The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
TO
Filters: Collection: "ehsl_heal"
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 26 |
 |
Binucleated plasma cell in peripheral blood smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). A large plasma cell with two nuclei. The chromatin is coarsely clumped. The cytoplasm is intensive basophilic due to the large RER content for purpose of antibody production. Note the clear zone (Golgi area) between the nuclei. | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 27 |
 |
Circulating phagocytic cells | Electron microscopy, a set of the ultrastuctural features of different types of phagocytic cells. Top left side (A): Circulating monocyte with phagocytized latex particles (peripheral blood, human). The nucleus is large and with a long small indentation. Close to the nucleus several individually in... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 28 |
 |
Contamination with osteoblasts of a bone marrow puncture (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). In bone marrow smears from a sternum puncture sometimes osteoblasts are found. Osteoblasts may occur in groups, are oval with a usually eccentric, relatively small nucleus. The chromatin is often coarse with 1-3 nucleoli. The cytoplasm is mostly light blue and may co... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 29 |
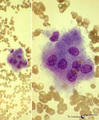 |
Contamination with osteoclasts of a bone marrow puncture (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). In the procedure for preparing a bone marrow smear from a sternum puncture osteoclasts are frequently found in the bone marrow smears. The osteoclasts are multinucleated giant cells for the destruction of bone in the process of remodelling and growth. The cytoplasm m... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 30 |
 |
Contamination with squamous cell cells in peripheral blood smear (A) and in a bone marrow smear (B) (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). In blood and bone marrow smears incidentally squamous epithelial cells from the skin tissues are found. (A-1) is an epithelial cell from the keratinized stratified (upper) epidermis; (A-2) a young neutrophil with a few vacuoles in the cytoplasm (probably degeneration... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 31 |
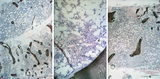 |
Crista biopsies of normal, hypoplastic and malignant bone marrow (human) | Stain: Hematoxylin and eosin. The composition of three slides shows a normal bone marrow section (A), an aplastic bone marrow (B), and a malignant lymphoma in bone marrow (C). (1) Cristae. (2) Fat tissue or fat cells. (3) Erythrocytes and (4) erythroblasts with dark nuclei. | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 32 |
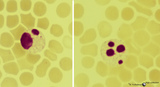 |
Degenerating granulocytes in peripheral blood smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG).Two neutrophils with degenerated nuclei. Note the pyknotic pattern (like mature erythroblast) of the separated and rounded nuclear lobes and the granules in the cytoplasm. Normally only a small number of granulocytes die in the blood. | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 33 |
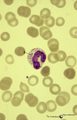 |
Dhle bodies in mature neutrophils in peripheral blood smear (human) | : May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). In adults the usual response to a bacterial infection is a neutrophil leukocytosis with a shift to the left, toxic granulation, Dhle bodies and, when the infection is severe, cytoplasmic vacuolation and swelling occur. Dhle bodies (1, arrow) are small, pale-blue-grey cyto... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 34 |
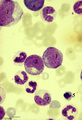 |
Differentiation stages of myeloid cells in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). (1) Promyelocytes with coarse primary azurophilic granules and nucleoli. (2) Myelocyte with starting indentation of the nucleus (primary plus secondary granules). (3) Neutrophilic metamyelocytes with kidney shaped nuclei. (4) Band form of neutrophilic granulocytes (b... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 35 |
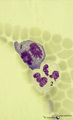 |
Dividing cells (mitosis) in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). (1) Shows a dividing cell (mitotic figure) possibly an erythroblast cell type. (2) Shows two segmented neutrophils. | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 36 |
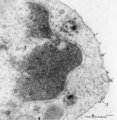 |
Endocytosis in lymphocyte (peripheral blood, rat) | Electron microscopy. Thorotrast is a suspension of thorium dioxide particles and was formerly used as a contrast medium in X-ray diagnostics. These particles were found to accumulate in spleen, lymph nodes and most likely in macrophages and phagocytizing reticular cells. Generally lymphocytes do not... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 37 |
 |
Enflurane | Enflurane is a halogenated ether used as an anesthetic. This structure has been used in an introductory organic/biochemistry course to illustrate how the basic structure of an ether has been modified to produce a less flammable, but still effective, anesthetic agent. | HEAL Open Review Collection | |
| 38 |
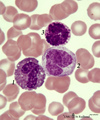 |
Eosinophil, monocyte and basophil in blood smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). (1) eosinophilic granulocyte with two nuclear lobes and large eosinophilic granules in the cytoplasm. (2) monocyte with a large indented nucleus that is much more transparent than the nuclei of the two other cells. (3) basophilic granulocyte with aggregated dark purp... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 39 |
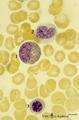 |
Eosinophilic (meta)myelocyte in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The granules of the eosinophilic (meta)myelocyte (1) are large and brown-blue stained in contrast to the hardly visible, dust-like granules in the neutrophilic band form (2). (3) orthochromatic erythroblast. | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 40 |
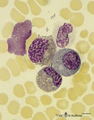 |
Eosinophilic (meta)myelocytes in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). Three eosinophilic (meta)myelocytes (1) at slightly different maturation stages. Notice the brown blue large solitary granules. (2) neutrophilic metamyelocyte. (3) smudged cell. | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 41 |
 |
Eosinophilic granulocyte | Scheme electron microscopy. A 11-15 m cell with a bilobed nucleus (1) moderate amount of organelles, mitochondria (2), Golgi area (3), many vesicles (5) and numerous specific eosinophilic granules (4). These granules contain a central electron-dense angular crystalloid core embedded in a finely gran... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 42 |
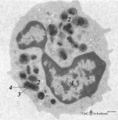 |
Eosinophilic granulocyte (peripheral blood, human) | Electron microscopy. A 11-15 m cell with a partially cut bilobed nucleus (1) and moderate amount of organelles and vesicles. The specific eosinophilic granules (2) contain a central electron-dense angular crystalloid core (3) embedded in a finely granular matrix (4). The crystalloid consists of an a... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 43 |
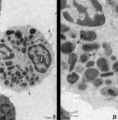 |
Eosinophilic granulocyte (peripheral blood, human) | Electron microscopy. (A) Overview of the cell. Note two nuclear lobes (1) due to the section. There are numerous specific eosinophilic granules (2) and a Golgi area (3). Few thin filopodia (↓, arrows) are present. (B) Detail: some vesicles and many specific eosinophilic granules of varying sizes. ... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 44 |
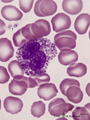 |
Eosinophilic granulocyte in peripheral blood smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The eosinophil (11-15 μm) contains a bilobed nucleus and numerous large solitary brown-orange granules. The eosinophils are the first line of defense against parasites but also take part in allergic reactions (bronchial asthma). Arrow (↓) points to two platelets. | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 45 |
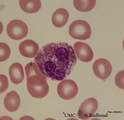 |
Eosinophilic granulocyte in peripheral blood smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The eosinophilic granulocyte usually has two to three nuclear lobes. The brown-orange granules are large, solitary and contain pharmacologically active mediators. The cell surface is occupied with IgE receptors. | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 46 |
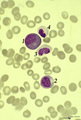 |
Eosinophilic myelocyte and neutrophilic myelocyte in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The eosinophilic myelocyte (1) contains brown-like granules (not orange) in the bluish basophilic cytoplasm. Nucleoli are still visible. Maturation of eosinophils parallels that of neutrophils except for the production of the secondary, specific granules in myelocyte... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 47 |
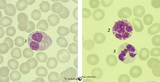 |
Eosinophilic, neutrophilic and basophilic granulocytes in peripheral blood smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The eosinophil (1) is slightly larger than the neutrophil with a diameter of 12-17 m. The nucleus is usually bilobed (occasionally trilobed). Eosinophil granules are considerably larger than those of neutrophils, and are stained reddish-orange. These cells are very f... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 48 |
 |
Erythroblast and neutrophilic myelocytes in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). (1) an older basophilic erythroblast with slightly condensed nuclear chromatin. (2) two neutrophilic myelocytes with azurophilic primary granules. | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 49 |
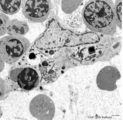 |
Erythroblastic island (bone marrow, rabbit) | Electron microscopy. In the bone marrow close associations of developing red blood cells with reticular cells are required during erythropoiesis. Different stages of erythroblasts (2, 3) are exposed in close vicinity of a reticular cell (1). (4) Reticulocyte. The centrally localized phagocytic retic... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 50 |
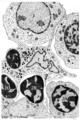 |
Erythroblastic island in bone marrow | Scheme electron microscopy. Different stages of maturing erythroblasts (2) are exposed in this scheme. The centrally localized phagocytic reticular cell (1) has many long cytoplasmic extensions that form a network with similar cells within the bone marrow. Its nucleus is irregular. The cytoplasm has... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset |
