The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
TO
Filters: Collection: "ehsl_heal"
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1001 |
 |
Scabies, diagnosis | This demonstrates the application of mineral oil to suspected scabies lesions prior to scraping. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1002 |
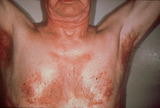 |
Seborrheic dermatitis | Seborrheic dermatitis involving the chest and armpits. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1003 |
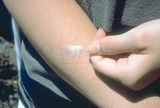 |
Stratum corneum | The stratum corneum, the barrier layer, is very thin, and can be removed with scotch tape and by applying scotch tape to the skin repeatedly for 15 or 20 times. Even though it is physically thin it is a very resilient and effective barrier layer. | Stratum Corneum | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology |
| 1004 |
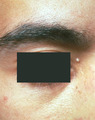 |
Milium near the medial canthus of the right eye | Milium near the medial canthus of the right eye. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1005 |
 |
Body lice | Body lice often are located in the seams of the clothing. The treatment is simply physically washing the lice off the body, and destroying them within the clothing by washing them in hot water or dry-cleaning them. Itching can be relieved with the use of topical steroids, oral antihistamines, or ora... | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1006 |
 |
Punch biopsy | This demonstrates anesthetizing the skin before doing a punch biopsy. The target is the epidermis and dermis, and the upper portion of the fat, and all those areas should be injected with local anesthetic. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1007 |
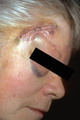 |
Basal cell carcinoma: excision removal | A layered closure was done using 4-0 absorbable suture as a deep dermal suture, and 4-0 nonabsorbable monofilament suture in a running pattern. Note the wound eversion. | Surgical Methods | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology |
| 1008 |
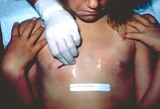 |
Children with scabies | At least 20 red papules are scraped with a #15 blade or a curette. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1009 |
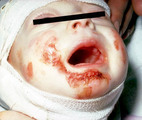 |
Recessive epidermolysis bullosa | Same child with recessive epidermolysis bullosa. The slightest abrasion on the skin would tear the epidermis from the underlying dermis, and this was true of the mucosa as well. The child had broad areas of dermis that were exposed, and the child was treated as a burn victim with Silvadene cream and... | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1010 |
 |
Benign nevus in a child | Benign nevus in a child. It has been found that if a nevus grows rapidly in a child that this is the most common indicator of melanoma, and is more important than the usual criteria of mixture of colors and/or jagged border. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1011 |
 |
Pustules in scalp | Pustules in scalp. There is a type of folliculitis or, some say, a form of acne vulgaris that presents as red papules and pustules in the scalp. Regardless, this generally responds to tetracycline, 500 mg twice daily, or minocycline, 100 mg twice daily. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1012 |
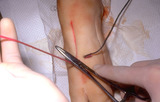 |
Excision: suturing vertical mattress | When the long arm (needle bearing end) of the suture is held upward, it forms a natural V, and the needle holder is placed on the inside the long arm of the V. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1013 |
 |
Ectodermal dysplasia | Ectodermal dysplasia on the vulvae. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1014 |
 |
Scabies mite | Scabies mite | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1015 |
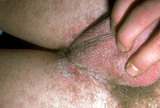 |
Pubic lice | The patient often experiences itching throughout the groin area, and there are often numerous nits in the pubic hair. The lice can range from about the knees up to the eyelashes. It is important to examine the body hair to ensure that all areas that are infested are treated adequately. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1016 |
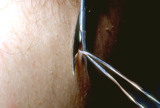 |
Skin tags | Skin tags can be snipped off with scissors. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1017 |
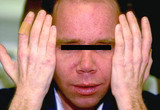 |
Phototoxic eruption in a patient using tetracycline | Phototoxic eruption in a patient using tetracycline. | Phototoxic | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology |
| 1018 |
 |
Oral antibiotic | If a patient has more than 15 red papules and pustules in association with the comedos, then usually an oral antibiotic is required in addition to the previously shown therapy (see Slide 37), and I generally use tetracycline, 500 mg tid, or minocycline, 100 mg bid as the oral antibiotic choice. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1019 |
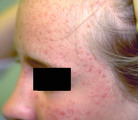 |
Moderate papulopustular acne | Same patient as shown in 64 with moderate papulopustular acne. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1020 |
 |
Ingrown nail | A broad band tourniquet is applied to the digit. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1021 |
 |
Excising with scalpel | A partial or full thickness cut is made, and the blade should be kept perpendicular to the skin or angled outward. | Surgical Methods | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology |
| 1022 |
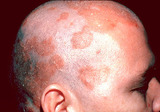 |
Seborrheic dermatitis | Seborrheic dermatitis involving the scalp; for whatever reason the patient shaved his scalp. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1023 |
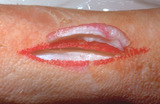 |
Specimen removal | The specimen of skin that is removed should be the same thickness throughout so that there is not an uneven appearance of the skin when the skin is closed with suture. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1024 |
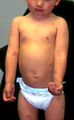 |
Chigger mite bites | This patient was thought to be infested with chiggers and had exaggerated insect bite reaction. | Chiggers | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology |
| 1025 |
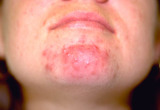 |
Papulopustular flare of acne vulgaris | Close-up of the papulopustular flare of acne vulgaris in this patient. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1026 |
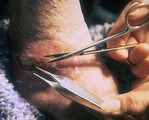 |
Necrotic tissue in ulcer | If an ulcer has any necrotic tissue, it then has to be removed. The necrotic tissue simply provides potential nutrition for the bacteria, and is of no benefit to the healing process. I found that ulcers on the malleoli are very sensitive and the slightest touching or movement induces significant pai... | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1027 |
 |
Trendelenburg position | In anaphylaxis the patient should be placed in the head down (Trendelenburg) position. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1028 |
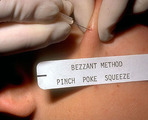 |
Opening acne lesions | This summarizes the Bezzant method of picking. My experience with trying to tell people not to pick is that it doesn't work. I, therefore, teach them this method of opening acne lesions as it seems to cause much less trauma and has less potential for scarring than picking with fingernails or with ho... | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1029 |
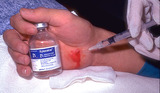 |
Puncture wounds | Puncture wounds, such as the one shown here in the hand should be anesthetized with lidocaine or lidocaine and bupivacaine without epinephrine. Epinephrine will further decrease oxygenation of the tissue and potentially facilitate the growth of anaerobic bacteria. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1030 |
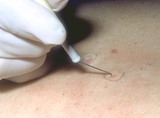 |
Hyfrecator: burning skin lesions | When using the hyfrecator one should ensure that it is plugged into low, and for small growths a setting of 30 (3 watts) is used, and on larger growths a setting of 50 (5 watts) is used. | Hyfrecator | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology |
| 1031 |
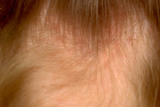 |
Head lice | Infestation with head lice at the nape of the neck produces redness and scaling of the skin, and the black/brown/gray nits (eggs) can be seen on the hair shafts, and occasionally the adult lice can be seen on the skin. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1032 |
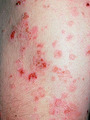 |
Pemphigus vulgaris on the trunk | Pemphigus vulgaris on the trunk. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1033 |
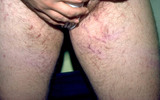 |
Striae formation in the groin | Striae formation in the groin secondary to the use of topical steroids. Striae formation, often calledfracturesof the skin, are currently considered irreversible. | Striae | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology |
| 1034 |
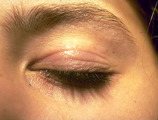 |
Atopic dermatitis involving the eyelids | Atopic dermatitis involving the eyelids. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1035 |
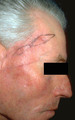 |
Basal cell carcinoma: excision removal | This gentleman had two basal cell carcinomas. | Surgical Methods | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology |
| 1036 |
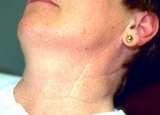 |
Radiation therapy for acne vulgaris | This patient had radiation therapy for her acne vulgaris, and has a scar demonstrating previous thyroidectomy for thyroid cancer presumably induced by the radiation, and has developed a basal cell carcinoma on her left cheek. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1037 |
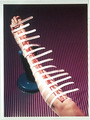 |
Leg measurement | This demonstrates measurement of the leg before custom support hose is made. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1038 |
 |
Nasal mask | Nasal mask, in a variety of sizes for adults and children. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1039 |
 |
Exaggerated insect bite reaction | Exaggerated insect bite reaction. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1040 |
 |
Lichen simplex chronicus | After repeated scratching, the epidermis thickens and darkens as shown here; this is called lichenification. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1041 |
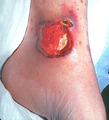 |
Occlusion of blood flow to the skin | Occlusion of blood flow to the skin, either from internal vessel damage or from external pressure, an ulcer can be created. | Skin blood supply | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology |
| 1042 |
 |
Mild inflammatory acne | When a patient has comedos and associated red papules and/or pustules, a topical antibacterial is required. | Anti-Bacterial Agents | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology |
| 1043 |
 |
Topical acne therapy | The first few weeks of topical acne therapy can be accompanied by redness and flaking of the skin. Lubricants will help to control scaling, and if necessary, one can add 1% hydrocortisone lotion or cream twice daily to help to reduce the inflammation. | Drug Effects | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology |
| 1044 |
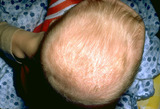 |
Atopic dermatitis in children | Atopic dermatitis in children often manifests ascradle cap. This is redness and scaling involving the scalp, and can be the lone manifestation of this problem. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1045 |
 |
Head lice | Infestation with head lice. Generally, there is dermatitis at the nape of the neck, and the itching tends to be accentuated there. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1046 |
 |
Halogenated steroids | Halogenated steroids, particularly fluorinated steroids, applied to the facial skin for over several weeks will often induce a dermatitis around the mouth, nose, and lower eyelids; this is called periorificial dermatitis. This inflammation usually, but not always, resolves spontaneously within seve... | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1047 |
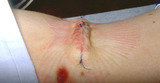 |
Eversion of a wound | This demonstrates eversion of the wound on the trunk created by a deep dermal suture. Often 3-0 absorbable suture has to be used on the trunk so that the suture does not break when it is being tied. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1048 |
 |
Body louse | This is a body louse on the clothing of the same patient shown in 81. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1049 |
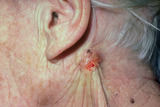 |
Basal cell carcinoma | Basal cell carcinoma. This patient had spent her younger years in Chihuahua, Mexico, and had been exposed to a lot of sunlight as a young person. This basal cell carcinoma originated within the epidermis and extended through the skin fat, and attached to the underlying muscle. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1050 |
 |
Stasis dermatitis | If the patient has acute stasis dermatitis, then an Unna boot can be applied. This consists of a roll of gauze that is saturated with zinc oxide ointment, and an elastic wrap that is applied on top of it. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1051 |
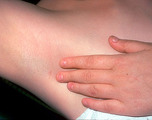 |
Ectodermal dysplasia | Ectodermal dysplasia in the axillae. The patient also had abnormal nail plates and teeth. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1052 |
 |
Undermining with scissors | This demonstrates undermining with scissors. The closed jaws are inserted beneath the dermis, and | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1053 |
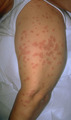 |
Thickness biopsy | When a patient has an eruption and the diagnosis is unknown, it is best to do a full thickness biopsy by doing a punch or small excision of one of the lesions. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1054 |
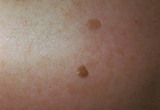 |
Seborrheic keratoses | Seborrheic keratoses. They are a benign thickening and darkening of the epidermis with varying amounts of loose adherent scale. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1055 |
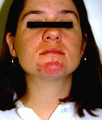 |
Papulopustular eruption | Close-up view of the papulopustular eruption on this pregnant patient. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1056 |
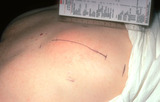 |
Layered closure | Large lesions can be removed using the layered closure. This was a large lipoma on the back of a patient, and I removed this in my office. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1057 |
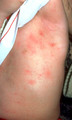 |
Children with scabies | Children who have scabies generally have inflammatory lesions in the axillae. This shows typical axillary lesions. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1058 |
 |
Pregnant patient with papulopustular flare of acne vulgaris | Pregnant patient with papulopustular flare of acne vulgaris. To our knowledge, oral erythromycin or ampicillin or amoxicillin can be used safely, and topical erythromycin, clindamycin, or benzoyl peroxide also appear to be safe. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1059 |
 |
Skin Tumor | Tumors of various sorts can be produced by anything that grows within the dermis.This demonstrates that the tumor was within the skin, and moves freely with the skin. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1060 |
 |
Treatment of comedonal acne | When a patient has comedos along with less than about 15 red papules and pustules, one can use the regimen shown either on the patient's left or the patient's right. The method I usually use is shown on the patient's right: The patient is to apply benzoyl peroxide 2.5% gel to the face q am, and Reti... | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1061 |
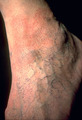 |
Venous pressure | With increased venous pressure induced by incompetent valves within the venous system of the leg, there is extravasation of fluid from the capillaries into the surrounding tissue. This separates the capillaries from the cells to which they supply nutrition, and those cells are damaged or even die. T... | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1062 |
 |
Ingrown nail | Appearance of ingrown nail. The nail plate is dystrophic, and in this case has induced significant foreign body reaction and secondary infection. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1063 |
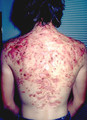 |
Severe nodulocystic acne | This is the back of the same patient shown in Slide 16, and the nodules, cysts, and scarring are evident. This is both painful and disfiguring, and can have a profound detrimental psychological effect on the person who suffers this. Thankfully, we do have effective therapy now for it. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1064 |
 |
Children with scabies | Child with scabies showing pruritic red papules around the ankle. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1065 |
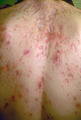 |
Severe acne vulgaris | Severe acne vulgaris involving the back. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1066 |
 |
Exaggerated insect bite reaction | Exaggerated insect bite reaction. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1067 |
 |
Excision: suturing | The second throw is initiated by placing the needle holder on the inside the long arm (needle bearing end) of the V. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1068 |
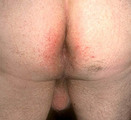 |
Atopic dermatitis involving the perianal area | Atopic dermatitis involving the perianal area. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1069 |
 |
Freezing with liquid nitrogen | Freezing is done to mainly destroy epidermal growths. As long as the indicated freezing times are followed, generally there is no scarring. Occasionally the dermis is injured as shown here, and hypertrophic or keloid scars can be formed, especially on areas of tension, such as the elbow. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1070 |
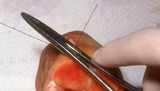 |
Excision: knot tying | The needle holder is placed on the inside the long arm (needle bearing end) of the V as shown. Before beginning to tie the knot, insure that the two ends of the suture come out the same side of the loop, and that the order is: loop, short (non-needle bearing) end, long (needle bearing) end. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1071 |
 |
Recessive epidermolysis bullosa | This child has recessive epidermolysis bullosa. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1072 |
 |
Treatment for rosacea | Typical treatment for rosacea is to take 500 mg of tetracycline in the morning, and . . . | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1073 |
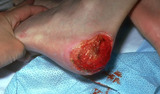 |
Normal fat at the base of a debrided wound of the heel | This shows normal fat, but note is bleeding freely. I found when debriding a wound it is best to give an oral or injected analgesic before debridement, and when the patient is quite relaxed I then infuse the area to be debrided with a mixture of lidocaine and bupivacaine with epinephrine. | Surgical Methods | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology |
| 1074 |
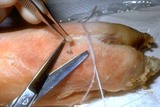 |
Punch biopsy | The plug should be gently lifted with forceps, and the fatty strand at the base should be snipped. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1075 |
 |
Stasis dermatitis | The area should be first cleansed with sterile saline or soap and water. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1076 |
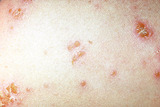 |
Nummular dermatitis | Lesions of acute (red and oozing) nummular dermatitis on the trunk. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1077 |
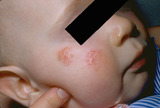 |
Atopic dermatitis in children | Atopic dermatitis often involves the cheeks of children. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1078 |
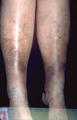 |
Incompetent venous system of the legs | The next step in damage to the skin from an incompetent venous system of the legs is lipo dermatosclerosis. In this condition, there is an increased amount of fibrous tissue both within the dermis and the underlying fat. The extremities appear tense and shiny, and they feel woody and hard to the tou... | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1079 |
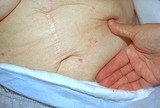 |
Scabies with inflamed lesions in a paraumbilical distribution | Same nursing home patient with scabies with inflamed lesions in a paraumbilical distribution. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1080 |
 |
Milium extraction | The appearance after extraction of the milium. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1081 |
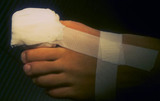 |
Ingrown nail | After cleaning the blood from the toe with hydrogen peroxide and removing the tourniquet, I apply a bulky dressing to absorb the blood, as it may bleed for up to about an hour if the foot is dependent. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1082 |
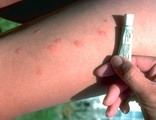 |
Insect Bites | Itchy insect bites can be treated with a topical steroid; I prefer to use an ultra-potent topical steroid, such as Temovate, twice daily to the inflamed lesions. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1083 |
 |
Undermining with scalpel | This demonstrates undermining of the dermis using a scalpel. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1084 |
 |
Scabies with flexural wrist involvement | Same patient with flexural wrist involvement. In this scenario, not only should the patient be treated, but all family members who have had skin-to-skin contact with the patient, as well as nursing personnel and housekeeping personnel who have had contact with the patient. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1085 |
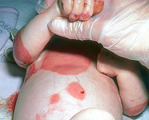 |
Recessive epidermolysis bullosa | A baby with recessive epidermolysis bullosa. This patient links adequate numbers of anchoring fibrils (collagen type 7) to attach epidermis to the underlying dermis. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1086 |
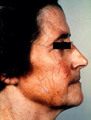 |
Atrophy of facial skin | Atrophy of facial skin induced by overuse of topical steroids to facial skin. The vessels of the deeper dermis and fat can be seen through the thin epidermis/dermis. Upon cessation of use of the steroids, the skin should regain its normal thickness, but it takes months to years for that to occur in ... | Adverse Effects | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology |
| 1087 |
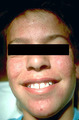 |
Acne surgery | The person appears blotchy immediately after acne surgery, and it takes one to two days for that to resolve. I always ask the patient about upcoming social events or photo sessions over the next several days before initiating acne surgery. | Surgical Methods | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology |
| 1088 |
 |
Atopic dermatitis involving the neck | Atopic dermatitis involving the neck. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1089 |
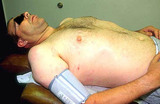 |
Anaphylactic shock | During anaphylactic shock, blood pressure should be monitored regularly. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1090 |
 |
Acute stasis dermatitis | Acute stasis dermatitis, manifested as redness and oozing. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1091 |
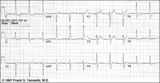 |
LVH - best seen in the frontal plane leads! | LVH - best seen in the frontal plane leads! | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 1092 |
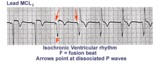 |
Isochronic ventricular rhythm | An isochronic ventricular rhythm is also called an accelerated ventricular rhythm because it represents an active ventricular focus. This arrhythmia is a common reperfusion arrhythmia in acute MI patients. It often begins and ends with fusion beats and there is AV dissociation. Treatment is usuall... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 1093 |
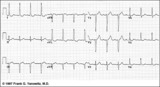 |
LVH: limb lead criteria | In this example of LVH, the precordial leads don't meet the usual voltage criteria or exhibit significant ST segment abnormalities. The frontal plane leads, however, show voltage criteria for LVH and significant ST segment depression in leads with tall R waves. The voltage criteria include 1) R in... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 1094 |
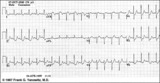 |
ST segment depression | ST segment depression is a nonspecific abnormality that must be evaluated in the clinical context in which it occurs. In a patient with angina pectoris ST depression usually means subendocardial ischemia and, unlike ST elevation, is not localizing to a particular coronary artery lesion. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 1095 |
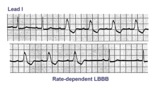 |
Rate-dependent LBBB | In this rhythm strip of sinus arrhythmia, the faster rates have a LBBB morphology. In some patients with a diseased left bundle branch, the onset of LBBB usually occurs initially as a rate-dependent block; i.e., the left bundle fails to conduct at the faster rate because of prolonged refractoriness... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 1096 |
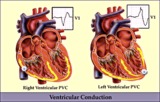 |
RV vs LV PVC's - marquette | RV vs LV PVC's - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 1097 |
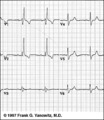 |
RBBB: Precordial leads | RBBB: Precordial leads | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 1098 |
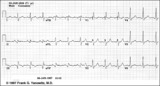 |
Inferior MI and RBBB | Inferior MI and RBBB | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 1099 |
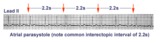 |
Atrial parasystole | Parasystolic rhythms involve an independent ectopic pacemaker resulting in nonfixed coupled premature beats. Parasystole may occur in the atria, as seen in this example, in the AV junction, and in the ventricles. Note the common inter-ectopic interval separating the parasystolic PAC's. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 1100 |
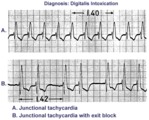 |
Digitalis intoxication: junctional tachycardia with and without exit block | In A the rhythm is junctional tachycardia with RBBB. In B there is 2nd degree exit block with a 3:2 conduction ratio; i.e., every 3rd junctional impulse fails to reach the ventricles... at least for the first two groupings on 1.4sec. | Knowledge Weavers ECG |
