The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
TO
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
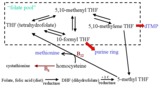 | Folate Pool - The Role of B Vitamins in One-Carbon Metabolism | This figure depicts the pathway for folate utilization and the role of vitamins B6 and B12 in the metabolism of methyl-tetrahydrofolate and homocysteine. | Folate; Folicin | HEAL Open Review Collection |
| 2 |
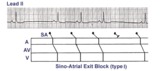 | Sino-atrial exit block, type I or wenckebach | This example illustrates 2nd degree sino-atrial exit block. In type 1 S-A block the conduction time between sinus firing and atrial capture progressively prolong, but this cannot be seen on the ECG tracing; type I exit block is inferred if the P-P intervals gradually shorten before the pause and if... | Wenckebach AV Block; Ladder Diagram | Knowledge Weavers ECG |
| 3 |
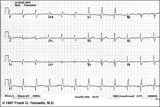 | Inferior & Anteroseptal MI + RBBB | Pathologic Q waves are seen in leads II, III, aVF (inferior MI) and in leads V1-3 (anteroseptal MI). RBBB is recognized by the wide QRS (>0.12s) and the anterior/rightwards orientation of terminal QRS forces. When an anteroseptal MI complicates RBBB (or visa versa) the rSR' complex in V1 (typical ... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 4 |
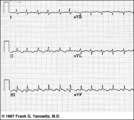 | Atrial flutter with 3:2 conduction ratio: frontal plane leads | Note the subtle bigeminy in the RR intervals. The best way to identify the flutter waves in this example is to imagine what lead III would look like if the QRS complexs disappeared; what remains is a reasonable saw-tooth pattern characteristic of atrial flutter with a flutter rate of about 300 bpm... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 5 |
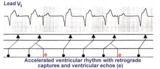 | Accelerated ventricular rhythm with retrograde atrial capture and echo beats | Retrograde atrial captures from an accelerated ventricular focus are occurring with increasing R-P intervals, When the longer R-P occurs, the impulse traversing the AV junction finds a route back to the ventricles, and the result is a ventricular echo. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 6 |
 | ECG components diagram - marquette | ECG components diagram - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 7 |
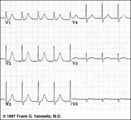 | Postero-lateral MI: Precordial Leads | Postero-lateral MI: Precordial Leads | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 8 |
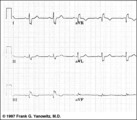 | Indeterminate frontal plane QRS axis | Indeterminate frontal plane QRS axis | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 9 |
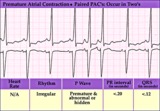 | PAC couplet - marquette | PAC couplet - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 10 |
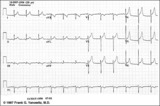 | Normal variant: Early repolarization | Early repolarization, a misnomer, describes a pattern of localized or diffuse ST segment elevation. This is especially seen in leads with prominent R waves. In this example leads I, II, V5 and V6 illustrate the early repolarization pattern. ST segments usually have a concave upwards pattern and ta... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 11 |
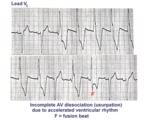 | AV dissociation by usurpation | Normal sinus rhythm is interrupted by an accelerated ventricular rhythm whose rate is slightly faster than the sinus rhythm. Fusion QRS complexes occur whenever the sinus impulse enters the ventricles at the same time the ectopic ventricular focus initiates its depolarization. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 12 |
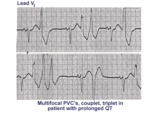 | Long QT mischief | The long QT ECG has many causes: electrolyte abnormalities including hypo-K, hypo-Mg, and hypo-Ca; drugs including type I antiarrhythmics; CNS injury; and hereditary syndromes. Ventricular arrhythmias are thought to be caused by afterdepolarizations or triggered automaticity. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 13 |
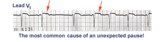 | Nonconducted and conducted PAC's | The pause in this example is the result of a nonconducted PAC, as indicated by the first arrow. The second arrow points to a conducted PAC. The most common cause of an unexpected pause in rhythm is a nonconducted PAC. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 14 |
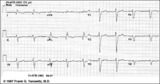 | Atypical LBBB with Q waves in leads I and aVL | In typical LBBB, there are no initial Q waves in leads I, aVL, and V6. If Q waves are present in 2 or more of these leads, myocardial infarction is present. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 15 |
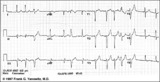 | Old inferior MI, PVCs, and atrial fibrillation | Old inferior MI, PVCs, and atrial fibrillation | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 16 |
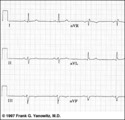 | Frontal plane QRS axis = -45 degrees | Frontal plane QRS axis = -45 degrees | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 17 |
 | LVH & PVCs: Precordial Leads | LVH & PVCs: Precordial Leads | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 18 |
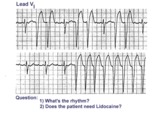 | Atrial flutter with variable AV block and rate-dependent LBBB | The basic rhythm is atrial flutter with variable AV block. When 2:1 conduction ratios occur there is a rate-dependent LBBB. Don't be fooled by the wide QRS tachycardia on the bottom strip. It's not ventricular tachycardia, but atrial flutter with 2:1 conduction and LBBB. Lidocaine is not needed ... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 19 |
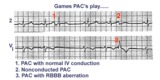 | three fates of PAC's | As illustrated, PAC's can have three fates: PAC-1enters the ventricles and encounters no conduction delays, therefore causing a narrow QRS; PAC-2 occurs a little earlier and can't get through the AV junction, therefore beingnonconducted; PAC-3 seen inlead V1 makes it into the ventricles but encounte... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 20 |
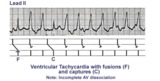 | Ventricular tachycardia with AV dissociation, captures, and fusions | Approximately 50 percent of ventricular tachycardias are associated with AV dissociation. In these cases atrial impulses can enter the ventricles and either fuse with a ventricular ectopic beat or completely capture the ventricles. This ladder diagram illustrates these events. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 21 |
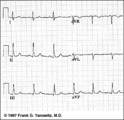 | Frontal plane QRS axis = +75 degrees | Since there is no isoelectric lead in this ECG, the two closest leads are I and aVL. If I were isoelectric, the axis would be +90 degrees; if aVL were isoelectric, the axis would be +60 degrees. A nice compromize is +75 degrees. (The two closest leads are always 30 degrees apart.) | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 22 |
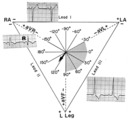 | Right axis deviation: QRS axis = +130 degrees | Lead aVR is almost isoelectric; lead I is mostly negative, and lead III is very positive. The QRS axis, therefore, is +130 degrees. Note that the slightly more positive AVR moves the axis slightly beyond +120 degrees; i.e., closer to the + pole of the aVR lead. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 23 |
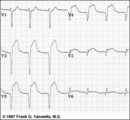 | Extensive anterior/anterolateral MI: precordial leads | Extensive anterior/anterolateral MI: precordial leads | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 24 |
 | LVH: strain pattern + left atrial enlargement | LVH: strain pattern + left atrial enlargement | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 25 |
 | Ventricular asystole - marquette | Ventricular asystole - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG |
