The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
TO
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
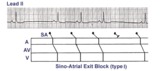 | Sino-atrial exit block, type I or wenckebach | This example illustrates 2nd degree sino-atrial exit block. In type 1 S-A block the conduction time between sinus firing and atrial capture progressively prolong, but this cannot be seen on the ECG tracing; type I exit block is inferred if the P-P intervals gradually shorten before the pause and if... | Wenckebach AV Block; Ladder Diagram | Knowledge Weavers ECG |
| 2 |
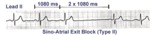 | Type II, 2nd degree sino-atrial block | Two types of 2nd degree SA block have been described. In type-I, or SA Wenckebach, the P-P interval of the pause is less than 2x the preceding P-P intervals. In type-II SA block the P-P interval of the pause is approximately 2x the normal P-P interval. The distinction between types I and II is no... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 3 |
 | Nonconducted PACs and junctional escapes | Although at first glance this looks like 2nd degree AV block, the P waves indicated by the arrows are premature and not sinus P waves. The pause is long enough to encourage a junctional escape focus to take over. Note the sinus P waves just before the escape beats. Had the escapes not occurred, t... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 4 |
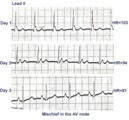 | ECG of the century: A most unusual 1st degree AV block | On Day 1, at a heart rate of 103 bpm the P waves are not clearly defined suggesting an accelerated junctional rhythm. However, on Day 2, at a slightly slower heart rate the sinus P wave suddenly appears immediately after the QRS complex. In retrospect, the sinus P wave in Day 1 was found burried i... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 5 |
 | Right Axis Deviation & RAE (P pulmonale): Leads I, II, III | Right Axis Deviation & RAE (P pulmonale): Leads I, II, III | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 6 |
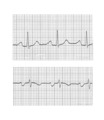 | Left atrial enlargement | Left atrial enlargement is illustrated by increased P wave duration in lead II, top ECG, and by the prominent negative P terminal force in lead V1, bottom tracing. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 7 |
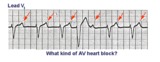 | A very subtle 1st degree AV block | Where are the P waves??? They are hiding in the T waves as indicated by the arrows. How do we know? The PVC unmasked the sinus P wave, and now it is seen in the pause following the PVC. The PR interval is, therefore, about 500 ms. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 8 |
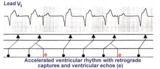 | Accelerated ventricular rhythm with retrograde atrial capture and echo beats | Retrograde atrial captures from an accelerated ventricular focus are occurring with increasing R-P intervals, When the longer R-P occurs, the impulse traversing the AV junction finds a route back to the ventricles, and the result is a ventricular echo. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 9 |
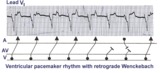 | Ventricular paced rhythm with retrograde wenckebach | Retrograde atrial captures from a ventricular paced rhythm are occurring with increasing R-P intervals; i.e., retrograde Wenckebach. The ladder diagram indicates that after the blocked retrograde event, a single sinus P wave is seen dissociated from the ventricular rhythm. | Wenckebach AV Block | Knowledge Weavers ECG |
| 10 |
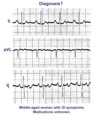 | A very subtle atrial tachycardia with 2:1 block | Although at first glance this looks like normal sinus rhythm at 95 bpm. On closer look, there are 2 P waves for every QRS; the atrial rate is 190 bpm. Note the hidden P in the T waves. This rhythm is likely due to digitalis intoxication, as are the GI symptoms. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 11 |
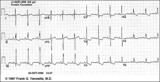 | Right Ventricular Hypertrophy (RVH) & Right Atrial Enlargement (RAE) | In this case of severe pulmonary hypertension, RVH is recognized by the prominent anterior forces (tall R waves in V1-2), right axis deviation (+110 degrees), and P pulmonale (i.e., right atrial enlargement). RAE is best seen in the frontal plane leads; the P waves in lead II are >2.5mm in amplitud... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 12 |
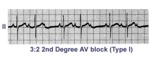 | Second degree AV block, type I, with 3:2 conduction ratio | There are two types of 2nd degree AV Block. In this example of Type I or Wenckebach AV block there are 3 P waves for every 2 QRSs; the PR interval increases until a P wave fails to conduct. This is an example of group beating. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 13 |
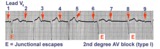 | 2nd degree AV block, type I, with junctional escapes | Junctional escapes are passive, protective events whenever the heart rate slows below that of the escape mechanism. In this example of 2nd degree AV block, type I, the escapes occur following the non-conducted P waves. Arrows indicate the position of the P waves. Note that the escape beats have a... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 14 |
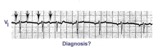 | Atrial tachycardia with 3:2 and 2:1 AV block | The ectopic atrial rate is 150 bpm. Some of the ectopic P waves are easily seen and indicated by the arrows. Other P waves are burried in the T waves and not so easily identified. Atrial tachycardia with AV block is often a sign of digitalis intoxication. 3:2 and 2:1 AV block is seen in this examp... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 15 |
 | 2nd degree AV block, type I, with accelerated junctional escapes and a ladder diagram | The ladder diagram illustrates a Wenckebach type AV block by the increasing PR intervals before the blocked P wave. After the blocked P wave, however, a rev-ed up junctional pacemaker terminates the pause. Note that the junctional beats have a slightly different QRS morphology from the sinus beats... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 16 |
 | Atrial tachycardia with exit block and AV block | The ectopic P waves, easily seen in this example,occur in groups, separated by short pauses. This is likely due to an exit block just distal to the atrial pacemaker. Because not all of the P waves make it to the ventricles, there is also 2nd degree AV block. Therefore, two levels of block are pre... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 17 |
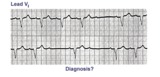 | LBBB and 2nd degree AV block, mobitz type I | Mobitz II 2nd degree AV block is usually a sign of bilateral bundle branch disease. One of the two bundle branches should be completely blocked; in this example the left bundle is blocked. The nonconducted sinus P waves are most likely blocked in the right bundle which exhibits 2nd degree block. ... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 18 |
 | Diagram: type I vs. type II 2nd degree AV block | In type I 2nd degree AV block the PR progressively lengthens until a nonconducted P wave occurs. The PR gets longer by smaller and smaller increments; this results in gradual shortening of the RR intervals. The RR interval of the pause is usually less than the two preceding RR intervals. The RR i... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 19 |
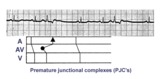 | Premature junctional complexes with retrograde P waves | The ladder diagram illustrates the PJC with retrograde atrial capture | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 20 |
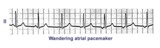 | Wandering atrial pacemaker | Wandering atrial pacemaker is a benign rhythm change where the pacemaker site shifts from the sinus node into the atrial tissues. P-wave morphology varies with the pacemaker site. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 21 |
 | Left Atrial Abnormality & 1st Degree AV Block | The P-wave is notched, wider than 0.12s, and has a prominent negative (posterior) component in V1 - all criteria for left atrial abnormality or enlargement (LAE). The PR interval >0.20s. Minor ST-T wave abnormalities are also present. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 22 |
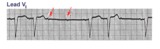 | Mobitz II 2nd degree AV block with LBBB | The QRS morphology in lead V1 shows LBBB. The arrows point to two consecutive nonconducted P waves, most likely hung up in the diseased right bundle branch. This is classic Mobitz II 2nd degree AV block. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 23 |
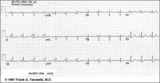 | Right Atrial Enlargement (RAE) & Right Ventricular Hypertrophy (RVH) | RAE is recognized by the tall (>2.5mm) P waves in leads II, III, aVF. RVH is likely because of right axis deviation (+100 degrees) and the Qr (or rSR') complexes in V1-2. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 24 |
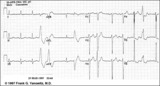 | LVH and many PVCs | The combination of voltage criteria (SV2 + RV6>35mm) and ST-T abnormalities in V5-6 are definitive for LVH. There may also be LAE as evidenced by the prominent negative P terminal force in lead V1. Isolated PVCs and a PVC couplet are also present. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 25 |
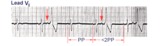 | PAC's with RBBB aberrant conduction | PAC's are identified by the arrows. Note that the PP interval surrounding the PAC is less than 2x the basic sinus cycle indicating that the sinus node has been reset by the ectopic P wave. The pause after the PAC, therefore, is incomplete. | Knowledge Weavers ECG |
