The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
TO
Filters: Collection: "ehsl_heal"
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 251 |
 |
Shave biopsy | If the skin eruption is vesicular, the shave or punch biopsy should be done of apparently normal skin that is next to the edge of the blister. The 4 mm diameter specimen can be cut in half, and half submitted for standard stains, and half submitted for immunofluorescent staining. | Shave Biopsy | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology |
| 252 |
 |
Shave biopsy | Diagnosis of basal or squamous cell carcinoma can be achieved usually by using a shave biopsy. The double-edged blade is held between the thumb and third finger to ensure stability. | Shave Biopsy | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology |
| 253 |
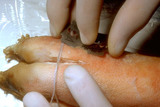 |
Shave technique | This demonstrates a shave technique on a pig's foot. Because there are no protruding lesions, I start by angling the blade at about 45 degrees from the skin surface, and while advancing the blade forward, I have a slight side to side sawing motion, and when I am about halfway through the target, I t... | Shave Biopsy | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology |
| 254 |
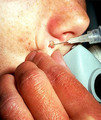 |
Shave technique | This demonstrates the shave technique. Local anesthetic can be injected into the fat beneath the target lesion, or within the lesion itself. One should be extremely careful to inject as little anesthetic as necessary to anesthetize the skin, because the anesthetic will artifactually enlarge and dist... | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 255 |
 |
Shave technique | The blade is held between the thumb and third finger using the index finger for curvature. Of course, gloves should always be used. The lesion should be shaved flush with the surrounding skin. | Shave Biopsy | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology |
| 256 |
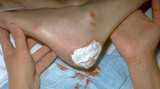 |
Silvadene | I placed Silvadene on the wound. Silvadene is an excellent antibacterial cream to apply to a wound after debridement. One must insure that an 1/8 inch to 1/4 inch coat is applied to help insure that the dressing doesn't absorb all the cream and allow the wound to subsequently dry out. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 257 |
 |
Skin tags | Skin tags. They are rather small, and have a pedunculated base giving them the appearance of a teardrop. | Skin Tags | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology |
| 258 |
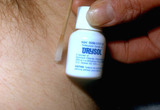 |
Skin tags | This shows Drysol being applied to the site of the skin tag removal to staunch bleeding. The Drysol hurts more than the snipping in my estimation. | Skin Tags | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology |
| 259 |
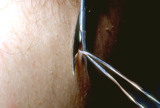 |
Skin tags | Skin tags can be snipped off with scissors. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 260 |
 |
Skin Tumor | Tumors of various sorts can be produced by anything that grows within the dermis.This demonstrates that the tumor was within the skin, and moves freely with the skin. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 261 |
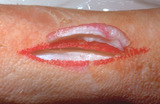 |
Specimen removal | The specimen of skin that is removed should be the same thickness throughout so that there is not an uneven appearance of the skin when the skin is closed with suture. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 262 |
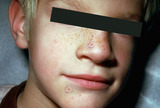 |
Spider telangiectasia | The red lesion on the nose is a spider telangiectasia. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 263 |
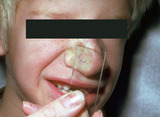 |
Spider telangiectasia | A spider telangiectasia is compressible and blanchable with adequate pressure. Generally, as the pressure is released the central feeding vessel can be seen and often pulsates. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 264 |
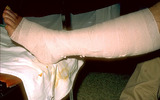 |
Stasis dermatitis | The area should then be wrapped with the gauze that is impregnated with zinc oxide ointment. The wrap should be started just above the toes, and continue to just below the knee. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 265 |
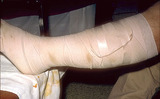 |
Stasis dermatitis | An elastic wrap is then applied on top of the gauze. The elastic wrap should be applied as tightly as the patient can stand around the foot and ankle, and the pressure is gradually reduced as the wrap is continued up to below the knee. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 266 |
 |
Stasis dermatitis | Stasis dermatitis (shown here) that is not oozing, is best treated with a support hose. The optimum ankle pressure is around 30 to 40 mm Hg, and generally a hose that comes to just below the knee is adequate. The hose should be worn at all times when the extremity is in the dependent position, such ... | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 267 |
 |
Stasis dermatitis | If the patient has acute stasis dermatitis, then an Unna boot can be applied. This consists of a roll of gauze that is saturated with zinc oxide ointment, and an elastic wrap that is applied on top of it. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 268 |
 |
Stasis dermatitis | The area should be first cleansed with sterile saline or soap and water. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 269 |
 |
Stratum corneum | The thick stratum corneum of the palms and soles prevents chemicals from readily entering those areas. This patient worked around a chemical to which he became allergic, and you can see the line of demarcation along the sides of his hands indicating the thinner stratum corneum on the dorsum of the h... | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 270 |
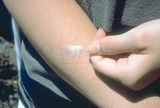 |
Stratum corneum | The stratum corneum, the barrier layer, is very thin, and can be removed with scotch tape and by applying scotch tape to the skin repeatedly for 15 or 20 times. Even though it is physically thin it is a very resilient and effective barrier layer. | Stratum Corneum | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology |
| 271 |
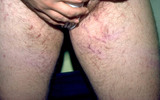 |
Striae formation in the groin | Striae formation in the groin secondary to the use of topical steroids. Striae formation, often calledfracturesof the skin, are currently considered irreversible. | Striae | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology |
| 272 |
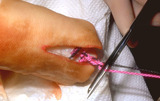 |
Suturing | After placing four throws to create a square knot, the suture is then cut just above the knot. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 273 |
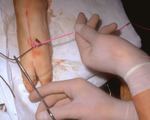 |
Suturing | The suture is then tightened by crossing the non-dominant (left) hand over the dominant (right) hand. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 274 |
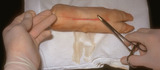 |
Suturing | This demonstrates tightening of the double loop along the long axis of the wound using suture. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 275 |
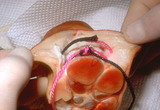 |
Suturing | This demonstrates the deep dermal suture properly placed with the loop, which will be just on the under-surface of the dermis, and the knot will be buried well within the fat. This will prevent the knot from extruding through the dermis and out through the wound. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology |
