The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
TO
Filters: Collection: "ehsl_heal"
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 901 |
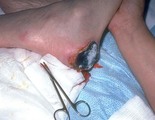 |
Necrosis of the skin | The necrotic skin must be removed. Normally the dermis is red and bleeds easily, and the underlying fat is yellow. If the tissues are a different color than that, then they need to be surgically removed. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 902 |
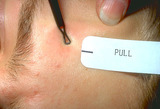 |
Opening comedos | The third step in opening comedos with a comedo extractor is to pull to the side while pushing and this generally forces out the comedo. | Comedo | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology |
| 903 |
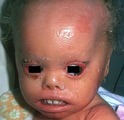 |
Lamellar ichthyosis | Lamellar ichthyosis. The abnormal stratum corneum has produced what appears as very thick scale on the skin, and with an abnormal barrier layer these patients commonly get secondary staphylococcal and yeast infections. Note that there are other associated ectodermal problems such as the teeth, hair,... | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 904 |
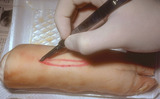 |
Excising with scalpel | When excising the scalpel should be held as if holding a pencil. A puncture should be made at one end of the ellipse. | Surgical Methods | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology |
| 905 |
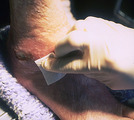 |
Necrotic tissue | If a transparent semipermeable dressing is to be used, the skin around the ulcer has to be cleansed with alcohol. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 906 |
 |
Nasal mask placement | This demonstrates placement of the nasal mask. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 907 |
 |
Puncture wounds of the foot | Puncture wounds of the foot need to be explored because they often contain fragments of shoe, stocking, or other foreign material. It is best to expore the wound by extending the opening sufficiently to be able to clearly see to the base of the wound to insure complete debridement/cleansing. The w... | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 908 |
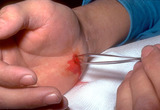 |
Puncture wounds | Visualization of the base of the wound and debridement is crucial. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 909 |
 |
Excision procedure | The wound that has been created in cross-section; note the beveling of the wound edges. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 910 |
 |
Scabies mite magnification | The scraping is viewed under the microscope at low magnification. The scabies mite measures about .1 to .3 mm in diameter, and is not visible with the naked eye, but very slight magnification will make it visible. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 911 |
 |
Milium extraction | Milium can be extracted by incision with a large needle and gently flipping out the contents. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 912 |
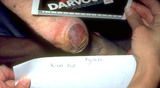 |
Necrosis of the skin | Pressure applied for too long to an area of skin compromises blood flow, and the skin necrosis. The purple/brown area on this heel is an area of necrosis of the skin. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 913 |
 |
Head lice | On close observation, you can often see the adult lice as, but it is much easier to see the pinhead size nits on the scalp hair. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 914 |
 |
Atopic dermatitis | In adults who suffer atopic dermatitis, often the eyelids are red and scaly. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 915 |
 |
Nitric oxide pressure gauges | This demonstrates the pressure gauges attached to the tanks. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 916 |
 |
Nitric oxide | Copper tubing is used to allow for interrupted transfer of energy from the expanding gases. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 917 |
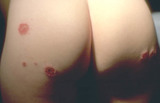 |
Nummular dermatitis | Lesions of acute (red and oozing) nummular dermatitis on the buttocks. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 918 |
 |
Nummular dermatitis | Lesions of nummular dermatitis. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 919 |
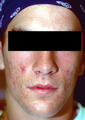 |
Mild acne vulgaris | Mild acne vulgaris. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 920 |
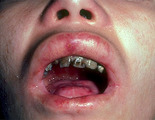 |
Recessive epidermolysis bullosa | An adult with recessive epidermolysis bullosa showing ulcers in the mouth and multiple dental caries secondary to inability to maintain proper dental hygiene. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 921 |
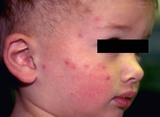 |
Exaggerated insect bite reaction, possibly secondary to chigger bites | Exaggerated insect bite reaction. Other lesions were red plaques that measured 1.5 to 2.0 cm, and were very pruritic. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 922 |
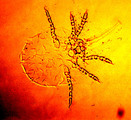 |
Chigger's mite | Chigger's mite. It is generally visible only with magnification. Its bite forms a red papule/wheal. | Chiggers | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology |
| 923 |
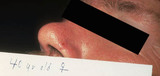 |
Basal cell carcinoma | This is a basal cell carcinoma on the edge of the nose. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 924 |
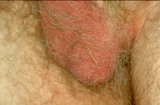 |
Halogenated steroids | Halogenated steroids, particularly fluorinated steroids, will often induce inflammation of the skin of the scrotum, vulvae, as well as the face. Halogenated steroids should never be used, with rare exception, on these areas, and then for the briefest period of time possible. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 925 |
 |
Ticks | The maximum incubation period for the tick-borne diseases seen in Utah would be seven days. If you were asked by someone who has had a tick how long they have to wait before they are out of the woods (so to speak), the answer is one week. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology |
