The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
TO
Filters: Collection: "ehsl_heal"
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1301 |
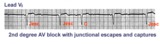 |
2nd degree AV block with junctional escapes and captures | Second degree AV block is present; conducted beats are identified by those QRS's that terminate shorter cycles than the junctional escape cycle; i.e., the 3rd and probably the 4th QRS's are captures; the other QRS's are junctional escapes. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 1302 |
 |
Atrial fibrillation with moderate ventricular response - Marquette | Atrial fibrillation with moderate ventricular response - Marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 1303 |
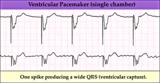 |
Ventricular pacing in atrial fibrillation - marquette | Ventricular pacing in atrial fibrillation - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 1304 |
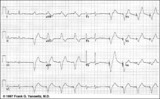 |
Ventricular pacemaker: demand mode functioning | Ventricular pacemaker: demand mode functioning | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 1305 |
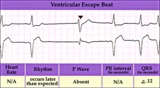 |
Ventricular escape beat - marquette | Ventricular escape beat - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 1306 |
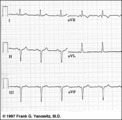 |
LAFB: frontal plane leads | LAFB: frontal plane leads | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 1307 |
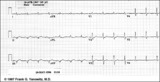 |
Old infero-posterior MI | Old infero-posterior MI | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 1308 |
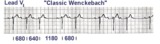 |
2nd degree AV block, type I | The 3 rules of classic AV Wenckebach are: 1. decreasing RR intervals until pause; 2. the pause is less than preceding 2 RR intervals; and 3. the RR interval after the pause is greater than the RR interval just prior to pause. Unfortunately, there are many examples of atypical forms of Wenckebach wh... | Wenckebach AV Block | Knowledge Weavers ECG |
| 1309 |
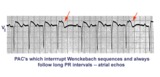 |
Atrial echos | In this example a typical Wenckebach sequence is interrupted by what looks like a PAC - indicated by red arrows. Atrial echos are more likely, however, because the preceding beat has a long PR interval, a condition that facilitates reentry and echo formation. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 1310 |
 |
Anteroseptal MI with RBBB: precordial leads | Anteroseptal MI with RBBB: precordial leads | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 1311 |
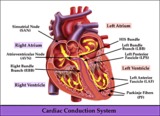 |
Cardiac conduction system diagram - marquette | Cardiac conduction system diagram - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 1312 |
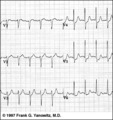 |
ST segment depression: precordial leads | ST segment depression: precordial leads | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 1313 |
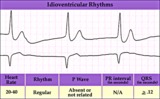 |
Idioventricular escape rhythm | Idioventricular escape rhythm | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 1314 |
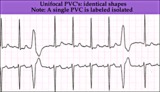 |
Unifocal PVCs - marquette | Unifocal PVCs - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 1315 |
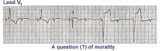 |
Two Wrongs Sometimes Make a Right | The question mark is over a normal looking QRS that occurs during 2:1 AV block with RBBB. Following this QRS a ventricular escape rhythm takes over. The normal looking beat is actually a fusion beat resulting from simultaneous activation of the ventricles; the sinus impulse enters the left ventric... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 1316 |
 |
WPW type preexcitation | Note the short PR and the subtle delta wave at the beginning of the QRS complexes. The delta wave represents early activation of the ventricles in the region where the AV bypass tract inserts. The rest of the QRS is derived from the normal activation sequence using the bundle branches. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 1317 |
 |
Long QT interval | The QT interval duration is greater than 50% of the RR interval, a good indication that it is prolonged in this patient. Although there are many causes for the long QT, patients with this are at risk for malignant ventricular arrhythmias, syncope, and sudden death. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 1318 |
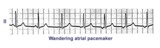 |
Wandering atrial pacemaker | Wandering atrial pacemaker is a benign rhythm change where the pacemaker site shifts from the sinus node into the atrial tissues. P-wave morphology varies with the pacemaker site. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 1319 |
 |
QRS axis = +60 degrees | Lead aVL is isoelectric; leads II and III are mostly positive. The QRS axis, therefore, is +60 degrees. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 1320 |
 |
Electronic ventricular pacemaker rhythm - marquette | Electronic ventricular pacemaker rhythm - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 1321 |
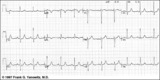 |
High lateral wall MI (seen in aVL) | High lateral wall MI (seen in aVL) | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 1322 |
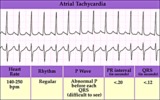 |
Atrial tachycardia - marquette | Atrial tachycardia - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 1323 |
 |
LVH with Strain | LVH with Strain | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 1324 |
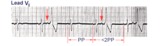 |
PAC's with RBBB aberrant conduction | PAC's are identified by the arrows. Note that the PP interval surrounding the PAC is less than 2x the basic sinus cycle indicating that the sinus node has been reset by the ectopic P wave. The pause after the PAC, therefore, is incomplete. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 1325 |
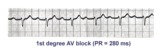 |
1st degree AV block | The normal PR interval is 0.12 - 0.20 sec, or 120 -to- 200 ms. 1st degree AV block is defined by PR intervals greater than 200 ms. This may be caused by drugs, such as digoxin; excessive vagal tone; ischemia; or intrinsic disease in the AV junction or bundle branch system. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 1326 |
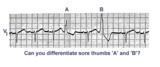 |
Sore thumbs | Two funny looking premature beats are seen in this rhythm strip. Beat A is preceded by a PAC which distorts the T wave, making this an aberrantly conducted PAC. Beat B is a PVC. The notch on the down slope of the QRS complex clearly identifies this as a PVC and not aberrancy. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 1327 |
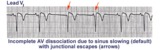 |
AV dissociation by default | If the sinus node slows too much a junctional escape pacemaker may take over as indicated by arrows. AV dissociation is incomplete, since the sinus node speeds up and recaptures the entricles. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 1328 |
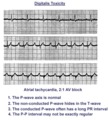 |
Atrial tachycardia with 2:1 AV block: a manifestation of digitalis intoxication | Atrial tachycardia with 2:1 AV block: a manifestation of digitalis intoxication | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 1329 |
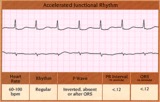 |
Accelerated junctional rhythm - marquette | Accelerated junctional rhythm - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 1330 |
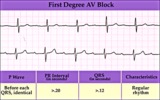 |
First degree AV block - marquette | First degree AV block - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 1331 |
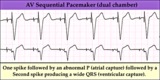 |
AV sequential pacemaker - marquette | (Summary) | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 1332 |
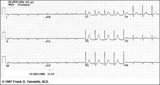 |
Postero-lateral MI: Fully Evolved | The true posterior MI is recognized by pathologic R waves in leads V1-2. These are the posterior equivalent of pathologic Q waves (seen from the perspective of the anterior leads). Tall T waves in these same leads are the posterior equivalent of inverted T waves in this fully evolved MI. The loss o... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 1333 |
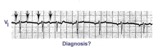 |
Atrial tachycardia with 3:2 and 2:1 AV block | The ectopic atrial rate is 150 bpm. Some of the ectopic P waves are easily seen and indicated by the arrows. Other P waves are burried in the T waves and not so easily identified. Atrial tachycardia with AV block is often a sign of digitalis intoxication. 3:2 and 2:1 AV block is seen in this examp... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 1334 |
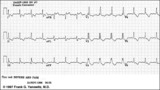 |
RBBB with primary ST-T wave abnormalities | RBBB is recognized by 1) rR' in V1; 2) QRS duration>0.12s; 3) terminal QRS forces oriented rightwards and anterior. In RBBB the ST-T waves should be oriented opposite to the terminal QRS forces. In this example there areprimary ST-T wave abnormalitiesin leads I, II, aVL, V5, V6. In these leads th... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 1335 |
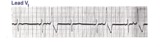 |
What are those funny looking beats???? | The differential diagnosis of funny-looking-beats, or FLB's, primarily considers beats of supraventricular origin with aberrant conduction and ventricular ectopic beats. In this example the two FLB's have an easily seen ectopic P wave before them; therefore these are PAC's with RBBB aberration. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 1336 |
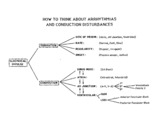 |
Conceptual framework: aArrhythmias and conduction abnormalities | Conceptual framework: aArrhythmias and conduction abnormalities | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 1337 |
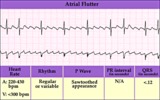 |
Atrial flutter with variable AV block - marquette | Atrial flutter with variable AV block - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 1338 |
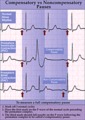 |
Compensatory vs. non-compensatory pauses - marquette | Compensatory vs. non-compensatory pauses - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 1339 |
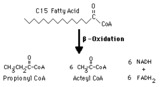 |
Propionyl CoA production from odd-chain fatty acids | Beta-oxidation of fatty acids with an odd number of carbons inthe chain yields the three-carbon propionyl CoA as the final fragment. | Biosynthesis | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids |
| 1340 |
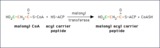 |
Transfer of a malonyl group to the acyl carrier peptide | During fatty acid synthesis the incoming two carbon fragment is introduced as the three-carbon malonyl group. It is added to the -SH group of the acyl carier peptide domain of fatty acid synthase. In a subsequent reaction the carbon shown in green will be lost as bicarbonate ion. | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids | |
| 1341 |
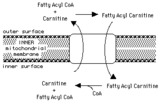 |
Transport of fatty acyl CoA into mitochondria by the carnitine shuttle | Fatty acyl CoA cannot cross the inner mitochondrial membrane, so it is carried in the form of fatty acyl carnitine. | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids | |
| 1342 |
 |
Hydroxymethylglutaryl CoA lyase reaction | In this mitochondrial process hydroxymethylglutaryl CoA is converted to acetoacetate, a ketone body. Acetyl CoA is another product. | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids | |
| 1343 |
 |
Acetyl CoA metabolism -- overview | Major metabolic sources of acetyl CoA and some of the processes in which it serves as a substrate. | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids | |
| 1344 |
 |
Oleic acid structure | Oleic acid is a typical monounsaturated fatty acid. | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids | |
| 1345 |
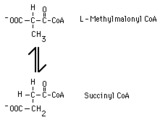 |
methylmalonyl CoA mutase reaction | In the metabolism of propionyl CoA L-methylmalonyl CoA is converted to succinate by methylmalonyl CoA mutase. Succinate can then be metabolized throgh the tricarboxylic acid cycle. | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids | |
| 1346 |
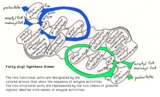 |
Mammalian fatty acyl synthase dimer | This schematic diagram is intended to show the sequence of enzyme activities in the two subunits of a mammalian fatty acyl synthase dimer. It is not intended to imply anything about the detailed spatial relationships of the activities. | Coenzyme A Synthetases | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids |
| 1347 |
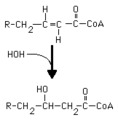 |
Hydration of an enoyl CoA | Hydration of the double bond is catalyzed by enoyl CoA hydratase. The product is an L-3-hydroxyacyl CoA. This reaction is a step in the beta-oxidation of fatty acids. | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids | |
| 1348 |
 |
Acetyl CoA structure | Acetyl CoA Structure. The thioester bond linking the acetyl group to CoA is ahigh energybond. | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids | |
| 1349 |
 |
Use of greek letters to designate carbons in fatty acids | The carbon next to the -COOH group is the alpha carbon; the next one is the beta carbon, and so forth. The carbon most distant from the -COOH group is designated omega. Carbons close to the omega carbon may be designated in relation to it. E.g., the third carbon from the end is omega - 3, and the... | Nomenclature | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids |
| 1350 |
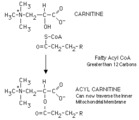 |
Acylation of carnitine by a long chain fatty acyl CoA | Long chain fatty acyl CoA cannot cross the inner mitochondrial membrane to participate in beta-oxidation. The fatty acyl group is therefore transferred to a carrier, carnitine, in a reversible reaction catalyzed by carnitine acyl transferase I. The resulting fatty acyl carnitine crosses the membra... | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids | |
| 1351 |
 |
Four systems for denoting fatty acids | There are four commonly used ways of designating fatty acids. The first two columns show samples of names, and the last two columns show systems of abbreviating these names. | Nomenclature | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids |
| 1352 |
 |
Reduction of 2-enoyl acyl carrier peptide | A 2-enoyl acyl group on the acyl carrier peptide is reduced by NADPH in a reaction catalyzed by enoyl acyl carrier peptide reductase. | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids | |
| 1353 |
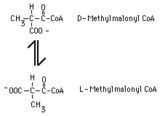 |
methylmalonyl CoA racemase reaction | In the metabolism of propionyl CoA, D-methylmalonyl CoA is produced by a carboxylase reaction. This product must be converted to L-methylmalonyl CoA in order to be metabolized further. The conversion is catalyzed by methylmalonyl CoA racemase. | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids | |
| 1354 |
 |
Oxidation of a polyunsaturated fatty acid -- part I | The cycles of beta-oxidation prior to the one involving the original Delta-12 double bond act to get past the Delta-9 double bond. | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids | |
| 1355 |
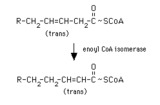 |
enoyl CoA isomerase reaction | Enoyl CoA isomerase converts a trans-3-enoyl CoA to a trans-2-enoyl CoA. Thus a Delta-9 fatty acyl CoA or the product of the 2,4-dienoyl CoA reductase reaction can proceed through beta-oxidation. | Enoyl CoA Isomerase Reaction | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids |
| 1356 |
 |
Structures of the ketone bodies | These are the structures of the ketone bodies. Acetoacetate and beta-hydroxybutyrate are important physiological substrates. Acetone is a byproduct, and is not metabolized further. It is excreted in the urine and in expired air. | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids | |
| 1357 |
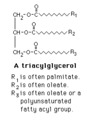 |
Triacylglycerol structure | The structure of a typical triacylglycerol (triglyceride). | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids | |
| 1358 |
 |
Dehydrogenation of fatty acyl CoA | Fatty acyl CoA is dehydrogenated by FAD in a reaction catalyzed by one of the acyl CoA dehydrogenases. Note that the dehydrogenation occurs between the alpha- and beta-carbons. | FAD | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids |
| 1359 |
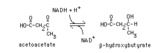 |
Reduction of acetoacetate | Acetoacetate is reduced by NADH in a reversible reaction catalyzed by beta-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase. This reaction is the source of beta-hydroxybutyrate in the blood of individuals with ketosis. | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids | |
| 1360 |
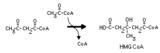 |
Hydroxymethylglutaryl CoA synthase reaction | This irreversible reaction occurs in the mitochondria, where it is the first step in ketone body synthesis. It also occurs in the cytoplasm, where it leads to isoprenoid and steroid synthesis. | Biosynthesis | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids |
| 1361 |
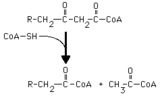 |
Thiolase reaction | Thiolase (3-ketoacyl CoA thiolase) cleaves a long chain fatty acyl CoA, forming acetyl CoA and a long chain fatty acyl CoA that is two carbons shorter. | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids | |
| 1362 |
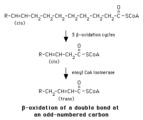 |
Beta-oxidation of a delta-9 fatty acyl CoA | Enoyl CoA isomerase is required to move the double bond in a Delta-9 fatty acyl CoA to a position where it can continue in beta-oxidation. | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids | |
| 1363 |
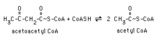 |
Thiolase reaction with acetoacetyl CoA | Thiolase (3-ketoacyl CoA thiolase) cleaves acetoacetyl CoA, forming two molecules of acetyl CoA. | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids | |
| 1364 |
 |
Stearic acid structure | Stearic acid is a typical long chain saturated fatty acid. | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids | |
| 1365 |
 |
Fatty acid elongation in mitochondria | This shows the overall reaction of fatty acid elongation in mitochondria. The process is essentially a reversal of beta-oxidation, except that one NADPH and one NADH are required (beta-oxidation yields two NADH). Mitochondrial fatty acid elongation acts primarily on fatty acyl CoA substrates short... | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids | |
| 1366 |
 |
Fatty acyl CoA elongation in the endoplasmic reticulum | This shows the overall process of fatty acyl elongation in the endoplasmic reticulum. The process resembles that catalyzed by fatty acyl synthase, but the individual activities appear to be on separate enzymes. | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids | |
| 1367 |
 |
Propionyl CoA carboxylase reaction | Propionyl CoA is metabolized by a process that first converts it to D-methylmalonyl CoA. The reaction is catalyzed by propionyl CoA carboxylase,and requires energy in the form of ATP. | Biosynthesis | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids |
| 1368 |
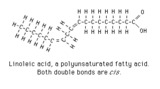 |
Linoleic acid structure | Linoleic acid is a typical polyunsaturated fatty acid. | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids | |
| 1369 |
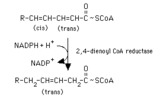 |
Reduction of a 2,4-dienoyl CoA | The reduction of 2,4-dienoyl CoA by NADPH is a step in the oxidation of polyunsaturated fatty acids. It is ironic that a reduction reaction is a required step in a process that is oxidative. | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids | |
| 1370 |
 |
Stearic, oleic and linoleic acid structures | Stearic, oleic and linoleic acid structures | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids | |
| 1371 |
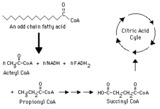 |
Complete oxidation of an odd-chain fatty acid -- overview | This diagram indicates production of propionyl CoA from an odd-chain fatty acid and the subsequent conversion of propionyl CoA to succinyl CoA, which can be metabolized through the citric (tricarboxylic) acid cycle. | Biosynthesis | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids |
| 1372 |
 |
Initiation of beta-oxidation | An acetyl group is transferred from acetyl CoA to the -SH group of the condensing enzyme domain of fatty acyl synthase, forming acetyl-CE. The reaction is catalyzed by the acyltransferase activity of fatty acyl synthase. | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids | |
| 1373 |
 |
Fatty acid metabolism -- schematic overview | Fatty acids are taken up by cells, where thy may serve as precursors in the synthesis of other compounds, as fuels for energy production, and as substrates for ketone body synthesis. Ketones bodies may then be exported to other tissues, where they can be used for energy production. | Biosynthesis | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids |
| 1374 |
 |
Condensation of an acyl group with a malonyl group | The acetyl group displaces the carboxyl of the malonyl group, forming a beta-ketoacyl group. This reaction is catalyzed by beta-ketoacyl Acyl Carrier Peptide synthase. The carboxyl released in the form of bicarbonate regenerates the bicarbonate used earlier in the acetyl CoA carboxylase reaction. | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids | |
| 1375 |
 |
Essential features of a fatty acid | The essential features of a fatty acid are a long hydrocarbon chain terminating in a carboxylic acid group. | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids | |
| 1376 |
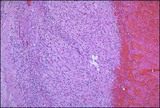 |
Corpus luteum cysts exhibit a convoluted lining with luteinized granulosa and theca cells. | Corpus luteum of the ovary, medium power. The granulosa cells have undergone proliferation and alteration to lutein cells that produce progesterone. The lutein cells are large and polyhedral and the cytoplasm is foamy and eosinophilic. | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction | |
| 1377 |
 |
Mucinous cystadenoma | These tumors comprise 20% of all neoplasms, and 50% of ovarian neoplasms found in women less than 20 years of age. They are frequently multiloculated. The favored hypothesis for their origin is metaplastic surface epithelium as they have a predominance of endocervical gland type epithelium. | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction | |
| 1378 |
 |
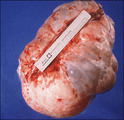
Ovarian tumor | A large vertical incision allows delivery and excision of an ovarian neoplasm. Pelvic washings for cytology and a frozen section rule out a malignancy. The cyst is excised carefully to avoid spilling contents into the abdomen. | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction | |
| 1379 |
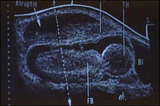 |
Ultrasound of placental abruption | The fetal body and bladder are labeled FB, and BL, respectively. | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction | |
| 1380 |
 |
Uterine rupture | Uterine rupture | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction | |
| 1381 |
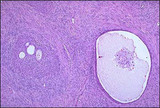 |
Brenner tumor | Solid and partially cystic epithelial nests are surrounded by a stroma composed of bundles of tightly-packed spindle shaped cells. The epithelial cells are polygonal and of the squamoid type, with pale, eosinophilic cytoplasm and oval nuclei having distinct nuclei and longitudinal grooving, a coffee... | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction | |
| 1382 |
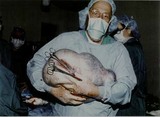 |
Mucinous cystadenoma | This tumor weighed 35 pounds. | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction | |
| 1383 |
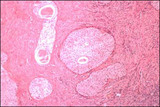 |
Brenner tumor | Brenner tumors are comprised of solid to partly cystic epithelial nests surrounded by stroma composed of bundles of tightly packed spindle-shaped cells. The epithelial cells are polygonal and of squamoid type, with pale, eosinophilic cytoplasm and oval nuclei with distinct nucleoli and longitudinal ... | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction | |
| 1384 |
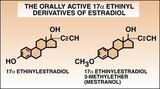 |
Estradiol | The structure of ethinyl estradiol and mestranol. | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction | |
| 1385 |
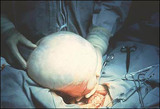 |
Mucinous cystadenoma | Neglected mucinous cystadenoma may become extremely large. | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction | |
| 1386 |
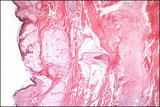 |
Mature cystic teratoma - Microscopic | Ectodermal tissue is usually most abundant and represented by: squamous epithelium and appendages, brain tissue, glia, retina, choroid plexus, and ganglia. Mesodermal tissue is represented by bone and cartilage. Endodermal tissue is represented by gastrointestinal and bronchial epithelium and glands... | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction | |
| 1387 |
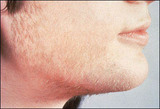 |
Hirsutism | This woman has polycystic ovarian syndrome and hyperandrogenemia resulting in hirsutism. | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction | |
| 1388 |
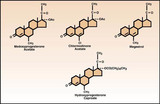 |
Structures of acetoxy progestins (pregnane steroids) | From C. Matthew Peterson, M.D. Progestogens, Progesterone Antagonists, Progesterone, and Androgens: Synthesis, Classification and Uses, Clinical Obstetrics and Gynecology, 1995; 38: 813-20. The structures of acetoxy progestins (pregnane steroids). | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction | |
| 1389 |
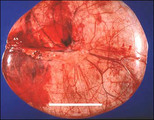 |
Serous cystadenoma | These tumors comprise 20% of all ovarian neoplasms. The epithelium is a single layer of regular cuboidal epithelium, with basal nuclei and rare mitoses. | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction | |
| 1390 |
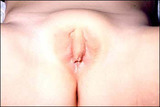 |
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia and clitoromegaly | Congenital adrenal hyperplasia and clitoromegaly | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction | |
| 1391 |
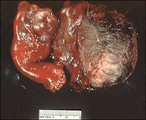 |
Mature cystic teratoma-torsed with adenexal structures | Elements of all three germ layers are present: endoderm, mesoderm, and ectoderm. They are classified as germ cell tumors and are thought to arise through parthenogenesis. They are found in the path of migration of the germ cells from the yolk sac to the primitive gonad. | Pathogenesis | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction |
| 1392 |
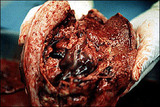 |
Total placenta previa: placenta accreta in uterine specimen | Placenta accreta or percreta may be associated with placenta previa especially if the patient has had a previous cesarean section. | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction | |
| 1393 |
 |
Ovarian follicular scanning | Ovarian follicular scanning. Ovaries are scanned transvaginally to determine the size of the developing follicles. | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction | |
| 1394 |
 |
Total placenta previa: schematic of complete placenta previa | The placenta completely covers the internal os of the cervix. | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction | |
| 1395 |
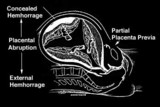 |
Abruptio placenta | Abruptio placenta | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction | |
| 1396 |
 |
Contraception for women in their later years | Contraception for women in their later reproductive years. | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction | |
| 1397 |
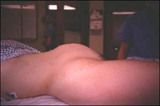 |
Pelvic mass | A pelvic mass may be present with abdominal distention from the mass, ascities, or both. | Abdominal Distention | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction |
| 1398 |
 |
Androgen insensitivity | Adapted with permission from Jaffe R.B. Disorders of Sexual Differentiation. In Yen SSC and Jaffe RB, eds, Reproductive Endocrinology, W.B. Saunders Co., Philadelphia, 1986, p 300. An inability to respond to testosterone through a target organ receptor defect in 60-70% and a post-receptor signalling... | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction | |
| 1399 |
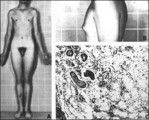 |
Klinefelter's syndrome | Adapted with permission from Grumbach M.M. and Conte F.A.,Disorders of Sexual Differentation. In Williams R.H. ed, Textbook of Endocrinology, W. B.Squanders Co., Philadelphia, 1981, p 451. Males with an XXY karyotype characteristically have long extremities, aeunuchoidal habitus, and gynecomastia. | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction | |
| 1400 |
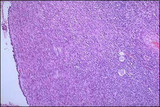 |
Polycystic ovaries | Polycystic ovary, high power view: Prominent layer of theca interna cells with extensive luteinization. Atretic follicles are more abundant in the cortex. | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction |
