The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
TO
1 - 25 of 5
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
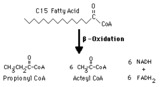 |
Propionyl CoA production from odd-chain fatty acids | Beta-oxidation of fatty acids with an odd number of carbons inthe chain yields the three-carbon propionyl CoA as the final fragment. | Biosynthesis | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids |
| 2 |
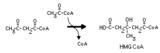 |
Hydroxymethylglutaryl CoA synthase reaction | This irreversible reaction occurs in the mitochondria, where it is the first step in ketone body synthesis. It also occurs in the cytoplasm, where it leads to isoprenoid and steroid synthesis. | Biosynthesis | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids |
| 3 |
 |
Propionyl CoA carboxylase reaction | Propionyl CoA is metabolized by a process that first converts it to D-methylmalonyl CoA. The reaction is catalyzed by propionyl CoA carboxylase,and requires energy in the form of ATP. | Biosynthesis | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids |
| 4 |
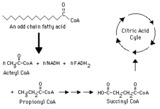 |
Complete oxidation of an odd-chain fatty acid -- overview | This diagram indicates production of propionyl CoA from an odd-chain fatty acid and the subsequent conversion of propionyl CoA to succinyl CoA, which can be metabolized through the citric (tricarboxylic) acid cycle. | Biosynthesis | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids |
| 5 |
 |
Fatty acid metabolism -- schematic overview | Fatty acids are taken up by cells, where thy may serve as precursors in the synthesis of other compounds, as fuels for energy production, and as substrates for ketone body synthesis. Ketones bodies may then be exported to other tissues, where they can be used for energy production. | Biosynthesis | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids |
1 - 25 of 5
