The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
Filters: Collection: "ehsl_heal"
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 26 |
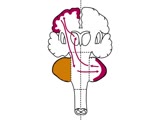 |
Coordination Exam: Anatomy: Cerebrocerebellum (x2) (includes Spanish audio & captions) | The 3rd subdivision of the cerebellum is the cerebrocerebellum. This system consists of connections from the cerebral cortex (predominantly motor) to the cerebellar hemispheres then back to the cerebral cortex. This system is important in motor planning. Dysfunction of the cerebellar hemispheres res... | Coordination Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 27 |
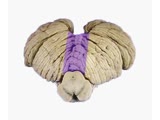 |
Coordination Exam: Anatomy: Exam Tests (includes Spanish audio & captions) | The following tests of the neuro exam can be divided according to which system of the cerebellum is being examined: Vestibulocerebellum and spinocerebellum (midline): - Station - Walking - Tandem gait Cerebrocerebellum (appendicular): - Rapid alternating movements - Finger-to-nose - To... | Coordination Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 28 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Anatomy: Exam Tests (x2) (includes Spanish audio & captions) | The following tests of the neuro exam can be divided according to which system of the cerebellum is being examined: Vestibulocerebellum and spinocerebellum (midline): - Station - Walking - Tandem gait Cerebrocerebellum (appendicular): - Rapid alternating movements - Finger-to-nose - To... | Coordination Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 29 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Anatomy: Introduction (includes Spanish audio & captions) | The principle area of the brain that is examined by the coordination exam is the cerebellum. The cerebellum is important for motor learning and timing of motor activity. It fine-tunes the force of agonist and antagonist muscle activity simultaneously and sequentially across multiple joints to produc... | Coordination Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 30 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Anatomy: Introduction (x2) (includes Spanish audio & captions) | The principle area of the brain that is examined by the coordination exam is the cerebellum. The cerebellum is important for motor learning and timing of motor activity. It fine-tunes the force of agonist and antagonist muscle activity simultaneously and sequentially across multiple joints to produc... | Coordination Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 31 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Anatomy: Midline Ataxia (includes Spanish audio & captions) | Clinically, the ataxic syndromes caused by vestibulocerebellar and spinocerebellar disease are lumped together and are called midline or equilibratory (gait) ataxias. The hallmarks of these midline ataxic syndromes are truncal instability manifested by titubation (tremor of the trunk in an anterior-... | Coordination Examination; Anterior Lobe of Cerebellum; Flocculonodular Lobe | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 32 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Anatomy: Midline Ataxia (x2) (includes Spanish audio & captions) | Clinically, the ataxic syndromes caused by vestibulocerebellar and spinocerebellar disease are lumped together and are called midline or equilibratory (gait) ataxias. The hallmarks of these midline ataxic syndromes are truncal instability manifested by titubation (tremor of the trunk in an anterior-... | Coordination Examination; Anterior Lobe of Cerebellum; Flocculonodular Lobe | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 33 |
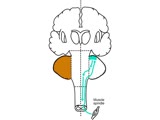 |
Coordination Exam: Anatomy: Spinocerebellum (includes Spanish audio & captions) | The 2nd subdivision of the cerebellum is the spinocerebellum. This system consists of the connections between the cutaneous and proprioceptive information coming from the spinal cord to the vermis and paravermis regions with corrective feedback predominantly to the muscles of truncal stability and g... | Coordination Examination; Anterior Lobe of Cerebellum; Spinocerebellum | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 34 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Anatomy: Spinocerebellum (x2) (includes Spanish audio & captions) | The 2nd subdivision of the cerebellum is the spinocerebellum. This system consists of the connections between the cutaneous and proprioceptive information coming from the spinal cord to the vermis and paravermis regions with corrective feedback predominantly to the muscles of truncal stability and g... | Coordination Examination; Anterior Lobe of Cerebellum; Spinocerebellum | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 35 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Anatomy: Subdivisions of the Cerebellum (includes Spanish audio & captions) | The cerebellum has 3 functional subdivisions, which function as feedback and feed forward systems. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics and the Office of Education at the University of Nebraska M... | Coordination Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 36 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Anatomy: Subdivisions of the Cerebellum (x2) (includes Spanish audio & captions) | The cerebellum has 3 functional subdivisions, which function as feedback and feed forward systems. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics and the Office of Education at the University of Nebraska M... | Coordination Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 37 |
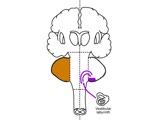 |
Coordination Exam: Anatomy: Vestibulocerebellum (includes Spanish audio & captions) | The first subdivision of the cerebellum is the vestibulocerebellum. This consists of the connections between the vestibular system and the flocculonodular lobe. Dysfunction of this system results in nystagmus, truncal instability (titubation), and truncal ataxia. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported b... | Coordination Examination; Flocculonodular Lobe; Vestibulocerebellum | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 38 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Anatomy: Vestibulocerebellum (x2) (includes Spanish audio & captions) | The first subdivision of the cerebellum is the vestibulocerebellum. This consists of the connections between the vestibular system and the flocculonodular lobe. Dysfunction of this system results in nystagmus, truncal instability (titubation), and truncal ataxia. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported b... | Coordination Examination; Flocculonodular Lobe; Vestibulocerebellum | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 39 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Normal Exam: Check Reflex (includes Spanish audio & captions) | Examiner pulls on actively flexed arm then suddenly releases. The patient should be able to check or stop the arm's movement when released. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics and the Office of ... | Coordination Examination; Check Reflex | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 40 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Normal Exam: Check Reflex (x2) (includes Spanish audio & captions) | Examiner pulls on actively flexed arm then suddenly releases. The patient should be able to check or stop the arm's movement when released. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics and the Office of ... | Coordination Examination; Check Reflex | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 41 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Normal Exam: Finger-to-nose (includes Spanish audio & captions) | The patient moves her pointer finger from her nose to the examiner's finger as the examiner moves his finger to new positions and tests accuracy at the furthest outreach of the arm. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, th... | Coordination Examination; Finger-to-nose Test | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 42 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Normal Exam: Finger-to-nose (x2) (includes Spanish audio & captions) | The patient moves her pointer finger from her nose to the examiner's finger as the examiner moves his finger to new positions and tests accuracy at the furthest outreach of the arm. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, th... | Coordination Examination; Finger-to-nose Test | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 43 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Normal Exam: Foot - Rapid Alternating Movements (includes Spanish audio & captions) | Patient taps her foot on the examiner's hand or on the floor. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics and the Office of Education at the University of Nebraska Medical Center. Viewing the video requ... | Coordination Examination; Rapid Alternating Movements | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 44 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Normal Exam: Foot - Rapid Alternating Movements (x2) (includes Spanish audio & captions) | Patient taps her foot on the examiner's hand or on the floor. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics and the Office of Education at the University of Nebraska Medical Center. Viewing the video requ... | Coordination Examination; Rapid Alternating Movements | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 45 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Normal Exam: Hand - Rapid Alternating Movements (includes Spanish audio & captions) | Finger tapping, wrist rotation and front-to-back hand patting. Watch for the rapidity and rhythmical performance of the movements noting any right-left disparity. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediat... | Coordination Examination; Rapid Alternating Movements | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 46 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Normal Exam: Hand - Rapid Alternating Movements (x2) (includes Spanish audio & captions) | Finger tapping, wrist rotation and front-to-back hand patting. Watch for the rapidity and rhythmical performance of the movements noting any right-left disparity. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediat... | Coordination Examination; Rapid Alternating Movements | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 47 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Normal Exam: Heel-to-shin (includes Spanish audio & captions) | The patient places her heel on the opposite knee then runs the heel down the shin to the ankle and back to the knee in a smooth coordinated fashion. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics and the O... | Coordination Examination; Heel-shin Test | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 48 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Normal Exam: Heel-to-shin (x2) (includes Spanish audio & captions) | The patient places her heel on the opposite knee then runs the heel down the shin to the ankle and back to the knee in a smooth coordinated fashion. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics and the O... | Coordination Examination; Heel-shin Test | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 49 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Normal Exam: Normal Gait (includes Spanish audio & captions) | The patient should be observed walking as she normally would. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics and the Office of Education at the University of Nebraska Medical Center. Viewing the video requ... | Coordination Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 50 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Normal Exam: Normal Gait (x2) (includes Spanish audio & captions) | The patient should be observed walking as she normally would. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics and the Office of Education at the University of Nebraska Medical Center. Viewing the video requ... | Coordination Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
