The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
TO
Filters: Collection: "ehsl_heal"
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1601 |
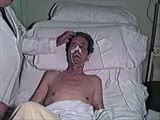 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerve 7 - Motor | The first patient has weakness of all the muscles of facial expression on the right side of the face indicating a lesion of the facial nucleus or the peripheral 7th nerve. The second patient has weakness of the lower half of his left face including the orbicularis oculi muscle but sparing the forehe... | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach | |
| 1602 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Abnormal Examples: Heel-to-shin (x2) (includes Spanish audio & captions) | The patient with ataxia of the lower extremity will have difficulty placing the heel on the knee with a side-to-side irregular over- and undershooting as the heel is advanced down the shin. Dysmetria on heel-to-shin can be seen in midline ataxia syndromes as well as cerebellar hemisphere disease so ... | Coordination Examination; Heel-shin Test | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1603 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Abnormal Examples: Finger-to-nose (x2) (includes Spanish audio & captions) | Under (hypometria) and over (hypermetria) shooting of a target (dysmetria) and the decomposition of movement (the breakdown of the movement into its parts with impaired timing and integration of muscle activity) are seen with appendicular ataxia. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from th... | Coordination Examination; Finger-to-nose Test | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1604 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Normal Exam: Finger-to-nose (includes Spanish audio & captions) | The patient moves her pointer finger from her nose to the examiner's finger as the examiner moves his finger to new positions and tests accuracy at the furthest outreach of the arm. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, th... | Coordination Examination; Finger-to-nose Test | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1605 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Normal Exam: Heel-to-shin (includes Spanish audio & captions) | The patient places her heel on the opposite knee then runs the heel down the shin to the ankle and back to the knee in a smooth coordinated fashion. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics and the O... | Coordination Examination; Heel-shin Test | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1606 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Anatomy: Exam Tests (x2) (includes Spanish audio & captions) | The following tests of the neuro exam can be divided according to which system of the cerebellum is being examined: Vestibulocerebellum and spinocerebellum (midline): - Station - Walking - Tandem gait Cerebrocerebellum (appendicular): - Rapid alternating movements - Finger-to-nose - To... | Coordination Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1607 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Normal Exam: Check Reflex (x2) (includes Spanish audio & captions) | Examiner pulls on actively flexed arm then suddenly releases. The patient should be able to check or stop the arm's movement when released. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics and the Office of ... | Coordination Examination; Check Reflex | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1608 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Normal Exam: Speech - Rapid Alternating Movements (x2) (includes Spanish audio & captions) | Having the patient say lah-pah-kah can test rapid alternating movements of the tongue, lips, and palate. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics and the Office of Education at the University of Nebr... | Coordination Examination; Rapid Alternating Movements | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1609 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Normal Exam: Rebound (x2) (includes Spanish audio & captions) | Tap outstretched arms. Patient's arms should recoil to original position. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics and the Office of Education at the University of Nebraska Medical Center. Viewing... | Coordination Examination; Rebound | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1610 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Normal Exam: Rebound (includes Spanish audio & captions) | Tap outstretched arms. Patient's arms should recoil to original position. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics and the Office of Education at the University of Nebraska Medical Center. Viewing... | Coordination Examination; Rebound | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1611 |
 |
Gait Exam: Normal Exam: Station | The patient should be able to stand still with her feet less then shoulder width apart. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics and the Office of Education at the University of Nebraska Medical Cent... | Gait Examination; Station | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1612 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Anatomy: Exam Tests (includes Spanish audio & captions) | The following tests of the neuro exam can be divided according to which system of the cerebellum is being examined: Vestibulocerebellum and spinocerebellum (midline): - Station - Walking - Tandem gait Cerebrocerebellum (appendicular): - Rapid alternating movements - Finger-to-nose - To... | Coordination Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1613 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Normal Exam: Tremor (x2) (includes Spanish audio & captions) | Patient's arms are held outstretched and fingers extended. Watch for postural or essential tremor. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics and the Office of Education at the University of Nebraska M... | Coordination Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1614 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Abnormal Examples: Check Reflex (x2) (includes Spanish audio & captions) | The patient is unable to stop flexion of the arm on sudden release so the arm may strike the chest and doesn't recoil to the initial position. This is most likely due to failure of timely triceps contraction. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at th... | Coordination Examination; Check Reflex | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 1615 |
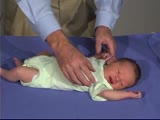 |
PediNeuroLogic Exam: Newborn: Normal: Tone - Arm Recoil (x2) | Arm recoil tests tone and action of the biceps. The arms are held in flexion against the chest for a few seconds, then are quickly extended and released. The arms should spring back to the flexed position. The hypotonic infant will have slow incomplete recoil. Asymmetry to this response with lack of... | PediNeuroLogic Exam | |
| 1616 |
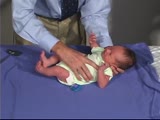 |
PediNeuroLogic Exam: Newborn: Normal: Primitive Reflexes - Galant | The Galant reflex (trunk incurvation) is obtained by placing the baby in ventral suspension, then stroking the skin on one side of the back. The baby's trunk and hips should swing towards the side of the stimulus. PediNeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Developmen... | PediNeuroLogic Exam | |
| 1617 |
 |
testing | test | test | Peer Review Pending |
| 1618 |
 |
GraceTestSubmitJsp | log message: wrong name: org/apache/jsp/submit/submitinstructions_jsp | Testing | Peer Review Pending |
| 1619 |
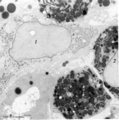 |
Peroxidase reaction in reticular cell and myelocytes (postnatal liver, rat) | Electron microscopy (peroxidase reaction with diaminobenzidin staining). The elongated reticular cell (1) shows peroxidase activity within the perinuclear space as well as the rough endoplasmic reticulum (species-dependent). It is surrounded by three eosinophilic myelocytes (2) with a positive react... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1620 |
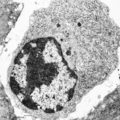 |
Plasma cell (liver, rat) | Electron microscopy. The mature plasma cell or plasmacyte shows an eccentric nucleus with a characteristic chunky distribution of heterochromatin along the inner nuclear membrane (spoke-wheel effect in light microscopy). Juxtanuclearly an elaborate Golgi area (2) (cytocentrum/centrosome). The cytopl... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1621 |
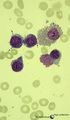 |
Three basophilic erythroblasts in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). Three basophilic erythroblasts (1) with intense blue stained cytoplasm, and some so called ears or cytoplasmic projections (arrows). Chromatin strands are thicker than in the proerythroblast. Generally no nucleoli are seen. (2) Damaged or smudged eosinophilic myelocy... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1622 |
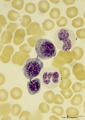 |
Polychromatic erythroblasts and neutrophilic granulocytes in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). Three polychromatic erythroblasts or normoblasts (1) and two neutrophils (2). The erythroblasts show light basophilic cytoplasm and well condensed nuclear chromatin. The lower neutrophil (more mature) has a more segmented nucleus than the upper one. | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1623 |
 |
Erythron in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The erythron or erythroblastic island consists of a large reticulum cell (1) surrounded by erythroblastic cell types (2) at varoius stages of differentiation. The nucleus of the reticulum cell (histiocyte) usually contains a noticeable nucleolus. At distance, some my... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1624 |
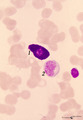 |
Mast cell in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The mast cell (1) is characterized by the presence of coarse purple-black granules and a nucleus with oval, central nucleus. The granules contain pharmacologically active mediators such as heparin, histamine, neutrophil- and eosinophil-chemotactic factors, vasoactive... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1625 |
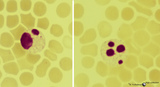 |
Degenerating granulocytes in peripheral blood smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG).Two neutrophils with degenerated nuclei. Note the pyknotic pattern (like mature erythroblast) of the separated and rounded nuclear lobes and the granules in the cytoplasm. Normally only a small number of granulocytes die in the blood. | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1626 |
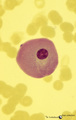 |
Giant plasma cell in peripheral blood smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). A giant plasma cell with diffusely spread immunoglobulins in the cytoplasm. The Golgi area remains unstained (white area). | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1627 |
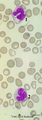 |
Vacuolar degeneration of neutrophils in peripheral blood smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). Toxic degeneration of neutrophil resulting in vacuolization of cytoplasm (1); cell with beginning vacuolization (2). | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1628 |
 |
Activated lymphocyte (liver inflammation, human) | Electron microscopy. A cytotoxic T cell (2) is localized within the sinusoid (3) in the liver (8), surrounded by erythrocytes (1) and debris. The lymphocyte with an irregular indented nucleus shows juxta-nuclearly partly swollen Golgi areas (*) and aggregation of mitochondria (4) in the cytoplasm. F... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1629 |
 |
Monocyte (peripheral blood, human) | Electron microscopy. In this picture the large nucleus (1) of this cell (diameter of 12-20 μm) is twice sectioned. Golgi areas (2) and centriole, profiles of rough endoplasmic reticulum (3) and many free ribosomes are present. There are many mitochondria (4) as well as scattered homogeneous electro... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1630 |
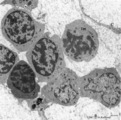 |
Erythroblasts (bone marrow, rabbit) | Electron microscopy. (1) shows basophilic erythroblasts or early normoblasts with clumped heterochromatin in the nucleus and numerous polysomes. (1m) points to a mitotic figure of a basophilic erythroblast. A late polychromatic erythroblast or intermediate normoblast (2) marks a maturing stage in wh... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1631 |
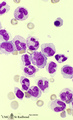 |
Myelopoiesis in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The smear shows a group of myeloid cells in different stages of maturation, in which series the alterations in the nucleus can be noticed clearly going from (1) to (5), i.e. the nucleus gets more and more condensed, indented and subsequently segmented in lobes. (1) p... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1632 |
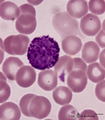 |
Basophilic granulocyte in peripheral blood smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The basophilic granulocyte has large, coarse dark purple-stained granules that contain mediators such as eosinophilic chemotactic factors, heparin, histamine, myeloperoxidase. The nuclear lobes are irregular, badly visible and covered by the granules. | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1633 |
 |
Band and hyper segmented neutrophils in peripheral blood smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). (A) shows a young band neutrophil with a non-segmented nucleus. (B) shows mature neutrophils with more than 6 nuclear lobes (hyper segmented). The smear also shows anisocytosis with both microcytes and macrocytes. | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1634 |
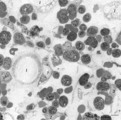 |
Survey of bone marrow (bone marrow, rabbit) | Electron microscopy. Within the loose reticular tissue a great variety of different stages of young erythrocytes (3, 4) as well as of young granulocytes (5) is present. (2) indicates reticular cells and (2b) phagocytizing reticular cells. (1) fat cells (adipocytes); (6) myeloid cell; (7) capillary. | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1635 |
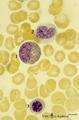 |
Eosinophilic (meta)myelocyte in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The granules of the eosinophilic (meta)myelocyte (1) are large and brown-blue stained in contrast to the hardly visible, dust-like granules in the neutrophilic band form (2). (3) orthochromatic erythroblast. | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1636 |
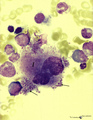 |
Granular megakaryocyte producing platelets in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The centrally located megakaryocyte (1) has a huge nucleus (polyploidy) and an extended cytoplasm from which platelets are released at the periphery (arrows). | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1637 |
 |
Mast cell (lung, dog) | Electron microscopy. This mucosal mast cell of the lung is localized in the vicinity of a blood vessel. Notice the smooth muscle cells (1) of a small arteriole and collagen fibers (2). Most obvious is the presence of granules varying in shape and size. These membrane-bound vesicles (so-called compou... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1638 |
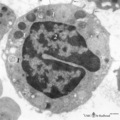 |
Basophilic granulocyte (peripheral blood, human) | Electron microscopy. The bilobed nucleus (2) is surrounded by moderate amount of organelles. The cell exhibits few short filopodia (arrows). The large coarse basophilic granules (1) (specific granules) vary in density and contain vasoactive mediators such as heparin, histamine, sulphated proteoglyca... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1639 |
 |
Mott cell in peripheral blood smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). Plasma cells that contain abundant globular inclusions or vacuoles (Russell bodies) composed of immunoglobulin are called Mott cells (1) morular cells or grape cells. Russell bodies can stain blue-violet or pink but may also be dissolved during fixation and staining.... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1640 |
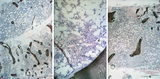 |
Crista biopsies of normal, hypoplastic and malignant bone marrow (human) | Stain: Hematoxylin and eosin. The composition of three slides shows a normal bone marrow section (A), an aplastic bone marrow (B), and a malignant lymphoma in bone marrow (C). (1) Cristae. (2) Fat tissue or fat cells. (3) Erythrocytes and (4) erythroblasts with dark nuclei. | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1641 |
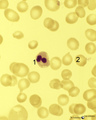 |
Karyorrhexis of polychromatic erythroblast in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The nucleus of the polychromatic erythroblast (1) shows abnormal karyorrhexis due to vitamin B12 deficiency or folic acid deficiency. Normochromic normocyte (2, normal erythrocyte), poikilocytosis and oval macrocytes are seen. | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1642 |
 |
Binucleated plasma cell in peripheral blood smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). A large plasma cell with two nuclei. The chromatin is coarsely clumped. The cytoplasm is intensive basophilic due to the large RER content for purpose of antibody production. Note the clear zone (Golgi area) between the nuclei. | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1643 |
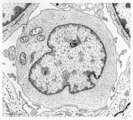 |
Lymphoblast | Scheme electron microscopy. The lymphoblast shows a high nucleus-cytoplasm ratio, it is a large cell (10-20 μm) with a large nucleus and distinct nucleolus. Apart from numerous ribosomes, a small juxta-nuclear Golgi area the cytoplasm is scanty with very few organelles. | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1644 |
 |
Erythron in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). In the center of the slide an erythron that consists of a reticular cell (1) surrounded by erythroblasts (2) at various maturational stages. | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1645 |
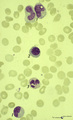 |
Neutrophilic metamyelocytes in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). (1) neutrophilic metamyelocytes. (2) polychromatic erythroblast. (3) segmented neutrophilic granulocyte. | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1646 |
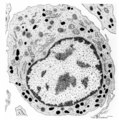 |
Neutrophilic myelocyte | Scheme electron microscopy. From CFU-S (colony forming units-spleen) stem cells arise CFU-GM (colony forming unit-granulocyte/monocyte) stem cells. The latter divide by mitoses and differentiate via promyeloblasts and myeloblasts into myelocytes (the last proliferative stage). The neutrophilic myelo... | Blood; Bone Marrow; Electron microscopy; Neutrophilic myelocyte; Neutrophilic granulocyte; Primary granule; Secondary granule; Azurophilic granule; Lysosome | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset |
| 1647 |
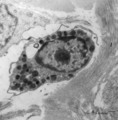 |
Mast cell (lung, human) | Electron microscopy. Mast cells (mastocytes) are oval (12 m) or spindle-shaped and show few thin microvilli at the surface. They are frequently found perivascularly or perineurally within the connective tissue (1). The cytoplasm is provided with a moderate amount of organelles. Most obvious is the p... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1648 |
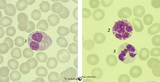 |
Eosinophilic, neutrophilic and basophilic granulocytes in peripheral blood smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The eosinophil (1) is slightly larger than the neutrophil with a diameter of 12-17 m. The nucleus is usually bilobed (occasionally trilobed). Eosinophil granules are considerably larger than those of neutrophils, and are stained reddish-orange. These cells are very f... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1649 |
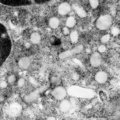 |
Neutrophilic granules in PMN (spleen, human) | Electron microscopy. A detail of the cytoplasm shows many granules of varying forms (round, elongated to dumb-bell), sizes and densities. The majority of these electron-grey to electron-lucent granules are the specific or secondary granules (diameter 0.2 up to length 0.8 μm). They contain substance... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1650 |
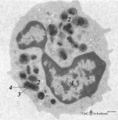 |
Eosinophilic granulocyte (peripheral blood, human) | Electron microscopy. A 11-15 m cell with a partially cut bilobed nucleus (1) and moderate amount of organelles and vesicles. The specific eosinophilic granules (2) contain a central electron-dense angular crystalloid core (3) embedded in a finely granular matrix (4). The crystalloid consists of an a... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1651 |
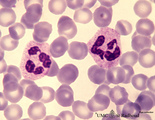 |
Neutrophilic granulocytes in peripheral blood smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The nucleus of the neutrophilic granulocytes (also called polymorphonuclear leukocyte or PMN) is segmented into three to five connected lobules. The cytoplasm displays many fine (dust-like) azurophilic granules. The majority called specific granules are filled with e... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1652 |
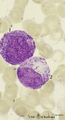 |
Promyelocyte and myelocyte in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The large promyelocyte (1) has a large nucleus with fine disperse chromatine and visible nucleoli. The cell contains primary, azurophilic granules. In the myelocyte (2) the nucleus is located eccentrically at one side of the cell, and the amount of cytoplasm is relat... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1653 |
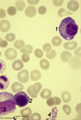 |
Plasma cell in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). (1) A plasma cell with vacuoles (containing Ig), basophilic cytoplasm and a clear halo (Golgi apparatus) in a bone marrow film. (2) represents a young polychromatic erythroblast. (3) neutrophilic myelocyte, and (4) is a cluster of platelets. | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1654 |
 |
Monocyte in peripheral blood smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The monocyte (12-20 μm) contains a large light-stained nucleus with a characteristic indentation with a distinct nucleolus in a light blue-stained apparently transparent cytoplasm. Small primary or azurophilic granules are hardly visible. | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1655 |
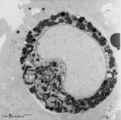 |
Peroxidase activity in neutrophilic myelocyte (postnatal liver, rat) | Electron microscopy (peroxidase reaction with diaminobenzidin staining). An early neutrophilic myelocyte with a large nucleus and well developed organelles, distinct Golgi areas (3) and granules. The Golgi areas, rough endoplasmic reticulum and nuclear membrane stain positively (species-dependent), ... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1656 |
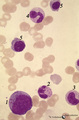 |
(Pro)myelocyte and neutrophilic granulocytes in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The promyelocyte (1) contains coarse primary, azurophilic granules in the basophilic cytoplasm. The absence of nucleoli indicates the late stage of the promyelocyte. (2) segmented neutrophilic granulocyte with toxic granulation (large irregular granules). (3) indicat... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1657 |
 |
Maturation stages of plasmablasts (spleen, liver rat) | Electron microscopy. The youngest (plasmacytoid) lymphocyte in (A) shows a slight indented nucleus with a distinct nucleolus. Apart from a few mitochondria the cytoplasm contains large amount of free ribosomes and polysomes, few profiles of long rough endoplasmic reticulum (1, RER) and Golgi areas (... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1658 |
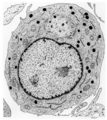 |
Promyelocyte | Scheme electron microscopy. The large promyelocyte (15-25 μm) contains a nucleus (1) with one or two nucleoli, the rough endoplasmic reticulum (4) is present and show many expanded profiles. Distinct also are numerous ribosomes and a well-developed Golgi area (2) where 'non-specific', primary or az... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1659 |
 |
Anisocytosis of erythrocytes in peripheral blood smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). (A) shows normal human erythrocytes in a blood film, while (B) shows anisocytosis. The small cells are called microcytes. Anisocytosis is an increase in the variability of erythrocyte size beyond that which is observed in a normal healthy subject. It is a common, non... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1660 |
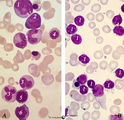 |
Normal pleiomorph and leukemic monomorph bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). In normal bone marrow smear (A) a pleimorph or heterogeneous collection of different cell types (A1-7) can be identified, while in the bone marrow smear of a leukemic patient a single type dominates (in this case lymphoid cells, B-1). | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1661 |
 |
Promyelocyte in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The promyelocyte is the largest cell in the myeloid series in bone marrow. The nucleus is still transparent with fine chromatin and nucleoli are well visible. The cytoplasm contains ample azurophilic, primary granules. | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1662 |
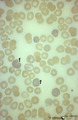 |
Reticulocytosis in peripheral blood smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The slightly pale blue stained cells (1) represent the reticulocytes. These young red blood cells are stained bluish because of the presence of ribosomal RNA. | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1663 |
 |
Mitosis in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). Increased mitotic activity can be observed in megaloblastic anemia. (1) Mitosis figure. (2) Basophilic erythroblasts. | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1664 |
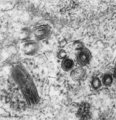 |
Mast cell (connective tissue, human) | Electron microscopy. Mast cells (mastocytes) are frequently found perivascularly or perineurally within the connective tissue. A detail of this mast cell shows granules varying in shape and size. These membrane-bound vesicles (so-called compound granules) show a metachromatic reaction in light micro... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1665 |
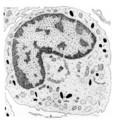 |
Neutrophilic metamyelocyte | Scheme electron microscopy. From CFU-S (colony forming units-spleen) stem cells arise CFU-GM (colony forming unit-granulocyte/monocyte) stem cells. The latter divide by mitoses and differentiate via promyeloblasts and myeloblasts into neutrophilic myelocytes (the last proliferative stage). The next ... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1666 |
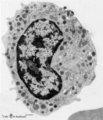 |
Band-form of neutrophilic granulocyte (peripheral blood, human) | Electron microscopy. Transition from late metamyelocyte to band form (9-12 μm). These are the earliest stages of the motile two-lobed neutrophilic granulocytes. (1) a slightly bended nucleus with a nucleolus. (2) Golgi area. Apart from a few mitochondria (3) and profiles of rough endoplasmic retic... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1667 |
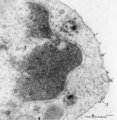 |
Endocytosis in lymphocyte (peripheral blood, rat) | Electron microscopy. Thorotrast is a suspension of thorium dioxide particles and was formerly used as a contrast medium in X-ray diagnostics. These particles were found to accumulate in spleen, lymph nodes and most likely in macrophages and phagocytizing reticular cells. Generally lymphocytes do not... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1668 |
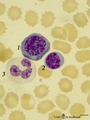 |
Basophilic erythroblast, plasmacytoid lymphocyte and neutrophilic granulocyte in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The basophilic erythroblast (1) contains a large, partly condensed but transparent nucleus with a distinct nucleolus. The cytoplasm is strong basophilic. The plasmacytoid lymphocyte (2) or activated B cell is much smaller and less basophilic. The young neutrophil (3)... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1669 |
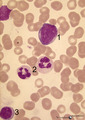 |
Myeloblast, neutrophilic granulocyte and lymphocyte in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The myeloblast (1) measures 12-20 m with 1-5 prominent nucleoli and fine diffuse chromatin. The slightly pale blue cytoplasm contains sometimes a few azurophilic granules (primary granules). (2) Indicates two segmented neutrophilic granulocytes with 3-5 nuclear lobes... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1670 |
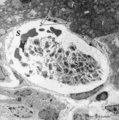 |
Aggregation of platelets (liver, rat) | Electron microscopy. Within a liver sinusoid (S) close to a small bile ductile (B) in the periportal area of the liver some erythocytes (E) and an aggregation of platelets (3) are present. (2) represents the space of Disse to which the liver parenchyma cells border (1). These disc-shaped anucleate p... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1671 |
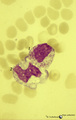 |
Toxic granulation and vacuolation in neutrophilic myelocytes in peripheral blood smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The myelocyte (1) and the metamyelocyte (2) show toxic granulation and vacuolation and cytoplasmic swelling. Vacuoles may represent the terminal stage of autophagocytosis. Granules may burst and their contents undergo autophagocytosis in a number of pathologic condit... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1672 |
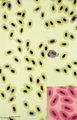 |
Nucleated erythrocytes in peripheral blood smear (bird) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). In contrast to human red blood cells mature erythrocytes of birds contain nuclei (1). (2) Indicates an eosinophilic granulocyte. Inset demonstrates chromatin pattern of the nuclei. | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1673 |
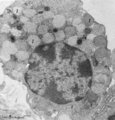 |
Mast cell (lung, golden hamster) | Electron microscopy. Mucosa mast cells (mastocytes) are frequently found perivascularly or perineurally. The mast cell shows long thin microvilli at the surface and the cytoplasm is stuffed with granules (1) varying in shape and size. At (2) a Golgi area and at (3) small mitochondria and some electr... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1674 |
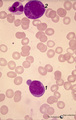 |
Myeloblast and promyelocyte in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The myeoloblast (1) measures 12-20 m and has a high nucleus-cytoplasm ratio and a round to oval nucleus. The nucleus has a fine disperse diffuse chromatin and one to five prominent nucleoli. The cytoplasm is pale blue (basophilic) with no or only scarce numbers of az... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1675 |
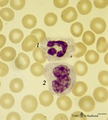 |
Neutrophilic granulocyte and monocyte in peripheral blood smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). (1) the neutrophil (12-15 μm) shows a dark-stained partly lobulated nucleus with the smaller lobe connected by a fine strand of chromatin to the larger nuclear part. The cytoplasm reveals very faintly small azurophilic (primary) granules. (2) the monocyte (12-20 μm... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1676 |
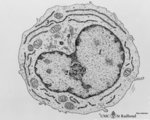 |
Plasmablast | Scheme electron microscopy. This plasmablast (up to 20 μm) shows an indented large nucleus (1) and a distinct nucleolus (2). In addition to free ribosomes long profiles of rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) (3) are being developed concomitant with Golgi packages (4). The cytoplasm is scanty with few... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1677 |
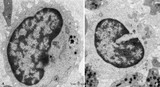 |
Lymphocyte (peripheral blood, human) | Electron microscopy. (Cytotoxic) lymphocyte (A) with a juxta-nuclear Golgi area (3) and centrioles (2), few mitochondria (4) and sparsely profiles of rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER). Dense-stained granules (1) are present. The surface exhibits short blunt microvilli. The right lymphocyte in (B) ha... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1678 |
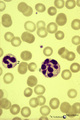 |
Hypersegmented neutrophil in peripheral blood smear of a hyperthermic patient (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). In hyperthermic patients the neutrophils (1) show hypersegmentation of the nuclear lobe (>5) and a pyknotic appearance. The nucleus appears like a bunch of grapes. (2) immature band neutrophil (juvenile unsegmented neutrophil). Hypersegmentation may also occur in meg... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1679 |
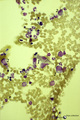 |
Pleiomorph bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). Low power view of a normal bone marrow smear. The bone marrow is pleiomorph and contains all cell types such as a large reticulum cells (1) with many granules or lysosomes (phagocytosis); myeloid cells (2); and erythroblasts (3). | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1680 |
 |
Promyelocyte in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The large promyelocyte contains nucleoli, coarse chromatin pattern, and abundant azurophilic granules in a basophilic cytoplasm. (2) A neutrophilic band form leukocyte with folded nucleus. | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1681 |
 |
Basophilic erythroblast and myeloid cells in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). (1) early basophilic erythroblast. (2) eosinophilic metamyelocyte. (3) neutrophilic myelocyte. (4) two band neutrophils. | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1682 |
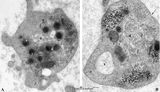 |
Platelets (peripheral blood, human) | Electron microscopy. These anucleate cells (2-4 μm) are derived from cytoplasmic fragments of a megakaryocyte and when free floating in the peripheral blood they develop thin extensions. These platelets contain among others few mitochondria (1), microtubules (2), glycogen (3), small vacuoles (4, op... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1683 |
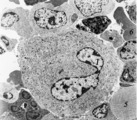 |
Megakaryocyte (bone marrow, rabbit) | Electron microscopy. A survey of a megakaryocyte demonstrates very well the differences in diameter between this giant polyploid cell (1) and the other young white blood cells (2-5). In the intermediate zone the (dark) granules (of the future platelets) are close associated with the electron-light i... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1684 |
 |
Megakaryocyte (peripheral blood, human) | Electron microscopy. A small part of a megakaryocyte (see also inset) shows two nuclear segments (1) and two areas of cytoplasm. Seen at this magnification and close to the perinuclear area, the granular population can be divided into homogeneous electron-dense (2) and electron-grey (3) granules. Th... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1685 |
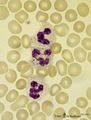 |
Neutrophilic granulocytes in peripheral blood smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The three neutrophilic granulocytes display segmented and lobulated nuclei. The lobes are connected with thin chromatin strands (→). The cytoplasm is ample filled with fine, dust-like granules and the majority are specific granules filled with enzymes such as lysoz... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1686 |
 |
Multiple myeloma, plasma cell leukemia in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). Mutiple myeloma (Kahler's disease) is characterized by proliferation of abnormal plasma cells (1, myeloma cells) in the bone marrow. In the great majority of patients secretion of a single homogenous immunoglobulin product (monoclonal component) occurs. Note the ecce... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1687 |
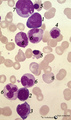 |
Pleiomorph normal bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The normal bone marrow with pleiomorphism, i.e. contains all stages of the erythroblastic differentiation series (1-5) as well as the stages of the myeloblastic series (6). (1) Basophilic erythroblast. (2),(3),(4) Polychromatic erythroblasts. (5) Orthochromatic er... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1688 |
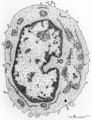 |
Lymphocyte | Scheme electron microscopy. A lymphocyte with an indented nucleus and (1) nucleolus shows a juxta-nuclear Golgi area (2) and centriole (3), several mitochondria (4) and sparsely profiles of rough endoplasmic reticulum (5) in the cytoplasm. Few dense-stained granules (6) are present. The granules con... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1689 |
 |
Small, medium and large lymphocytes in blood smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The picture shows three activation stages of lymphocytes as (1) small, (2) medium and (3) large lymphocytes. In that range the nucleus becomes less condensed and more transparent, while the amount of cytoplasm increases. The large lymphocyte also contains some granul... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1690 |
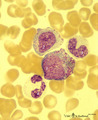 |
Myeloid cells in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). (1) promyelocyte is the largest cell in the myeloid series. It has a transparent nucleus with nucleoli and ample cytoplasm with many azurophilic granules. (2) myelocyte. (3) metamyelocyte with an indented nucleus. (4) beginning of nucleus segmentation in the band neu... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1691 |
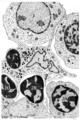 |
Erythroblastic island in bone marrow | Scheme electron microscopy. Different stages of maturing erythroblasts (2) are exposed in this scheme. The centrally localized phagocytic reticular cell (1) has many long cytoplasmic extensions that form a network with similar cells within the bone marrow. Its nucleus is irregular. The cytoplasm has... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1692 |
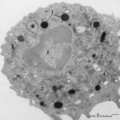 |
Peroxidase activity in neutrophilic granulocyte (peripheral blood, guinea pig) | Electron microscopy (peroxidase reaction with diaminobenzidin staining). The elongated nucleus (3) of this strongly ameboid phagocytic cell has several projections. These nuclear extensions are interconnected by thin heterochromatin strands. The cytoplasm exhibits moderate amounts of organelles, gly... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1693 |
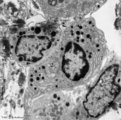 |
Plasma cells with Russell bodies (nose septum, rat) | Electron microscopy. Accumulation of few plasma cells. These mature plasma cells exhibit in their cytoplasm's dilated rough endoplasmic reticula (1) filled with electron-grey material (antibodies) as well as electron-dense granules (3) of varying sizes confirming their secretory activities. (2) indi... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1694 |
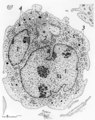 |
Pro-megakaryocyte | Scheme electron microscopy. The pro-megakaryocyte (20-80 m) develops from a basophilic megakaryoblast (up to 50 m) that originates from a committed stem cell. The large pro-megakaryocyte starts with the early synthesis of the characteristic granules of platelets. Apart from a bilobed nucleus (1) and... | Blood; Bone Marrow; Electron microscopy; Pro-megakaryocyte; Megakaryocyte | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset |
| 1695 |
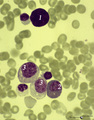 |
A bare megakaryocyte nucleus and myelocytes in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). (1) Indicates a bare large-sized polyploid nucleus of a megakaryocyte which has totally shed the cytoplasm. These cells are often seen in normal marrow and are ultimately removed by macrophages. There is no cytoplasm left, nor platelets are left around the nucleus. T... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1696 |
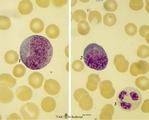 |
Promyelocyte and basophilic erythroblast in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The composition shows a (pro)myelocyte (1) along a basophilic erythroblast (2). The (pro)myelocyte nucleus is less condensed, contains nucleoli and the light basophilic cytoplasm is filled with azurophilic granules. The cytoplasm of the erythroblast is strong basophi... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1697 |
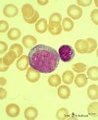 |
Myeloblast in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The myeloblast (1) shows a very transparent nucleus and several distinct nucleoli. The slightly basophilic cytoplasm is limited to a small rim in contrast to a promyelocyte. No granules are yet visible. (2) small lymphocyte. | Blood; Bone Marrow; Myeloblast; Lymphocyte | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset |
| 1698 |
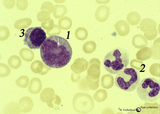 |
Promonocyte in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The promonocyte (1) has an irregular nucleus and shows the first step towards indentation (arrow). The cell has a characteristic greyish-blue cytoplasm. (2) Represents three young neutrophils. (3) A plasmacytoid lymphocyte. | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1699 |
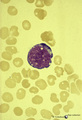 |
Reactive promyelocyte during sepsis or chemotherapy in peripheral bood smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). Neutrophilic promyelocyte with toxic granulation and vacuolar degeneration. Note that nucleoli are still visible. | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1700 |
 |
Platelets | Scheme electron microscopy. These disc-shaped anucleate cells (2-4 m) are derived from cytoplasmic fragments of the megakaryocyte. They contain few mitochondria, a canalicular system, a smooth tubular system, marginal localized microtubules, glycogen and different types of granula. A circumferential... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset |
