placenta and is distinct from the normal chorionic plate where the umbilical cord (2) inserts eccentrically with branches of the umbilical vessels. The inset shows a circumscript area with swollen transparent grape-like vesicles (chor... | partial hydatidiform mole ; chorioadenoma | Poja Histology Collection - Placenta |
| 2088 |
 |
Normal term placenta (human) | (A) Left (fetal surface): 30-90 cm long umbilical cord (1), remnant of ruptured transparent amnion (2→) , near the eccentric attachment of the umbilical cord to the chorion plate ramification of the umbilical vessels (3) (arteries are smaller than the veins). (B) Right (maternal surface). The su... | placenta; amnion; chorion plate; cotyledon | Poja Histology Collection - Placenta |
| 2089 |
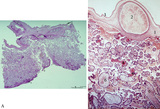 |
Survey and detail of the chorionic plate and intervillous space (human placenta, full-term) | Stain: (A) Perjodic acid-Schiff reaction (PAS); (B) Hematoxylin-azophloxine. (A) At the top the chorionic plate (1) with cross-sections of umbilical vessels (2). At (3) the folded amnion covering the chorionic plate. Ramifications of thicker stem villi (6) demonstrate free-floating terminal villi ... | placenta; chorionic plate; amnion; terminal villi | Poja Histology Collection - Placenta |
| 2090 |
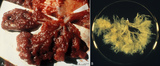 |
Fetal cotyledons (normal term human placenta) | After dissection of one placental lobe several cotyledons (2) are visible in (A). Each fetal cotyledon (2) consists of a main stem villus (1) and all its branches. (B) After trypsinization of a cotyledon the tree of arborisation of the stem villus and its branches becomes visible. (By courtesy... | placenta; cotyledon; villus; trypsinization | Poja Histology Collection - Placenta |
| 2091 |
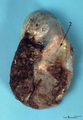 |
Macroscopy of fetus (human) | The fetus (1)is completely wrapped in a shiny transparent amnion (2) and closely associated with the brown-coloured placenta (3). (By courtesy of the Museum of Anatomy and Pathology, University Medical Center, St. Radboud University, Nijmegen, The Netherlands) | fetus; placenta; amnion | Poja Histology Collection - Placenta |
| 2092 |
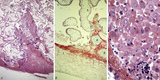 |
Surveys/detail of the decidua basalis and intervillous space of the placenta (human placenta, late midpregnancy) | Stain: Hematoxylin ?azophloxine (A, C), Trichrome (Goldner) (B). Left pictures (A, B): The maternal side at the bottom consists of a broad zone of the stripped basal decidua (1) intermingled with reddish matrix-type fibrinoid accumulations and streaks (Rohr) (2), close to the anchoring villi (3) an... | placenta; chorionic villi; fibrinoid; trophoblast shell | Poja Histology Collection - Placenta |
| 2093 |
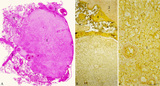 |
Chorioangioma (human) | Stain: (A) Hematoxylin-eosin (survey) and (B, C) van Gieson. (A) chorioangioma (1), chorionic plate (2), stem villus (3) and villi (5). (B) shows in (1) a large cellular mass with accumulated capillaries. At (2) part of the chorionic plate. Subchorionic fibrinoid stains yellow (4). (C) reveals t... | placenta; chorioangioma; villus; chorionic plate | Poja Histology Collection - Placenta |
| 2094 |
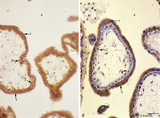 |
Immunohistochemistry of tertiary villi (human placenta, midpregnancy ) | Stain: Immunoperoxidase staining with diaminobenzidin (DAB) and hematoxylin counterstaining for keratin 7 (OVTL 12-30 antibody) at the left (A) and for human anti-chorionic gonadotrophin (hCG-DAKO 231antibody) at the right (B). Tertiary villi show a keratin-positive reaction (brown-stained) in all ... | placenta; chorionic villi; HCG; syncytiotrophoblast; keratin 7; immunohistochemistry | Poja Histology Collection - Placenta |
| 2095 |
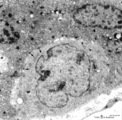 |
Electron microscopy of cytotrophoblast cell (human placenta, early pregnancy) | Below a single electron-light cytotrophoblast cell (CTC or Langhans cell, 1) covered by a syncytiotrophoblast cell (STC, 2) with two nuclei. A continuous basal lamina (3) separates the CTC and STC from the embryonic connective tissue. The CTC appears as a blast-like cell with a large electron-l... | placenta; tertiary villi; syncytiotrophoblast; placental barrier | Poja Histology Collection - Placenta |
| 2096 |
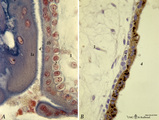 |
Tertiary villi (human placenta, early pregnancy) | Stain: (A, left) Azan. (B, right) Immunoperoxidase staining with diaminobenzidin (DAB) and hematoxylin counterstaining for human anti-chorionic gonadotrophin (hCG-DAKO 231 antibody). (A) shows blue grey-stained postmitotic multinucleated syncytiotrophoblast cells (STC, 1b), partially cut tangential... | placenta; chorionic villi; placental barrier; HCG | Poja Histology Collection - Placenta |
| 2097 |
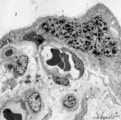 |
Electron microscopy of syncytiotrophoblast knot in tertiary villus (human placenta, almost full-term) | Electron microscopy. The mature villus, surrounded by intervillous space (1), contains capillaries (2) with erythrocytes and pericytes (3) embedded in fetal connective tissue elements (4). Two capillaries are localised close to the covering multinucleated syncytiotrophoblast cell (STC, 5) (vasculosy... | placenta; chorionic villi; syncytial knot; electron microscopy; vasculosyncytial membrane | Poja Histology Collection - Placenta |
| 2098 |
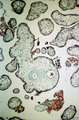 |
Intervillous space with villi (human placenta, midpregnancy, cross-section) | Stain: Trichrome (Goldner). In the middle a thick stem villus (cross-sections of left artery (1) and right vein (2) of the umbilical circulation in the thick embryonic connective tissue) with ramifications into terminal villi (tertiary). Most tertiary villi of varying diameters contain capillaries a... | placenta; chorionic villi; fibrinoid; cytotrophoblast; syncytiotrophoblast | Poja Histology Collection - Placenta |
| 2099 |
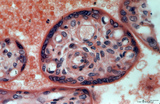 |
Tertiary villi (human placenta, full-term, cross-sectioned) | Stain: Hematoxylin-azophloxine. The central villus is lined by epithelial multinucleated syncytiotrophoblast cells (1) and sparsely light-stained cytotrophoblast cells (Langhans, (2)). The fetal stroma contains vessels and mostly fibroblasts, note capillaries (3) in close association with the epithe... | placenta; tertiary villus; syncytiotrophoblast | Poja Histology Collection - Placenta |
| 2100 |
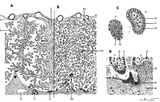 |
Scheme of placental tissues (human) | See the http://www.healcentral.org/http://library.med.utah.edu/healassets/content/collections/poja_placenta/POJA-L1227-FemReprOrg-Placenta-scheme+introduction Placenta.pdf>detailed Legends for this slide (PDF file). | placenta; uterus; chorionic villi; decidua; trophoblast; cytotrophoblast | Poja Histology Collection - Placenta |
