The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
TO
Filters: Collection: "ehsl_heal"
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1801 |
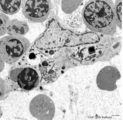 |
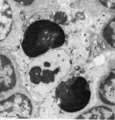
Erythroblastic island (bone marrow, rabbit) | Electron microscopy. In the bone marrow close associations of developing red blood cells with reticular cells are required during erythropoiesis. Different stages of erythroblasts (2, 3) are exposed in close vicinity of a reticular cell (1). (4) Reticulocyte. The centrally localized phagocytic retic... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1802 |
 |
Basophilic granulocyte (peripheral blood, human) | Electron microscopy. The detail shows close to the nucleus characteristic developing basophilic granules (specific granules) (8-13 μm). At thin arrow (↓) a small Golgi area with a small specific granule. At (***) granules with different osmiophilic internal structures. The basophilic granules var... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1803 |
 |
Eosinophilic granulocyte | Scheme electron microscopy. A 11-15 m cell with a bilobed nucleus (1) moderate amount of organelles, mitochondria (2), Golgi area (3), many vesicles (5) and numerous specific eosinophilic granules (4). These granules contain a central electron-dense angular crystalloid core embedded in a finely gran... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1804 |
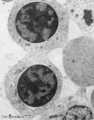 |
Polychromatic erythroblasts (bone marrow, rabbit) | Electron microscopy. Shown are two polychromatic erythroblasts or intermediate normoblasts between other erythroblasts and reticulocytes (2). Few mitochondria and polysomes are present but there is a decrease in amount of all organelles and nuclear clumping starts to take place. During this maturing... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1805 |
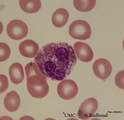 |
Eosinophilic granulocyte in peripheral blood smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The eosinophilic granulocyte usually has two to three nuclear lobes. The brown-orange granules are large, solitary and contain pharmacologically active mediators. The cell surface is occupied with IgE receptors. | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1806 |
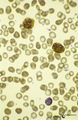 |
Peroxidase staining of granulocytes in peripheral blood smear (human) | Stain: peroxydase staining with DAB (diaminobenzidin). Blood smear showing two strongly positively stained granulocytes and one negative lymphocyte. The (myelo-) peroxidase activity is localized in the granules. | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1807 |
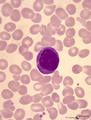 |
Plasmablast in peripheral blood smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The oval shaped cell with a slightly excentric nucleus and coarsely clumped chromatin has a basophilic blue cytoplasm in which the Golgi area usually remains unstained (white area). | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 1808 |
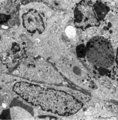 |
Dendritic cells in spleen (rat) | Electron microscopy. The interdigitating dendritic cells (1) (so-called antigen-presenting cell, APC) exhibit numerous slender cell projections (1). (2) shows a macrophage with large lysosomes with heterogeneous contents. Small elongated fibroblastic reticular cells (3) form a structural framework ... | electron microscopy; dendritic cell | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1809 |
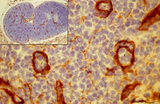 |
Immunohistochemistry of laminin in cortex lymph node (rat) | Anti-laminin-antibody and immunoperoxidase staining with diaminobenzidin (DAB) and hematoxylin counterstained on frozen section. Using an antibody against laminin brown-stained basement membranes (BM) are outlined demonstrating postcapillary venules (1) in the paracortical areas, as well as larger b... | paracortex; high endothelial venule (HEV); laminin; immunohistochemistry | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1810 |
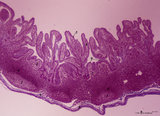 |
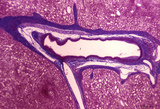
Ileum with Peyer's patches ('gut-associated lymphatic tissue' or GALT) (human) | Stain: Azan. Survey ileum (see also Digestive System: Ileum) A large amount of non-encapsulated diffuse lymphatic tissue or mucosa-associated lymphatic tissue (MALT) is located in the subepithelial lamina propria/submucosa of the ileum and called 'gut-associated lymphatic tissue' (GALT). These so-c... | follicle; lymph node; germinal center | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1811 |
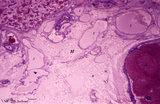 |
Hilum side of lymph node (human) | Stain: Azan. Site of the hilum of a lymph node includes part of the medulla and medullary cords (1) and medullar sinuses (2). In the hilum (H) dilated efferent lymphatic vessels (3) and draining veins (4) and entering arteries (5) are present. (6) represents adipose tissue embedding the efferent ves... | hilum; lymphatic vessels; medullary cords; paracortex | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1812 |
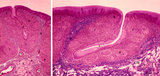 |
Lingual tonsil ('lymphoepithelial tissue', 'gut-associated lymphatic tissue' or GALT) (human) | Stain: Azan. A: Survey; B: detail of the crypt. The lingual tonsil consists of accumulations of bulging lingual lymphatic follicles in the dorsal part of the tongue behind the terminal sulcus, and belongs to the so-called Waldeyer's ring of pharyngeal lymphatic tissue. The left (A) and right (B) ... | lingual tonsil; GALT; Non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium; crypt | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1813 |
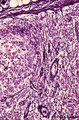 |
Lymph node (human) | Stain: Silver stain (Gomori). Due to the argyrophilia of reticular fibres the reticular network is black-stained among others such as collagen type I, III, IV. From the fibrous capsule (1) a meshwork of fine reticular fibres penetrates into the cortex of a lymph node crossing the subcapsular (or m... | germinal center; argyrophilia; reticular fibers | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1814 |
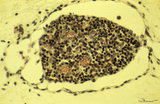 |
Lymph node (fetus, human) | Stain: Trichrome (Goldner). Along the course of lymphatic vessels lymph nodes develop. Lymphatic vessels dilate and form lymphatic sacs and lymphocytes aggregate around these sacs. A tiny developing lymph node with dense-stained thymocyte nuclei is closely associated with dilated lymph capillaries. ... | fetal lymph node; development | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1815 |
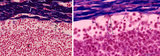 |
Lymph node (human) | Stain: Azan. Left: subcapsular (or marginal) sinus in lymph node. Right: higher magnification. Both pictures show a thick capsule (1), at (2) subcapsular (or marginal) sinus filled with lymphocytes indicate (lining) littoral cells (?). Reticular cells (3) are localized perpendicularly through sin... | subcapsular sinus; reticular cell | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1816 |
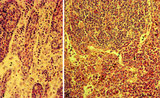 |
Lymph nodes (rat) | Stain: Hematoxylin & pyronin. Pyronin was formerly used to demonstrate young blast cell types rich in polysomes and packed rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) resulting in a reddish stain of the cytoplasm. A: Part of the medulla with medullary cords (1) and medullary sinuses (2) close to the hilum o... | infection; medullar cord; plasma cells ; macrophages | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1817 |
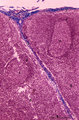 |
Lymph node (human) | Stain: Azan. Part of the cortex of a lymph node with the capsule (1) and subcapsular (or marginal) sinus (2) filled with lymphocytes. From the blue-stained dense capsule a long trabecula (3) flanked by paratrabecular (intermediate) sinuses penetrates between the paracortical areas (6). Paratrabecula... | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset | |
| 1818 |
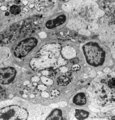 |
Lymph node (rat) | Electron microscopy. In the paracortical area (inner cortex) of a lymph node interdigitating cells (1) are found (so-called IDC, antigen-presenting cell or APC). They show branched extensions (3) in between the closely apposed surrounding T lymphocytes (2). In the cytoplasm of the IDC lysosomal inc... | electron microscopy; interdigitating cell; antigen-presenting cell | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1819 |
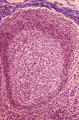 |
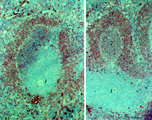
Lymph node (human) | Stain: Azan. Part of the cortex of a lymph node with the capsule (1) and subcapsular (or marginal) sinus (2) filled with lymphocytes. Below the subcapsular sinus a darkly stained rim or corona (3) of small lymphocytes (B cells) surrounds the lucid stained germinal centre (4). The white spaces repre... | follicle; germinal center | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1820 |
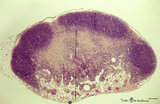 |
Lymph node (mouse) | Stain: Hematoxylin & eosin. For comparison with the human lymph node a survey of a small rodent lymph node is demonstrated. Basically the same divisions are found: (1) a cortex (outer cortex zone, nodular cortex or superficial cortex) covered with a (2) thin capsule and subcapsular sinus; a paracor... | follicle; hilum; medulla; cortex | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1821 |
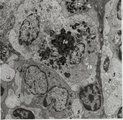 |
Lymph node (rat) | Electron microscopy. Within the reticular framework of lymph nodes a variety of active reticular cells are present, some of them (1) have phagocytised foreign material (1a) and contain numerous lysosomal structures (1a) and large Golgi areas (1b)). Others are less active (2). (3) wandering interdig... | electron microscopy; interdigitating cell; antigen-presenting cell | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1822 |
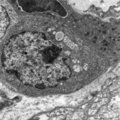 |
Lymphoblast in splenic cord of red pulp (rat) | Electron microscopy. A free circulating more matured lymphoblast with a conspicuous nucleus and nucleolus (1) still contains many polysomes (2), the swollen mitochondria (3) are obvious. A single fat droplet (4) and Golgi vesicles (5) are present. The cell is partly surrounded by reticular cell exte... | electron microscopy; lymphoblast | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1823 |
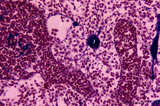 |
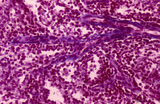
Medullary part of lymph node (human) | Stain: Azan. Part of the medulla with darkly stained medullary cords (1) and lightly stained medullary sinuses (2). The cords are stuffed with densely packed lymphocytes and reticular cells. Their blue-stained structures indicate massive bundles of reticular fibres. The sinuses are lined by flattene... | medulla; medullar cords; sinus | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1824 |
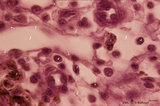 |
Medullary cords and sinus in lymph node (mouse) | Stain: Trichrome (Goldner). Detail of medullary sinus (1) flanked by part of medullar cords (2). The sinus space (1) is lined by flattened littoral cells (foamed cytoplasm) (?) and dispersedly filled with lymphocytes (4) and macrophages (brown hemo-pigment) (3). Within the medullary cords one finds ... | medullar cords; medullar sinus | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1825 |
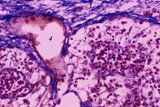 |
Medulla of lymph node (human) | Stain: Azan. Part of the medulla showing medullary cords (1) and medullary sinuses (2) close to the hilum and capsule (3). The medullary cords consist of a meshwork of reticular fibers and reticular cells (blue-stained). The cords (1) are more stuffed with lymphocytes and other blood cells. The sinu... | medullar cords; medullar sinus; hilum | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1826 |
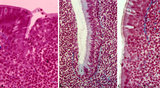 |
Pharyngeal tonsil ('gut-associated lymphatic tissue' or GALT) (human) | Stain: Azan. The combination demonstrates stages of infiltration (=diapedesis) of lymphocytes in the epithelium of the pharyngeal tonsil. The pharyngeal tonsil or adenoid is located in the nasopharyngeal roof. The agglomerations of lymphocytes (4) are covered by (1) pseudostratified ciliated epithel... | pharyngeal tonsil ; GALT; diapedesis; pseudostratified ciliated epithelium | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1827 |
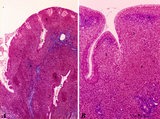 |
Pharyngeal tonsil ('lymphoepithelial tissues', 'gut-associated lymphatic tissue' or GALT) (human) | Stain Azan. The solitary pharyngeal tonsil is localized in the pharyngeal fornix and belongs to the so-called Waldeyer's ring of pharyngeal lymphatic tissue. A: The roof of the nasopharynx is covered by a columnar epithelium with faintly light-stained goblet cells (1) and part of a fold shows cle... | pharyngeal tonsil; GALT; pseudostratified columnar epithelium | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1828 |
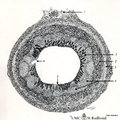 |
Scheme of appendix ('gut-associated lymphatic tissue' or GALT) (human) | Survey vermiform appendix (see also Digestive System: Appendix) A large amount of non-encapsulated diffuse lymphatic tissue or mucosa-associated lymphatic tissue (MALT) is located in the subepithelial lamina propria (e.g. respiratory passages, genitourinary tract). The gut-associated lymphatic tis... | GALT; follicle; scheme; germinal center | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1829 |
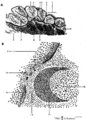 |
Scheme of lingual tonsil ('lymphoepithelial tissue') | Lingual tonsil (consisting of the accumulation of folliculi linguales). The root of the tongue contains invaginations or crypts or narrow caverns (3). In these crypts the ducts of the mucous glands (8) end up. The crypts are lined by multilayered, non-keratinizing squamous epithelium (2) and are sur... | lingual tonsil; scheme; germinal center; follicle | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1830 |
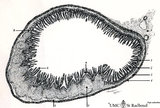 |
Scheme of ileum with Peyers patches (gut-associated lymphatic tissue or GALT) (dog) | Survey ileum (see also Digestive System: Ileum) A large amount of non-encapsulated diffuse lymphatic tissue or mucosa-associated lymphatic tissue (MALT) is located in the subepithelial lamina propria (e.g. respiratory passages, genitourinary tract). The gut-associated lymphatic tissues (GALT) are ... | GALT; follicle; scheme; germinal center | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1831 |
 |
Scheme of palatine and pharyngeal tonsils ('lymphoepithelial tissues') (human) | The palatine tonsils are covered by the multilayered, non-keratinizing squamous epithelium of the oral cavity (A-1). In contrast to the palatine and lingual tonsils, the epipharyngeal tonsil has a multilayered ciliated epithelium (respiratory-like epithelium, B-9). The Waldeyer's tonsillar ring i... | germinal center; scheme; follicle | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1832 |
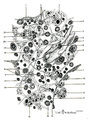 |
Scheme of reticular tissue in lymph node | Lymph node stroma does not contain stromal cells but instead the reticular meshwork is build by reticular cell types, macrophages and lymphoid cells and myeloid cells. Route (A) in the scheme represents morphological differentiation path from B lymphocytes to plasma cells. 1 endothelial ce... | reticular tissue; scheme; follicle; germinal center | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1833 |
 |
Section of lymph node (human) | Stain: Silver stain (Gomori). Due to the argyrophilia the reticular fibers are black-stained. They are derived from the fibrous capsule and penetrate into the deep cortex (i.e. paracortical area) and are embedded among other fibers such as collagen type III, IV. Note the postcapillary venules (*) ... | high endothelial venule (HEV); paracortex; argyrophilia; paracortex | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1834 |
 |
Survey and details of palatine tonsil ('lymphoepithelial tissues', 'gut-associated lymphatic tissue' or GALT) (human) | Stain: Azan. The survey in (A) shows that the palatine tonsil (localized in the lateral wall of the oropharynx) consists of crypts (1) and folds of the surface epithelium (stratified squamous) surrounded by accumulations of lymphoid cells organized in follicles (2). (B): the lining epithelium (5) i... | stratified squamous epithelium | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1835 |
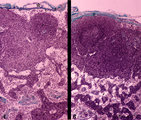 |
T cell depletion in lymph nodes (dog) | Stain: Trichrome (Goldner). Left and right: survey of lymph nodes. A: lymph node after treatment with anti-thymocyte-antiserum (ATS); B: normal, untreated lymph node ATS treatment results in a considerable depletion of the T cells in the paracortical area (2), while also the germinal centre (1) i... | T cell depletion; follicle; medulla; paracortex | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1836 |
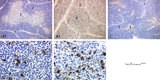 |
The effect of cyclophosphamide on the resident macrophages in thymus (rat) | Stain: Immunoperoxidase staining with diaminobenzidin (DAB) and hematoxylin counterstained on frozen section. A single injection with cyclophosphamide (CP, 70 mg/ml) induces a transient cortical involution after 4 days. The darkly stained cortex of th normal thymus (A1, A2) decreases its dark stain... | cyclophosphamide; ED1 macrophages ; immunosuppression; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1837 |
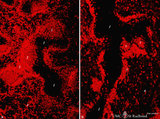 |
The effect of cyclophosphamide on B cells in spleen (rat) | Stain: Immunofluorescence of Vector red using Mark-1 antibody against B cells. A: Normal rat spleen. (1) the dark, unstained area represents the PALS (periarteriolar lymphatic sheath) filled with T cells. (2) red-stained germinal centre of a B cell follicle that is surrounded by the marginal zone (3... | cyclophosphamide; immunosuppression; immunofluorescence; B lymphocytes | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1838 |
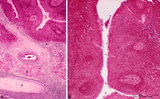 |
Tubal tonsil (human) | Stain: Azan. The tubal tonsil consists of a collection of lymphoid nodules near the auditory tube opening and forms part of the Waldeyers ring of defense in the nasopharyngeal cavity. This tonsil has fewer crypts (1), and the surface is covered by one to more layered ciliated epithelium (2). The la... | tubal tonsil; nasopharynx | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1839 |
 |
Lingual tonsil ('lymphoepithelial tissue', 'gut-associated lymphatic tissue' or GALT) (human) | Stain: Azan. A: Left side shows a secondary lymphatic follicle (1) separated by the connective tissue of the proper lamina (2) from the lining non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium (3). The mantle zone (4) is indicated by the peripheral dense aggregations of (memory) B lymphocytes. (5) diff... | lingual tonsil; GALT; non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1840 |
 |
Border of white pulp in spleen (mouse) | Monoaminooxidase (enzyme histochemistry on frozen section) with Nitro-BT as staining substrate resulting in a blue formazan precipitate. Despite the general activity of most cells in the spleen, the border cells or so-called metallophilic cells (1) or dendritic antigen-presenting cells (APC) show th... | monoamino oxidase; ED3 antibody; follicle; white pulp | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1841 |
 |
Colon ('gut-associated lymphatic tissue' or GALT) (human) | Stain: Hematoxylin-PAS. Solitary lymphatic nodule in colon (see also Digestive System: Colon) A large amount of non-encapsulated diffuse lymphatic tissue or mucosa-associated lymphatic tissue (MALT) is located in the subepithelial lamina propria of the colon and called gut-associated lymphatic tiss... | GALT; follicle; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1842 |
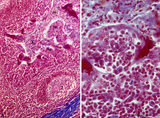 |
Palatine tonsil ('lymphoepithelial tissues', 'gut-associated lymphatic tissue' or GALT) (human) | Stain: Azan. A low magnification in A shows the thick blue connective septum (1) with a secondary lymphatic nodule (2). (3) is a cross-section of a crypt filled with detached squamous epithelium (3a) mixed up with keratinized material (red) and a huge amount of lymphocytes (3b). A higher magnificati... | follicle; germinal center; mantle layer; stratified squamous epithelium | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1843 |
 |
Hassall's corpuscle in thymus (human, puberty) | Stain: Hematoxylin. A larger magnification of the thymic medulla reveals the purple-stained structures in the centre of a so-called Hassall's (or thymic) corpuscle consisting of keratinized (*) epithelial cells. It is surrounded by recognizable flattened cells showing keratohyalin granules (-->). T... | thymic corpuscle (Hassalls); epithelioreticular cell (ERC); lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1844 |
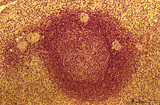 |
Spleen with secondary lymphatic nodule (human) | Stain: Hematoxylin & eosin. The splenic follicle as part of the white pulp is arranged around the cross sectioned central artery (1).The lymphatic sheath or PALS is composed of T cells (2). The darker stained mantle zone of mainly nave B lymphocytes (3) encompasses the lighter stained germinal centr... | white pulp; PALS; marginal zone; mantle layer | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1845 |
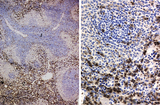 |
Immunohistochemistry of ED1-positive subset of macrophages in spleen (rat) | Stain: Immunoperoxidase staining using diaminobenzidin (DAB)/ hematoxylin counterstained on frozen section with the anti-macrophage antibody ED1. Most of the labeled (brown) macrophages are found in the red pulp (2) up to the marginal zone border (B). The PALS area (1) contains sparsely spread ED1 ... | ED1 ; macrophages; immunohistochemistry; marginal zone | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1846 |
 |
Spleen with secondary lymphatic nodule (human) | Stain: Azan. The white pulp of this perfused spleen consists of: at (1) a cross-section of the central artery, (2) tangential cut mantle zone and (3) the marginal zone. The red pulp contains empty venous sinusoids (4) and the perilymphoid zone (3a) is the zone of red pulp immediately surrounding ... | white pulp; germinal center; follicle; white pulp | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1847 |
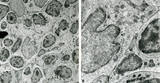 |
Part of lymphatic nodule in spleen (rat) | Electron microscopy. The left image (A) reveals part of a white pulp area stuffed with a dendritic cell (1) between a majority of different types of lymphocytes (2, 3). The right image shows a larger magnification of the same area with the dendritic cell (1) sandwiched in between the enclosing lymp... | dendritic cell; electron microscopy; white pulp | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1848 |
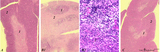 |
Thymus after cyclophosphamide treatment (rat) | Stain: Hematoxylin & eosin. A single injection with cyclophosphamide (CP, 4 70 mg/ml) induces a transient cortical involution, i.e. inhibition of the cell proliferation and maturation. A: Normal thymus with medulla (1) and cortex (2). B1: Inversion of thymic cortex and medulla 4 to 8 days after CP ... | cyclophosphamide; immunosuppression; involution; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1849 |
 |
Lymphoblast in splenic white pulp (rat, human) | Electron microscopy (A, rat) and Methyl green (B, human). Upon antigenic stimulation the lymphocytes in the germinal centre proliferate and generate activated B cells or lymphoblasts which seed towards marginal zone and red pulp while differentiating. Due to the increased number of lymphoblasts, ret... | electron microscopy; lymphoblast | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1850 |
 |
Phagocytosis in small splenic blood vessel (mouse) | Electron microscopy. Stain: Peroxidase reaction with diaminobenzidin staining. A diversity of red blood cells is black-stained due to the staining of hemoglobin by oxidized benzidin. Circulating lymphocytes (2) in the lumen (*) remain unstained. An oblong monocyte (1) developing into a macrophage h... | electron microscopy; phagocytosis | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1851 |
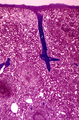 |
Survey of spleen (human) | Stain: Azan. The spleen is covered by a capsule (1) of dense connective tissue and elastic fibers. The capsule continues into the spleen as trabeculae (2) carrying blood vessels and nerve fibers. As arteries leave the trabeculae it becomes invested by a sheath of T cells forming a PALS (3) or periar... | white pulp; sinusoid; red pulp; PALS | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1852 |
 |
: Lymph node (human) | Stain: Azan. Specialized venules (1) or so-called high endothelial venules (HEV) are here located in the paracortical area (4) close to the lymphatic follicle (2+3). The HEVs are lined by cuboidal or columnar endothelial cells that possess specific homing receptors for antigen-primed B- and T ly... | paracortex; high endothelial venule (HEV); germinal center | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1853 |
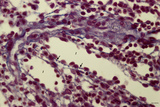 |
Red pulp of spleen with perfused venous sinusoids (human) | Stain: Azan. Cross-sectioned venous sinusoids with splenic cord (1). The wall of a sinusoid is composed of elongated rod-like endothelial cells that are orientated parallel to each other in the long axis of the sinusoid. There is a discontinuous pale-stained basement membrane (difficult to observe i... | sinusoid ; red pulp; splenic cord; central arteriole | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1854 |
 |
Venous circulation pattern in perfused spleen (human) | Stain: Azan. The composed picture shows part of the splenic circulation system at several enlargements (inset, A, B). The open venous sinusoids (1) drain via short pulp veins into thin-walled trabecular veins (2), subsequently into thick-walled trabecular veins (4). The trabeculae originate from the... | splenic circulation; trabecular veins; sinusoid ; PALS | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1855 |
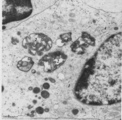 |
Thymus medulla (rat, young adult) | Electron microscopy. Epithelioreticular cells of the medulla (1) close to each other. The electron-light cytoplasm contains many small vesicles (1, Golgi area) as well as cross-sections of vacuoles (2) with small finger-like cytoplasmic extrusions in the lumen. Electron-dense lysosomal structures (3... | medullar epithelioreticular cell ; thymus medulla; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1856 |
 |
Thymus medulla (rat, young adult) | Electron microscopy. Surrounded by thymocytes (3) a medullary macrophage with an electron-light nucleus (1). The cytoplasm contains many electron-dense lysosomes of varying sizes and forms (2). | medullar macrophage; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1857 |
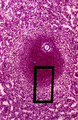
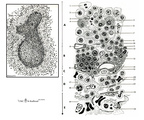 |
Scheme electron microscopy of the border of secondary nodule/red pulp in spleen | The left figure POJA-L974 shows a scheme of histological impression of a survey of a secondary splenic follicle or nodule. The rectangle is enlarged in the right figure POJA-L976B and shows the following elements: A. germinal centre; B. mantle zone; C. dendritic cell area; D. marginal zone; E. ... | white pulp; marginal zone; red pulp; antigen presenting cell (APC) | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1858 |
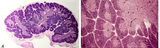 |
Thymus (human, newborn, low and higher magnification) | Stain: Hematoxylin & eosin. The infantile thymus is surrounded by connective tissue capsule (3) from where vascularized interlobular septa (or trabeculae, 3) penetrate into the lobulated organ. Each lobule consists of a darker stained cortex (2) and a lighter stained medulla (1). The medulla has a l... | Zhen; thymus cortex; thymus medulla; Hassall's corpuscle ; Lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1859 |
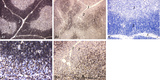 |
The effect of cyclophosphamide on the CD8-thymocytes in thymus (rat) | Stain: Immunoperoxidase staining with diaminobenzidin (DAB) and hematoxylin counterstained on frozen section. A single injection with cyclophosphamide (CP, 70 mg/ml) induces a transient cortical involution after 4 days, i.e. the darkly stained cortex and the lightly stained medulla in normal thymus ... | cyclophosphamide; CD8 monoclonal antibody; immunosuppression; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1860 |
 |
Detailed localization of heparan sulfate (HS) in spleen (rat) | Stain: Immunofluorescence of Alexa 594 red labeled single chain antibody 3C3 for heparan sulfate (HS). The antibody stains HS epitopes of the meshwork of reticulum cells and the basal membrane of blood vessels. A: survey white pulp spleen. B: marginal sinuses between PALS area and red pulp. C: red... | white pulp; PALS; heparan sulfate | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1861 |
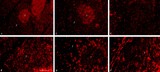 |
Immunohistochemistry with cellular markers in thymus (rat) | Stain: Alexa-594 red immunofluorescence. (1) medulla. (2) cortex. (A-survey, B-cortex): ER13 antibody stains for MHC-class II antigens on reticular cell types in medulla and cortex. (C): ED1 monoclonal antibody stains a single chain glycoprotein of 110 kDa on the lysosomal membrane of myeloid cel... | ER13 antibody; ED1 monoclonal antibody; ED2 monoclonal antibody; ER2 monoclonal antibody | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1862 |
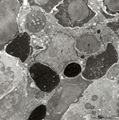 |
Phagocytosis in splenic red pulp (mouse) | Electron microscopy. Stain: Peroxidase reaction with diaminobenzidin staining. A diversity of red blood cells in the red pulp can be discerned due to the DAB staining of hemoglobin by oxidized benzidin (dark and light staining). The macrophage (1) shows peroxidase activity along the nuclear membran... | electron microscopy; phagocytosis | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1863 |
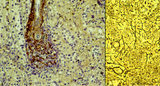 |
Red pulp of spleen with venous sinusoids (monkey, human) | Stain: A: Silver stain (Movat) (monkey); B: Silver stain (Gomori) (human). (A): The darkly stained fibres are conspicuous in the PALS (1) area arranged in parallel rows. The blood vessels continue in the surrounding splenic sinusoids (4). The wall of the sinusoid is built as a grid, the space is su... | sinusoid; reticular fibres | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1864 |
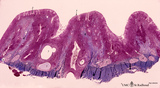 |
Survey of pharyngeal tonsil ('lymphoepithelial tissues', 'gut-associated lymphatic tissue' or GALT) (human) | Stain Azan. The solitary pharyngeal tonsil is localized in the pharyngeal fornix and belongs to the so-called Waldeyer's ring of pharyngeal lymphatic tissue. A survey shows the folded columnar epithelium (1) with faintly light-stained goblet cells with clefts (2) in between. The lamina propria co... | pharyngeal tonsil; GALT | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1865 |
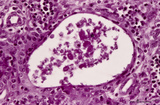 |
Cystic corpuscle in thymus (human, adult) | Stain: Azan. With age the remaining Hassall's corpuscles become more prominent and might represent large multiform structures of over hundreds of microns. The central cells (*) are keratinized. They might be swollen, calcify and become necrotic eventually, or undergo lysis, leaving a large cystic st... | thymic corpuscle (Hassalls); epithelioreticular cell (ERC); lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1866 |
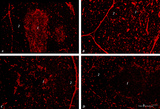 |
Immunohistochemistry of thymus (rat) | Stain: Alexa-594 red immunofluorescence. (1) Medulla. (2) Cortex. (A): Staining with a monoclonal antibody against vimentin illustrates that vimentin is localised in the stromal cells of the connective tissue of the capsule, of the septa or trabeculae that invade the cortex (2) and overwhelmingly ... | vimentin; laminin; fibronectin; ED2 monoclonal antibody | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1867 |
 |
Lymph node (human) | Stain: Azan. Left and right: survey of lymph nodes, compare the individual differences between the nodes. The pictures display the cortex (1) with capsule (3), and the medulla (2). The cortex consists of (secondary) follicles displaying a clear germinal centre (4). The paracortex (T cell area) is ... | follicle; paracortex; cortex; germinal center | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1868 |
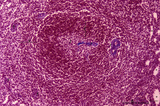 |
Spleen with central artery in secondary lymphatic nodule (human) | Stain: Azan. The white pulp consists of (1) a cross-section of the central artery, (2) the germinal centre with few branches of the central artery; the mantle zone (3) and the marginal zone (4) surrounded by a perilymphoid zone around the nodule. The perilymphoid zone is composed of concentricall... | germinal center; PALS; central artery; marginal zone | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1869 |
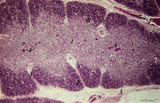 |
Thymus (human, newborn) | Stain: Hematoxylin & eosin. The thymus is a bilobed lymphoepithelial organ derived as an outgrowth from the third branchial (pharyngeal) pouch, and situated in the anterior mediastinum. Each lobe is divided into multiple lobules by fibrous septa or trabeculae (3). Each lobule consists of an outer co... | epithelioreticular cells (ERC); thymus hormones; Hassalls corpuscle ; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1870 |
 |
The effect of cyclophosphamide on CD3-thymocytes in thymus (rat) | Stain: Immunoperoxidase staining with diaminobenzidin (DAB) and hematoxylin counterstained on frozen section.. A single injection with cyclophosphamide (CP, 70 mg/ml) induces a transient cortical involution after 4 days, i.e. the dark-blue stained cortex and the lightly stained medulla in normal thy... | cyclophosphamide; CD3 monoclonal antibody; lymphoid tissue ; immunosuppression | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1871 |
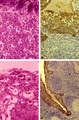 |
Follow-up of the process of diapedesis through stratified epithelium of the palatine tonsil (gut-associated lymphatic tissue or GALT) (human) | Stain: (A, C) Azan and (B, D) anti-keratin-antibody and immunoperoxidase staining using diaminobenzidin (DAB) on frozen section, counterstained with hematoxylin. (1) (keratinized) stratified squamous epithelial cells. (2) between desquamated epithelial cells the spaces are filled with infiltrated l... | stratified squamous epithelial cells; GALT | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1872 |
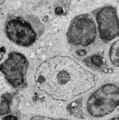 |
Thymus cortex (rat, young adult) | Electron microscopy. Within the thymic cortex a type II epithelioreticular cell or so-called (sometimes multinucleated) thymic nurse cell (TNC) shows a characteristic electron-light nucleus and nucleolus (1). The branches are squeezed between the thymocytes (2). In the cytoplasm a variety of empty a... | MHC class I and II expression; epithelioreticular cell type I and II; thymic nurse cell TNC; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1873 |
 |
Corpuscles in thymus (human, puberty) | Stain: Hematoxylin. A: Several thymic (Hassall's) corpuscles (*) of varying sizes within the medulla (1). The Hassall bodies are surrounded by recognizable flattened cells showing keratohyalin granules. The outer shell consists of more layers of close packed concentrically arranged cells with light-... | thymic corpuscle (Hassalls); epithelioreticular cell (ERC); thymus medulla; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1874 |
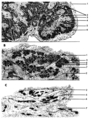 |
Scheme of the thymus during ageing (human) | Physiological changes in the course of human ageing lead to almost complete degeneration of the thymus (age involution). Both cortex and medulla become depleted of lymphocytes, and the distinction between both layers gradually becomes less. The remaining reticular meshwork of connective tissue is gr... | thymus involution; thymus development; thymus age; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1875 |
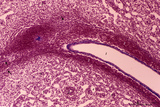 |
Spleen with central artery in lymphatic nodule (human) | Stain: Azan. A longitudinally cut central artery (1) of a lymphatic nodule or follicle, (white pulp) is invested by a distinct lymphatic sheath (PALS) composed of concentric layered T lymphocytes) (2). The red pulp consists of open venous sinusoids (4) and splenic cords (5, Billroth) with macrophage... | central artery; PALS; sinusoid ; Billroth | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1876 |
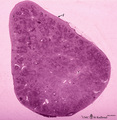 |
Survey of spleen (human) | Stain: Trichrome (Goldner). Encapsulated by a relatively thin fibroelastic capsule (1), the splenic parenchyma shows a preferable peripheral location of the red pulp (3). There are many secondary lymphatic nodules (2) as part of the white pulp, all showing a clear germinal centre. The red pulp is a ... | white pulp; red pulp | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1877 |
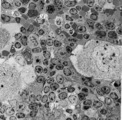 |
Survey of the border of splenic white and red pulp (rat) | Electron microscopy. Megakaryocytes (1) are commonly found in adult spleen of rodents. In this area they are located just at the border of the white pulp (WP) with a variety of lymphocytes (3). In the splenic cords (Billroth) of the red pulp (RP) erythrocytes (2) are found. | electron microscopy; white pulp; Billroth | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1878 |
 |
Scheme of blood circulation in the red pulp in the spleen | A. closed circulation B. open circulation A. The route of closed circulation proposes that blood empties from the capillaries directly into the splenic sinus. The central artery bifurcates into penicillar arterioles (1) and the blood slowly enters ensheathed capillaries, surrounded by agg... | white pulp; marginal zone; red pulp; open circulation | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1879 |
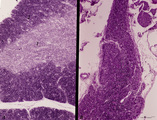 |
Accidental involution of thymus (mouse, malaria infection) | Stain: Hematoxylin & eosin. Due to the infection with malarial parasites (Plasmodium berghei in mice) a steroid-related involution of the thymus is induced in mice within 14 days. A: normal thymus with cortex (2) and medulla (1). B: There is still a quite large remnant of the original thymus tissue ... | malaria infection; thymus involution; Plasmodium berghei; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1880 |
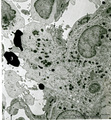 |
Border of a marginal zone in spleen (rat) | Stain: Immunoelectron microscopy (gold labeling of heparan sulfate in Lowicryl embedding, using the single chain antibody HS4C3). The zone of red pulp immediately surrounding a lymphatic nodule is called the marginal zone (perilymphoid zone) and is composed of a scaffold of basal lamina material w... | marginal zone; immuno electron microscopy; heparan sulfate; dendritic cell | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1881 |
 |
Scheme of the medullar changes in lymph node after antigen stimulation | Upon antigenic stimulation the reticular cells that line the medullar sinusoids start to phagocytise the antigens (i.e. infective agents) and change from small tiny stellate cells into swollen large cells due to phagocytosis. They detach from the medullar sinus wall. After ten days the situation has... | follicle; antigen stimulation; scheme; germinal center | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
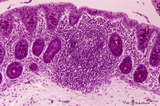
| 1882 |
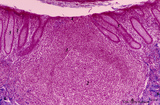 |
Appendix ('gut-associated lymphatic tissue' or GALT) (human) | A large nodule in the appendix extends through the proper lamina (1) and submucosa. The nodule is similar to that found in a lymph node with germinal centre (2) and darker-stained cap (crescent) (3) orientated towards the lumen of the gut showing a flattened dome area covered with discontinuous epit... | GALT; follicle; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1883 |
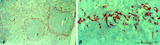 |
: Localization of ED3-positive subpopulation of macrophages in spleen (rat) | Stain: Immunohistochemistry of Vector red staining using the antibody ED3. The survey in (A) shows that the ED3-positive macrophages are found as a ring in the marginal zone border, as well as spread in the red pulp area (2). The cells are sometimes referred as marginal metallophilic macrophages. T... | metallophilic macrophages; ED3 antibody; marginal zone | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1884 |
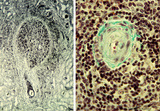 |
Spleen with central artery in lymphatic nodule (human) | Stain: A: Silver stain (Gomori). B: Trichrome (Goldner). In A: the reticular fibers (2) around the PALS (periarteriolar lymphatic sheath) and continuing in and around the marginal zone are stained black, illustrating the reticular framework of the lymphatic nodule. (1) central arteries. (4) red pulp... | central artery; PALS; white pulp; T cells | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1885 |
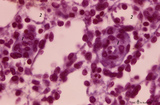 |
Macrophage-sheathed capillaries in spleen (human) | Azan. The branching of each penicillar arteriole gives rise to capillaries and a slow-down of the blood stream. In certain regions monocyte-derived macrophages leave the capillary and enter its wall where they develop into macrophages. Together with the present reticular cells these cell accumulatio... | macrophage-sheathed capillaries; penicillar arterioles; sinusoid | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1886 |
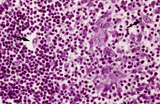 |
Medulla of thymus (human, puberty) | Stain: Hematoxylin. The light-stained medulla consists of a loosened framework of epithelial reticular cells, macrophages, thymocytes and capillaries. Accumulations of a specialized type of epithelial reticular cells (1) are localized between the thymocytes. These clusters represent precursors of fu... | thymic corpuscle (Hassalls); epithelioreticular cell (ERC); thymus medulla; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1887 |
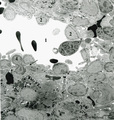 |
Splenic venous sinusoid in red pulp (rat) | Immunoelectron microscopy (gold labeling of heparan sulfate in Lowicryl embedding, using the single chain antibody HS4C3). (1) shows the open lumen of a venous sinusoid filled with few electron-dense erythrocytes and lining cells (2). (3) marks a neutrophilic granulocyte. (4) points to the diaped... | sinusoid; immuno electron microscopy; heparan sulfate | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1888 |
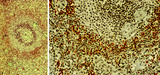 |
Secondary lymphatic nodule in the spleen (human) | Stain: Trichrome (Goldner). A: Survey of a follicle in the spleen. B: a higher magnification of a similar section shows part of a lymphatic nodule (follicle, white pulp) with cross-sections of the central artery (6). (1) germinal centre (filled with reticular cells, B-memory lymphocytes and macroph... | white pulp; PALS; germinal center; marginal zone | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1889 |
 |
Immunoperoxidase stained CD8 positive T cells in spleen (rat) | Stain: Immunoperoxidase staining using diaminobenzidin (DAB)/ hematoxylin counterstained on frozen section with anti-CD8 antibodies. A, B and C show brown-stained CD8-positive T cells or Tc cells at different enlargements. The CD8 Tc/s cells are localised predominantly in the PALS area (1), while th... | CD8 lymphocytes; immunohistochemistry; PALS | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1890 |
 |
Thymus (human, fetus) | Stain: Silver stain (Gomori). Reticular fibers are demonstrated in the interlobular septa in the thymic cortical area (2) of this lobule. In the medulla (1) the more loosened reticular framework is more distinct. The reticular fibers are produced by the epithelioreticular cells and are particular ... | thymic corpuscle (Hassalls); epithelioreticular cell (ERC); reticular fibers; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1891 |
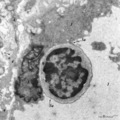 |
Thymus cortex (rat, young adult) | Electron microscopy. Type I epithelioreticular cells (4) separate connective tissue compartment (capsule, trabeculae, blood vessels) from the thymic parenchyma. At the left the capsule is bordered by a basal lamina (4a) of two projections (4) of type I epithelioreticular cells. Close to them, part o... | lymphoid tissue ; epithelioreticular cell type I; diapedesis | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1892 |
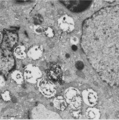 |
Thymus cortex (rat, young adult) | Electron microscopy. Two epithelioreticular cells type II or TEC2 (1) show the characteristic vacuoles (*) partly filled with granules (thymulin, lymphokines). At (--><--) small desmosomes. Apart from the mitochondria electron-dense lysosomal structures are present as well as tonofilaments (1, kera... | epithelioreticular cell II ; desmosome; MHC-II expression; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1893 |
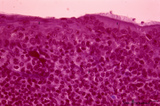 |
Detail of pharyngeal tonsils (human) | Stain: Azan. In contrast to the palatine and lingual tonsils, the epipharyngeal tonsil has a ciliated epithelium (1). Islands of multilayered squamous epithelium may interrupt it (transition zone, 2). The epithelium may be infiltrated with lymphocytes. The surface of this tonsil can be enlarged by m... | pharyngeal tonsil; GALT; squamous epithelium; ciliated epithelium | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1894 |
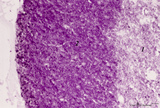 |
Thymus cortex (mouse, young adult) | Stain: Hematoxylin. Autoradiography after pulse labeling with tritiated thymidin. Most of the (black) radioactive labeling is found in the outer thymic cortex (3) where pre-T cells divide and subsequently migrate to the lighter stained medulla (1) that consists of a more loosened framework of epith... | thymus cortex; thymus medulla; thymidin labeling; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1895 |
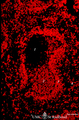 |
Localization of B cells in spleen (rat) | Stain: Immunofluorescence of Vector red using Mark-1 antibody against B cells. The T cells in the PALS (periarteriolar lymphatic sheath) remain unstained (1, dark). The red-stained B cells are packed in the germinal centre (2), the corona (3) or mantle layer that diffuses into the marginal zone and... | B lymphocytes; immunofluorescence; PALS | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1896 |
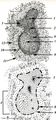 |
Scheme of secondary lymphatic nodule in spleen (human) | A. histological impression of a follicle or nodule B. outline of impression 1. pulpa artery; 2. central artery ; 3. lymphatic sheath; 4. lymphatic nodule; 5. thymus-dependent area (periarteriolar lymphatic sheath or PALS), composed of Th subset lymphocytes; 6. mantle zone with mainly nave B l... | white pulp; marginal zone; antigen presenting cell (APC) | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1897 |
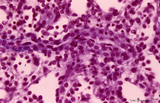 |
Splenic sheathed capillaries (human) | Stain: Azan. The blood flow in the spleen goes from splenic artery to trabecular artery to central or follicular artery (with a periarteriolar lymphatic sheath or PALS), and upon leaving the follicle the blood flows through penicillar arterioles and sheathed capillaries and terminal arterial capilla... | penicillar arterioles; red pulp; sheathed capillaries | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1898 |
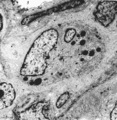 |
Thymus medulla (rat, neonate) | Electron microscopy. An interdigitating cell in the thymic corticomedullary region shows a large electron-light cytoplasm with a complex branching (7) at the periphery. The nucleus is sectioned twice (1). There is abundance of organelles as well as of quite uniform electron-dense lysosomal structure... | medullar epithelioreticular cell; interdigitating cell; corticomedullar region; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1899 |
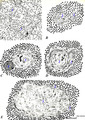 |
Scheme of the thymus medulla (human) | A-B: medullar epithelioreticular cells; C-D-E: development stages of thymic corpuscles (or Hassall bodies) (1): branching (-->) epithelioreticular cells in the medulla forming a meshwork (cytoreticulum) that normally is populated by thymocytes; (2): specialized epithelioreticular cells (2) often... | thymic corpuscle; Hassall ; epithelioreticular cells ; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1900 |
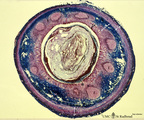 |
Appendix ('gut-associated lymphatic tissue' or GALT) (human) | Stain: Azan. Survey of vermiform appendix (see also Digestive System: Appendix) A large amount of non-encapsulated diffuse lymphatic tissue or mucosa-associated lymphatic tissue (MALT) is located in the subepithelial lamina propria/submucosa of the appendix and called gut-associated lymphatic tissue... | GALT; follicle; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1901 |
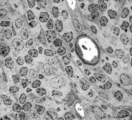 |
Survey of part of splenic lymphatic nodule (rat) | Electron microscopy. (1) shows an arteriolar branch of a central artery, and cross-sections of capillary branches (1a). Within the periarteriolar lymphatic sheath (PALS) mostly T lymphocytes (5) are present between concentric arranged reticular cells (2). Cells with larger lighter stained nuclei rep... | central artery ; electron microscopy; PALS; Antigen presenting cells (APC) | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1902 |
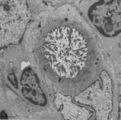 |
Cystic corpuscle in thymus (mouse, young adult) | Electron microscopy. This cystic corpuscle is lined by specialized epithelioreticular cells and exhibits a lumen (1) which is filled with long microvilli however, curiously derived from a flattened epithelial cell (2, nucleus). The cell contains few electron-dense keratohyalin granules (3). (-->) po... | epithelioreticular cells; thymic corpuscle; thymic cyst; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1903 |
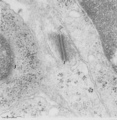 |
Thymus cortex (mouse, young adult) | Electron microscopy. (1) A well developed desmosome (1) of an epithelioreticular cells type II (TEC2). Apart from few free ribosomes, glycogen granules (2) are present in the electron-light cytoplasm. (3) part of an electron-grey thymocyte with many ribosomes. | epithelioreticular cell type II ; desmosome; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1904 |
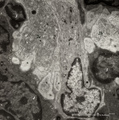 |
Dendritic cells in spleen (mouse) | Electron microscopy. The interdigitations (*) of the left dendritic cells (antigen-presenting cell or APC) (1 and 2a) are clearly shown. The right (2b) is a neighbour dendritic cell sectioned at the level of the Golgi area. (3) lymphocyte and (4) reticular cell. | electron microscopy; dendritic cell | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1905 |
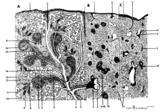 |
Scheme of the spleen (human) | Spleen: A. general diagram; B. adult; C. senium 1. capsule of dense irregular connective tissue with few elastic and smooth muscle fibers (it varies with the species); 2. trabecula (septum); 3. trabecular artery derived from the splenic artery; 4. trabecular vein; 5. when the pulpa artery ... | white pulp; red pulp | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1906 |
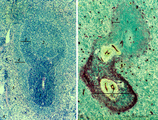 |
White pulp of spleen (mouse) | Stain: Hematoxylin & eosin in A and alkaline phosphatase in B (with substrate Naphtol Fast Blue RR). The general structure of the white pulp of the spleen and its specific microenvironment for T and B cells is well illustrated using alkaline phosphatase that strongly stains the capillaries around th... | alkaline phosphatase; PALS; T lymphocytes; white pulp | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1907 |
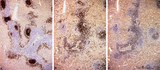 |
The effect of cyclophosphamide treatment on the B and T cells in spleen (rat) | Stain: Immunoperoxidase staining using diaminobenzidin (DAB)/ hematoxylin counterstained on frozen section with antibodies to B cells (Mark 1), CD3 and CD8 T cells. (A): B cells in the follicles, germinal centres (2) and corona are stained positive brown, while the PALS area (1) is negative (blue)... | CD3 lymphocytes; CD8 lymphocytes; B lymphocytes; cyclophosphamide | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1908 |
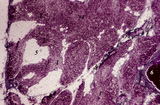 |
Age involution of thymus (human, postpuberal) | Stain: Azan. The size of the thymus is age-dependent, and undergoes a continuous process of involution, starting at postpuberal age. Due to depletion and reduced production of cortical thymocytes, as well as a gradual atrophy of the epithelial cells, the clear distinction between medulla (1) and cor... | thymus age; adipose cells; thymus involution; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1909 |
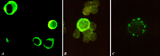 |
Immunohistochemical identification of splenic B cells (rat) | Stain: Immunofluorescence of FITC-labeled anti-Mark-1 antibody against rat B cells, carried out on spleen cells after fixation (A, B) or non-fixated spleen cells (C). (A) shows (young) plasma cells producing antibodies. (B) a green-stained B cell. The surrounding negative cells are likely T cells.... | immunofluorescence; B lymphocyte; capping | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1910 |
 |
Thymus cortex (mouse, young adult) | Electron microscopy. Surrounded by thymocytes (2) a cortical macrophage (starry-sky macrophage) is seen and shows an electron-light nucleus (N) and a distinct nucleolus. The cell has engulfed two apoptotic thymocytes (1). The cytoplasm also contains small electron-dense lysosomes and myelin figures ... | cortical macrophage; epithelioreticular cell type II ; apoptotic thymocyte; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1911 |
 |
Survey of splenic trabecular artery (human) | Stain: Azan. The splenic artery (or lienal artery) is the blood vessel that provides oxygenated blood to the spleen. Branches of the splenic artery divide into trabecular arteries (1) which enter the white pulp as central arteries (4) that is surrounded with lymphocytes (5,periarteriolar lymphatic s... | trabecular artery; PALS; sinusoid | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1912 |
 |
Immunohistochemistry of B cells in splenic white pulp (rat) | Stain: Immunohistochemistry of Vector red for Mark-1-antibody-stained B cells. (1) indicates the PALS area populated with unstained T cells located around the central artery of the white pulp. (2) indicates the positively red stained B cells in the germinal centre of the follicle. (3) the B-cells i... | marginal zone; immunohistochemistry; follicle | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1913 |
 |
Penicillar arterioles in spleen (human) | Stain: Azan. The central or follicular artery in the follicle of the spleen splits into many arterioles. These arterioles spread as so-called penicillar arterioles (1) shown here. They are still surrounded by a very thin perilymphatic sheath (PALS) that disappears as the arteries in a brush-like pat... | penicillar arterioles; red pulp | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1914 |
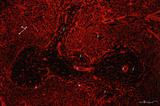 |
Localization of heparan sulfate (HS) in spleen (rat) | Stain: Immunofluorescence of Alexa 594 red labeled single chain antibody 3C3 for heparan sulfate (HS). The antibody stains HS epitopes of the meshwork of reticulum cells and the basal membrane of blood vessels. (1) central arteries in the T cell area of the PALS (2). The B cell area in the follic... | white pulp; heparan sulfate; PALS | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1915 |
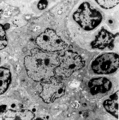 |
Thymic nurse cell (TNC) (mouse) | Electron microscopy. The thymic nurse cell (TNC) consists of an epithelial reticular cell (type II) enclosing thymocytes. The TNC exists as a sealed structure in situ, i.e. the lymphocytes within the TNC are isolated from the general thymic environment. TNC are located in the cortex, where mature ... | epithelioreticular cell type II; thymic nurse cell | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1916 |
 |
Scheme of lymph node (human) | Lymph node: A. survey; B. detail subcapsular (or marginal) sinus 1. adipose tissue; 2. capsule; 3. afferent lymph vessel with valves (B); 4. subcapsular (or marginal) sinus; 5. germinal centre of a secondary lymphatic nodule (or follicle); 6. crescent or mantle zone indicated by cap of per... | cortex; scheme; paracortex; germinal center | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1917 |
 |
Afferent lymph vessel in lymph node (human) | Stain: Azan. Left (A) and right (B): part of the cortex of a lymph node with the capsule (1) and subcapsular (or marginal) sinus (2) filled with lymphocytes. Left (A): (3) show perpendicularly localized reticular cells and fibres (blue) in the sinus. (4) indicate afferent lymph vessel with valves ... | lymph vessel; subcapsular sinus; follicle; cortex | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1918 |
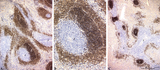 |
The effect of cyclophosphamide on splenic B cells (rat) | Stain: Immunoperoxidase staining using diaminobenzidin (DAB)/ hematoxylin counterstained on frozen section of B cells with the antibody Mark-1. The PALS area (1) contains T cells and remains unstained blue. The positively stained B cells (brown) are found in the germinal centres (2) and in the coron... | cyclophosphamide; immunosupression; B lymphocytes; Mark 1 antibody | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
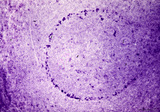
| 1919 |
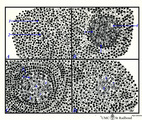 |
Scheme of development of germinal centre in lymphatic nodule (human) | A. primary nodule (or follicle) with mainly nave B lymphocytes and some memory cells, but no germinal centre; B. proliferation of lymphoblasts by mitosis (3,-->) and development of capillaries (*) in the centre of the follicle; C. so-called secondary nodule with lighter stained germinal centre wit... | follicle; antigen stimulation; scheme; germinal center | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1920 |
 |
Age involution of thymus (human) | Stain: Azan. A: Although the adipose tissue in the thymus of a patient of 65 years is predominant it still contains areas of remnants (arrows 1+2) of cortical (2) and medullary portions (1) of the thymus. B+C: Degradation of thymic tissues is less progressed in adults and shows less replacement of... | thymus age; thymus involution; adipose cells; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1921 |
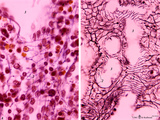 |
Splenic sinusoids (human) | Stain: A: Azan and B: Silver stain (Gomori). The splenic sinusoids are built in the form of a grid. The frame of the barrel consists of elongated endothelial cells (1) which are spirally wrapped around by reticular fibers (2). To this reticular fibers are attached many macrophages which control the... | sinusoid; reticular fibers | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1922 |
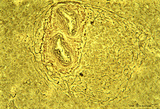 |
Circumscript reticular pattern of splenic lymphatic nodule (human) | Stain: Silver stain (Gomori). In this particular case the black-stained reticular network is beautiful organized in and around the nodule. Note also the reticulin staining between the myocytes in the wall of both cross-sectioned (1) central arteries. (2) follicle with lymphocytes. | sinusoid; reticular fibers; follicle | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1923 |
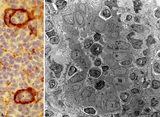 |
High endothelial venules (HEV) (rat lymph node, human palatine tonsil) | Stain: (A) Anti-laminin-antibody and immunoperoxidase staining using diaminobenzidin (DAB)/ hematoxylin counterstained on frozen section of lymph node; (B) electron microscopy (palatine tonsil). (A): Using an antibody against laminin brown-stained basement membranes are outlined demonstrating postc... | palatine tonsil; high endothelial venule (HEV); laminin; immunohistochemistry | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1924 |
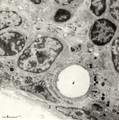 |
Thymus cortex (rat, young adult) | Electron microscopy. Type I epithelioreticular cells separate connective tissue compartment from the thymic parenchyma. With occludens junctions and desmosomes as barriers they form wide-mesh networks creating specific microenvironments for developing T cells. The extensions of type I cells (5) are... | thymus cortex; epithelioreticular cell type I; epithelioreticular cell type II; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1925 |
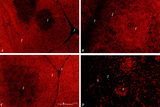 |
Immunohistochemistry with cellular markers in thymus (rat) | Stain: Alexa 594 red immunofluorescence. (1) medulla; (2) cortex; (3) septa. (A): Strong CD8 staining of the thymic cortical lymphocytes (single CD8+ and double positive CD4+CD8+ thymocytes). (B): OX19 staining for almost all T cells, equivalent to T1 human marker and Ly-1 mouse marker. Note that... | cyclophosphamide; CD8 monoclonal antibody; OX19 monoclonal antibody; ER1 monoclonal antibody | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1926 |
 |
Hassall's corpuscle in thymus (mouse) | Electron microscopy. The centre of a small Hassall's corpuscle consists of darker-stained cells (1) which are keratinizing and represent degenerating cytoplasmic remnants (2). (3) is an infiltrating monocyte and (*) indicate the presence of free keratohyalin granules from disintegrated epithelial ce... | thymic corpuscle (Hassalls); lymphoid tissue ; epithelioreticular cell (ERC) | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1927 |
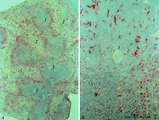 |
MHC-class II dendritic cells in spleen (rat) | Stain: Immunohistochemistry of Vector red staining of MHC-class II with ER13 antibody. The survey in (A) shows that MHC-class II expressing cells are conspicuously concentrated in dendritic cell types (B) in the transition zone between red pulp (2) and white pulp (1). These dendritic or antigen-pres... | MHC class II; dendritic cells; immunofluorescence | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1928 |
 |
Thymus medulla (rat, young adult) | Electron microscopy. Epithelioreticular cell of the medulla with an electron-light cytoplasm contains cross-sections of vacuoles with small finger-like cytoplasmic extrusions in the lumen (1). Electron-dense lysosomal structures (2) are also present as well as bundles of intermediate filaments (kera... | medullar epithelioreticular cell ; keratin filaments; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1929 |
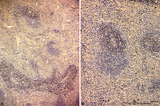 |
Immunoperoxidase stained CD3 positive T cells in spleen (rat) | Stain: Immunoperoxidase staining using diaminobenzidin (DAB)/ hematoxylin counterstained on frozen section with anti CD3 antibodies. Survey (A) and detail (B) show that CD3 marker for mature T cells stains positively (brown) in the PALS area (1) around the central arteries, while the adjacent follic... | CD3 lymphocytes; immunohistochemistry; PALS | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1930 |
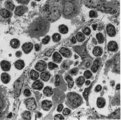 |
: Lymph node (rat) | Electron microscopy. A low magnification of a part of the medulla showing medullary cords surrounded by labyrinthine medullary sinus (*). In this picture the medullar cord runs from left bottom corner to right top corner, and is lined by flat reticular cell types. Within the cord one finds a star-sh... | medulla; electron microscopy; sinusoid | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1931 |
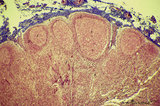
 |
Calcified bacterial plaque in palatine tonsil ('gut-associated lymphatic tissue' or GALT) (human) | Stain: Azan. A tonsillar crypt lined by squamous epithelium (2) that is infiltrated with lymphocytes (1). It is a normal finding that within the crypts free cells, plugs of lymphocytes (1) and calcified epithelial debris as well as colonies of oral commensally bacteria are present. (3) shows a calc... | bacterial plaque | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1932 |
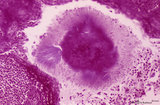
 |
Cortex of lymph node (human) | Stain: Azan. The cortex of the lymph node comprises the (secondary) follicles with germinal centres (1) and corona or mantle zone (2), all filled with B lymphocytes. The paracortical area (3) below the follicles largely comprises T cells. Afferent lymph vessels enter via the capsule (6) into the m... | cortex; paracortex | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 1933 |
 |
Cross-section of tooth in alveolar bone (cat, adult) | Stain: Picric acid and hematoxylin. From left to right: Periodontal ligament with blood vessels. Acellular cementum (dark purple rim). Dentin with radiair arrangement of dentinal tubules; fine incremental (imbrication) lines of von Ebner run at right angles to these tubules. These lines represent di... | oral cavity; incremental lines; von Ebner | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 1934 |
 |
Dentinal tubules in longitudinal section of tooth - human, adult. Thin ground section, polarizing microscopy - optical axes of the polarizing plates are crossed at 60. | Slightly oblique section shows dentinal tubules depicted by brown-stained hollow fiber-like structures containing odontoblastic processes (Tomes' fibers) in a semi-three dimensional way. Numerous fine secondary branches of these processes are anastomosing with those of neighboring tubules. | oral cavity; Tomes' Fibers; dentinal tubules | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 1935 |
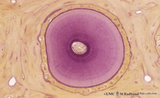 |
Cross section of tooth in alveolar bone - cat; low magnification | Stain: Picric acid and hematoxylin. From left to right: alveolar bone tissue with osteons; periodontal ligament with blood vessels; acellular cementum (dark purple rim); dentin with (purple) radiair arrangement of dentinal tubules; fine incremental (imbrication) lines of von Ebner run at right angl... | oral cavity; incremental lines; alveolar bone | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 1936 |
 |
Dentinal tubules in longitudinal section of tooth - human, adult. Thin ground section, polarizing microscopy - optical axes of the polarizing plates are crossed at 60. | Slightly oblique section shows dentinal tubules depicted by brown-stained hollow fiber-like containing odontoblastic processes (Tomes' fibers) in a semi-three dimensional way ('stubble-field' aspect). Darker stained clusters represent anastomosing secondary branches. | oral cavity; Tomes' Fibers; dentinal tubules | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 1937 |
 |
Dentinoenamel junction in longitudinal section of tooth (human, adult). Thin ground section. | From left to right: Enamel with fine striation (course of enamel rods or prisms). Few enamel tufts (left, dark) consisting of hypocalcified enamel rods and interprismatic substance arise from the junction. Scallop-like course of dentinoenamel junction. Dentin with dentinal tubules to the dentinoenam... | oral cavity; enamel tufts; dentinoenamel junction; dentinal tubules | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 1938 |
 |
Dentinal tubules in longitudinal section of tooth - human, adult. Thin ground section, polarizing microscopy - optical axes of the polarizing plates are crossed at 60. | Slightly oblique section shows dentinal tubules depicted by brown-stained stubble structures containing odontoblastic processes (Tomes' fibers) in a semi-three dimensional way. Numerous fine branches of these processes are obvious in dentin. | oral cavity; Tomes' Fibers; dentinal tubules | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 1939 |
 |
Dentin in cross section of tooth - human, adult | Stain: Hematoxylin and eosin. Cross-sectioned dentinal tubules demonstrate: a light stained center with the odontoblastic process (Tomes' fiber); darker stained peritubular dentin (highly mineralized), also called Neuman's sheath. Intertubular dentin (less mineralized) is present between the tubule... | oral cavity; dentinal tubules; secondary dentin | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 1940 |
 |
Dentin in cross section of tooth (human, adult) | Stain: Hematoxylin and eosin. Longitudinally sectioned dentinal tubules are parallely arranged, and numerous side branches are visible. | oral cavity; dentinal tubules | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 1941 |
 |
Dentinoenamel junction in the tooth (human, adult). Thin ground section of crown. | From left to right: Enamel with fine striation (composition of enamel rods or prisms); darker zones almost perpendicular to the striation are the incremental lines (Retzius) due to successive apposition of layers of enamel as the crown is formed. Dentinoenamel junction is shown as a narrow fissure f... | oral cavity; dentinal tubules; dentinoenamel junction; interglobular dentin; lines of Retzius | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 1942 |
 |
Dentinoenamel junction in the tooth - human, adult. Thin ground section of crown. | From left to right: Superficial dentin (bluish) in the crown with S-shaped course of dentinal tubules; They pass uninterrupted through the irregular black structures (due to filling with air) representing hypocalcified areas (interglobular dentin); Mineralization of dentin starts in small globular ... | oral cavity; dentinal tubules; dentinoenamel junction; interglobular dentin; lines of Retzius | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 1943 |
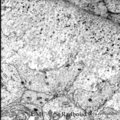 |
Dentinogenesis in tooth development - bell stage, gerbil, postnatal | Electronmicroscopy. At the top right corner side the distal cytoplasmic parts of presecretory ameloblasts resting on a thin grey basal lamina. In the central area predentin with collagen fibers (grey patches) and cross-sectioned small odontoblastic branches. In between them dispersed numerous dark-s... | oral cavity; predentin; matrix vesicles | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 1944 |
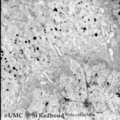 |
Dentinogenesis in tooth development - bell stage, gerbil, postnatal | Electronmicroscopy. At the bottom side of the predentin partly cross-sectioned odontoblasts with some organelles and many vesicular structures, the dark ones containing hydroxyapatite. Close to the odontoblasts a high concentration of secreted collagen fibers. Further away numerous matrix vesicles (... | oral cavity; predentin; matrix vesicles | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 1945 |
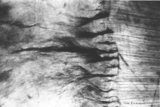 |
Dentinoenamel junction in longitudinal section of tooth - human, adult. Thin ground section. | From left to right: enamel with fine striation (composed of stalks of enamel rods or prisms); enamel tufts (dark) arise at the dentinoenamel junction, and these tufts consist of hypocalcified enamel prisms and interprismatic substance; dentin with dentinal tubules up to the dentinoenamel. | oral cavity; enamel tufts; dentinoenamel junction; dentinal tubules | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 1946 |
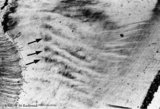 |
Enamel in longitudinal section of tooth - human, adult. Thin ground section. | From left to right: dentin with dentinal tubules; dentinoenamel junction; enamel with arrows pointing to bands (lines) of Hunter-Schreger; these alternating light and dark strips originate at the dentinoenamel junction and do not reach the enamel surface. This optical phenomenon is the result of the... | oral cavity; Hunter-Schreger bands; Retzius | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 1947 |
 |
Enamel in longitudinal section of tooth - human, adult. Thin ground section, polarizing microscopy - optical axes of the polarizing plates are crossed at 60. | Using polarizing microscopy the birefringence of the crystalline structure of enamel is colorful demonstrated. Incremental lines (striae) of Retzius are well shown as straight oblique zones. Note the parallel lines of enamel stacks at the left corner of the picture. At the right side the lightly col... | oral cavity; Retzius; dentinoenamel junction | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 1948 |
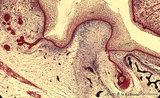 |
Early cap stage in tooth development - human, embryo; low magnification | Stain: Azan. From top to bottom: top left vestibular groove with gland formation; stratified ectoderm with dark red rim of basal cells from which a dental lamina sprouts downwards into the dental crypt (bony cavity) (bottom right corner); bone stains dark blue; connective tissue/mesenchym stains lig... | oral cavity; tooth development; dental lamina | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 1949 |
 |
Enamel in longitudinal section of tooth - human, adult. Thin ground section, polarizing microscopy - optical axes of the polarizing plates are crossed at 60. | Using polarizing microscopy the birefringence of the crystalline structure of enamel is colorful demonstrated. Incremental lines (striae) of Retzius are well shown as straight oblique zones. Top right a long dark fissure-like structure representing a crack. | oral cavity; Retzius; dentinoenamel junction | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 1950 |
 |
Enamel in longitudinal section of tooth - human, adult. Thin ground section, polarizing microscopy - optical axes of the polarizing plates are crossed at 60. | Left side enamel and at right side dark-stained striation of dentin. Wavy course of enamel prisms from dentinoenamel junction (right side, scalloped appearance) to the left. The transparent areas represent enamel lanes at a different polarizing angle. | oral cavity; dentinoenamel junction | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 1951 |
 |
Enamel in longitudinal section of tooth - human, adult. Thin ground section. | From left to right: incremental lines (striae) of Retzius are distinctly shown as oblique broad zones (at the left) to the enamel surface; during formation of the crown successive apposition of layers of enamel is deposited and results in these so-called incremental grow lines; surface of enamel in ... | oral cavity; incremental lines; Retzius | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 1952 |
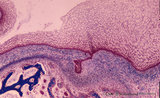 |
Early cap stage in tooth development - human, embryo; low magnification | Stain: Azan. From top to bottom: top left vestibular groove with gland formation; stratified ectoderm with ingrowth of the dental lamina (in the middle); bulbous growing end of dental lamina; bottom left alveolar bone formation (dark blue); and connective tissue/mesenchym stains light blue. | oral cavity; tooth development; dental lamina | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 1953 |
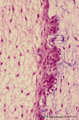 |
Enamel (odontogenic) organ in tooth development - bell stage, human, embryo | Stain: Azan. Outer surface of bell; from left to right: (avascular) Stellate reticulum; capillaries in this stage proliferate and invaginate between the outer dental epithelial cells; Part of fibrous tooth follicle. | oral cavity | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 1954 |
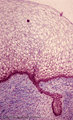 |
Early cap stage in tooth development - human, embryo | Stain: Azan. From top to bottom: stratified ectoderm with ingrowth of the dental lamina; knob-like end of the dental lamina; and collagen fibers of lamina propria are blue. | oral cavity; tooth development; dental lamina | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 1955 |
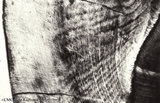 |
Enamel in longitudinal section of tooth - human, adult. Thin ground section. | At the left side surface of enamel in cuspal region; the parallel horizontal arrangement of stacks of rods (prisms) is evident. At the right side area of dentin (dark area). Incremental lines (striae) of Retzius run as curved lines (from bottom to middle top) and presented successive apposition of l... | oral cavity; incremental lines; Retzius; Hunter-Schreger bands | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 1956 |
 |
Enamel in longitudinal section of tooth - human, adult. Thin ground section. | Enamel is compact and acellular, and consists of vertical stacks of rods (prisms) as well as interrod (interprismatic) regions with less calcifying substance parallel to each other. Each prism is surrounded by an enamel sheath (a non-mineralized organic substance). From left to right: surface of ... | oral cavity; enamel rods; enamel prisms | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 1957 |
 |
Enamel rods (prisms) in tooth development - gerbil, postnatal | Electronmicroscopy. Cross-section of rods (prisms) demonstrate round aggregates with hydroxyapatite crystals. Between the round rods the interprismatic substance with crystals orientated in a different course. Note that twisting of the crystallites can be seen in the longitudinal bundles where grey ... | oral cavity; enamel prisms; hydroxyapatite crystals | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 1958 |
 |
Epithelial tooth bud in tooth development - tooth germ, human, embryo | Stain: hematoxylin. At the top stratified ectoderm. The proliferating basal cell layers are palisade-arranged with a light cytoplasm close to the basement membrane (right side). Below the basement membrane subepithelially an accumulation of inductive neural crest-derived mesenchymal cells is locally... | oral cavity; tooth bud; tooth development | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 1959 |
 |
Exocrine gland (salivary gland) | Scheme electronmicroscopy. Part of an acinus of mucous cells with different amount of mucous secretion. Supranuclearly the Golgi areas with maturing mucous secretion granules, basolateral the endoplasmic reticulum. At the top the lumen. The left cell shows an accumulation of the secretory droplets, ... | oral cavity; mucous gland | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 1960 |
 |
Exocrine gland (salivary gland) | Scheme electronmicroscopy. Part of an acinus of serous cells, basolaterally a well developed rough endoplasmic reticulum and apically secretion granules with different maturity towards the small lumen. On top stages of early formed secretion granule (left) and more matured ones (right). Note small j... | oral cavity; serous gland | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 1961 |
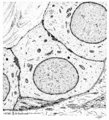 |
Exocrine gland - intercalated duct - salivary glands, pancreas | Scheme electronmicroscopy. Part of an intercalated duct, the low cuboidal epithelial cells contain sparsely organelles and some desmosomal structures. Between the lining cells and the basal lamina is squeezed part of a filament-rich myoepithelial cell. Lumen side top left quadrant. | oral cavity; intercalated duct | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 1962 |
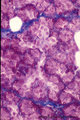 |
Exocrine gland - intercalated duct - submandibular gland, human | Stain: Azan. Branching intercalated duct draining several serous acini, the lining duct cells are lighter stained due to the content of organelles. Serous cells are darker stained (many organelles) with round nuclei. Note few fat cells, the septa are blue stained. | oral cavity; intercalated duct; serous gland | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 1963 |
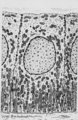 |
Exocrine gland - striated (intralobular) duct - salivary glands, pancreas | Scheme electronmicroscopy. Part of a striated duct with basally membrane infoldings and mitochondria accumulations in the tall columnar cells. Small junctional complexes as well as apically mitochondria and numerous vesicles are present. | oral cavity; striated duct | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 1964 |
 |
Exocrine gland - parotid gland, rat | Electronmicroscopy. Part of a striated duct with basally membrane infoldings and numerous mitochondria perpendicularly orientated to the basal membrane. Upper side is luminal side. Apically junctional complexes as well as mitochondria and many vesicles are present. | oral cavity; serous gland | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 1965 |
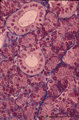 |
Exocrine gland - striated (intralobular) ducts - parotid gland, human | Stain: Azan. Cross-sections of striated ducts in upper part between serous acini. Note at the right bottom part of (lighter stained) lining cells of an intercalated duct. Connective tissues between the structures are blue stained. | oral cavity; striated duct | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 1966 |
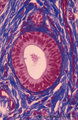 |
Exocrine gland - interlobular duct - submandibular gland, human | Stain: Azan. An interlobular duct with partly columnar as well as pseudostratified columnar epithelium. Note the dense connective tissue of the interlobular septum with small blood vessels. | oral cavity; seromucous glands | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 1967 |
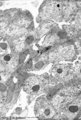 |
Exocrine gland - intercalated duct - submandibular gland, rat | Electronmicroscopy. The dark cells form an intercalated duct from the left lower corner to the right upper corner, and end in the acinus with lightly stained cells (serous). | oral cavity; intercalated duct; serous gland | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 1968 |
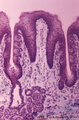 |
Foliate papillae of the tongue (dorsal side, rabbit) | Stain: Goldner trichrome. Foliate papil with primary and secondary connective tissue projections. Taste buds are localized in the lining, non-keratinized epithelium of the grooves. The serous gland of von Ebner (minor salivary gland) drains via an enlarged duct into the left groove of the papil. | oral cavity; foliate papillae; von Ebner | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 1969 |
 |
Free denticulus (pulp stone) in the tooth - longitudinal section of root pulp; human, adult | Stain: Hematoxylin and eosin. In the center of pulp connective tissue a free pulp stone (false denticulus). Dispersed through the pulp several small stones. Left of the central stone a longitudinal sectioned thin-walled blood vessel; right of the stone bundles of nerve fibers. | oral cavity; denticulus; pulp stone | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 1970 |
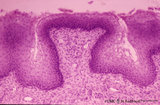 |
Fungiform papillae of the tongue (dorsal side, human) | Stain: Hematoxylin and eosin. A broad prominent papil of connective tissue (without secondary papils) covered by non-keratinized stratified epithelium. This specimen does not show any taste bud. Well vascularized lamina propria. | oral cavity; fungiform papillae | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 1971 |
 |
Filiform papillae of the tongue - dorsal side, human | Stain: Goldner trichrome. Detail of the threadlike keratinized extensions (red) of the stratified epithelium. Primary connective tissue papillae (green) divide in several small secondary ones. Note the absence of taste buds in filiform papillae. | oral cavity; filiform papillae | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 1972 |
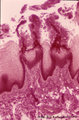 |
Filiform papillae of the tongue (dorsal side, human) | Stain: Heidenhain light bordeaux. Detail of the threadlike keratinized extensions of the stratified epithelium. Primary connective tissue papillae with 2 to 3 secondary papillae. Note the absence of taste buds in filiform papillae. | oral cavity; filiform papillae | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 1973 |
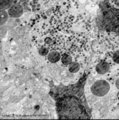 |
Exocrine gland - submandibular gland, gerbil | Electronmicroscopy. Part of a serous acinus of this mixed gland. Note characteristic electron-dense secretion granules, the mature ones are larger. At the lower bottom is shown part of a lining cell of the intercalated duct. | oral cavity; serous gland | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 1974 |
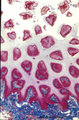 |
Filiform papillae of the tongue (dorsal side, human) | Stain: Azan. Oblique cross-section through the top of the filiform papillae. At the top of the picture keratinized extensions. Primary connective tissue papillae (blue) divide in several small secondary ones. | oral cavity; filiform papillae | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 1975 |
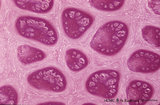 |
Filiform papillae of the tongue - dorsal side, human | Stain: Heidenhain light bordeaux. Transverse section through the middle of the filiform papillae showing secondary connective tissue papillae (lightly stained). | oral cavity; filiform papillae | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 1976 |
 |
Filiform papillae of the tongue (dorsal side, human, neonate) | Scanning electronmicroscopy. Slender, thin threadlike extensions of the filiform papillae. In between a broad fungiform papilla. | oral cavity; filiform papillae; fungiform papilla | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 1977 |
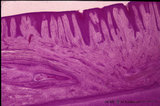 |
Gingiva - 'attached' gingiva of decalcified alveolar bone, human | Stain: Hematoxylin and eosin. Stratified squamous epithelium with parakeratosis (reddish) and deep papillae of the lamina propria. At the bottom, lamellar bone tissue (alveolar bone) with thickened periosteum (part of the periodontal ligament). At the bottom dentin. | oral cavity | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 1978 |
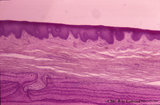 |
Gingiva ('attached' gingiva of decalcified alveolar bone, human, adult) | Stain: Hematoxylin and eosin. Thick layer of stratified squamous epithelium with parakeratosis (reddish) and shallow papillae of the lamina propria. At the bottom lamellar bone tissue (alveolar bone) with thickened periosteum. | oral cavity; alveolar bone | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 1979 |
 |
Gingiva - 'free' gingiva of decalcified alveolar bone, human | Stain: Hematoxylin and eosin. Thick layer of stratified squamous epithelium with parakeratosis (reddish) and broad papillae of the lamina propria. At the left, dense collagen tissue (projections of the the periodontal ligament). | oral cavity | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 1980 |
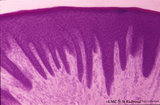 |
Gingiva ('free' gingiva of decalcified tooth, human, adult) | Stain: Hematoxylin and eosin. Thick layer of stratified squamous epithelium with parakeratosis (reddish) and many narrow papillae of the lamina propria. | oral cavity | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 1981 |
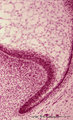 |
Late cap stage in tooth development - human, embryo | Stain: Azan. From top to bottom: Top side stellate reticulum (enamel pulp) consisting of a network of ectoderm-derived cells; Right side outer dental epithelium with part of the fibrous tooth follicle. This epithelium will further develop downwards as the outer layer of the Hertwig's epithelial root... | oral cavity | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 1982 |
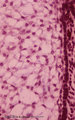 |
Late cap stage in tooth development - human, embryo | Stain: Azan. The stellate reticulum (enamel pulp) consists of a network of ectoderm-derived branched cells and fluid-filled spaces (a.o. proteoglycans). It is a specialized avascular layer as a support and protection for the inner dental epithelial cells. At the right side one layer of cuboidal oute... | oral cavity; tooth development; outer dental epithelium; stellate reticulum | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 1983 |
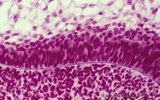 |
Late cap stage in tooth development - human, embryo | Stain: Azan. From top to bottom: At the top stellate reticulum (enamel pulp) consisting of a loose network of ectoderm-derived cells; Darker stained cell layers of the stratum intermedium; Columnar inner dental epithelium (presecreetory ameloblasts) at the distal side (secretion area) oriented towar... | oral cavity | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 1984 |
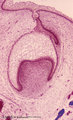 |
Late cap stage of tooth development - human, embryo; low magnification | Stain: Azan. From top to bottom: Stratified ectoderm with a distinct basal layer (red line) of cuboid cells; Dental lamina giving rise to the cap stage (center) and to the primordium of permanent tooth (right); Odontogenic organ or enamel organ (future deciduous tooth surrounded by fibrous tooth fol... | oral cavity; dental lamina | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 1985 |
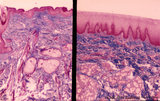 |
Lip (human), outer (left) and inner side (right) | Stain: Azan. Left image: keratinized squamous epithelium with thin red cornified layer, hair follicle, sebaceous glands and skeletal muscle fibers (orbicularis oris). Right image: non-keratinized epithelium with high, narrow dermal papillae and more capillaries. Mixed labial glands (seromucous), f... | oral cavity; lining mucosa | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 1986 |
 |
Lip (human), region between red zone (vermilion border) and mucosa inner surface | Stain: Azan. Bundles of skeletal muscle fibers (musculus orbicularis oris), highly vascularized lamina propria. Note the narrow dermal papillae on the left side (inner lip) and the broad irregular papillae on the right side (red zone of the lip). | oral cavity; lining mucosa; red zone; vermilion border | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 1987 |
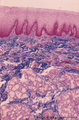 |
Lip (human), mucous inner surface | Stain: Azan. Non-keratinized epithelium with high, narrow dermal papillae and many capillaries. Mixed labial glands (seromucous) and few skeletal muscle fibers (orbicularis oris) in the submucosa. | oral cavity; lining mucosa; labial glands | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 1988 |
 |
Lip (human), mucoserous labial glands in mucous inner surface | Stain: Azan. Mixed labial glands with serous demilunes (von Ebner-Giannuzzi), a few myoepithelial cells, and a striated duct (right upper corner). | oral cavity; lining mucosa; labial glands | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 1989 |
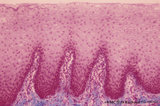 |
Lip (human), mucous inner surface | Stain: Azan. Non-keratinized epithelium with high, narrow dermal papillae and many capillaries. Note lymphocytic infiltrates and the capillaries in the dermal papillae. | oral cavity; lining mucosa | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 1990 |
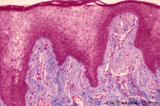 |
Lip (human), transitional zone (red zone or vermilion border) | Stain: Azan. Slightly cornified epithelium with high irregular dermal papillae and many capillaries. Note the epithelium is thicker, but less cornified than the epidermis. The red color of the lips is due to the rich vascularity of the lamina propria and the lucidity of the epithelium. | oral cavity; lining mucosa; red zone; vermilion border | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 1991 |
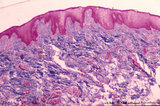 |
Lip (human), transitional zone (red zone or vermilion border) | Stain: Azan. Slightly cornified epithelium with high irregular dermal papillae and many capillaries. Fat cells and skeletal muscle cells are located in the submucosa. | oral cavity; lining mucosa; red zone; vermilion border | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 1992 |
 |
Odontoblast in tooth development - mammalian embryo | Scheme electronmicroscopy. A columnar and irregular shaped cell (mesenchymal origin) with a taperwise odontoblastic process within the predentin. The bottom side is adjacent to the future pulp cells. The cell body contains many organelles and especially a well-developed Golgi area with prosecretoy g... | oral cavity | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 1993 |
 |
Parotid gland (human) | Stain: Mallory trichrome. Survey: at the left bottom a large interlobular duct (in lumen remnants of secretion products) within a septum of dense connective tissue. At the top thinner (blue) septum, a thick (red-bluish) septum at the left. In the center three (intralobular) striated ducts between th... | oral cavity; serous gland | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 1994 |
 |
Papillae circumvallatae of the tongue (dorsal side, human) | Stain: Azan. Three broad papillae with taste buds facing the grooves in which the serous von Ebner glands drain. Striated skeletal muscles (musculus verticalis linguae and musculus longitudinalis superior) and lightly stained mucous glands (posterior lingual glands). | oral cavity; von Ebner; lingual muscles; lingual glands | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 1995 |
 |
Papillae filliformes of the tongue (dorsal side, human) | Stain: Heidenhain light bordeaux. Threadlike keratinized extensions of the stratified epithelium. Primary connective tissue papillae with 2 to 3 secondary papillae. The skeletal muscle fibers are arranged in three directions. | oral cavity; filiform papillae | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 1996 |
 |
Parotid gland (human) | Stain: Azan. The parotid gland: in most species the gland is composed entirely of serous acini. At the right a small (intralobular) striated duct; centrally one large interlobular duct with blood vessels. Scattered a few (white) fat cells. | oral cavity; serous gland | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 1997 |
 |
Papillae circumvallatae of the tongue (dorsal side, human) | Stain: Azan. A broad papilla with taste buds (lightly stained spots) facing the grooves in which the serous glands (von Ebner) drain. | oral cavity; von Ebner; circumvallate papillae | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 1998 |
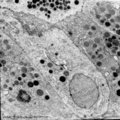 |
Parotid gland (rat) | Electronmicroscopy. Part of a serous acinus with characteristic secretion granules supranuclearly. Note different densities of the granules without any signs of fusion. | oral cavity; serous gland | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 1999 |
 |
Permanent tooth - canine, human, adult; low magnification of labiolingual section | Stain: Hematoxylin and scarlet red. From top to bottom: Crown region with dentin but without enamel (decalcified specimens); Neck region at the attachment of the gingiva to dentin (left and right); Cementum is visible as a dark small rim from the neck region to the bottom of the tooth; Periodontal l... | oral cavity; alveolar process | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 2000 |
 |
Premolar permanent tooth (human, adult; low magnification of labiolingual section) | Stain: Hematoxylin and eosin. From top to bottom: Crown region with enamel-dentin boundary (there is no enamel present in decalcified specimens); dentin (blue-pink) enwraps the whole pulp chamber (light) and here the lines of dentinal tubules appear S-shaped. Neck region at the attachment of the gin... | oral cavity; pulp canal | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
