John A. Moran Eye Center Neuro-Ophthalmology Collection: A variety of lectures, videos and images relating to topics in Neuro-Ophthalmology created by faculty at the Moran Eye Center, University of Utah, in Salt Lake City.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
| Title | Description | Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
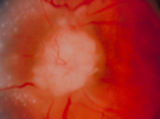 |
3-56a - Sarcoid | Image | |
| 2 |
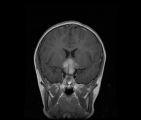 |
See-saw Nystagmus MRI 1 | MRI; See-saw Nystagmus | Image |
| 3 |
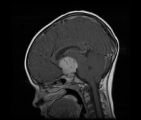 |
See-saw Nystagmus MRI 2 | MRI; See-saw Nystagmus | Image |
| 4 |
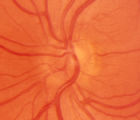 |
2-6a - Little Red Discs | Image | |
| 5 |
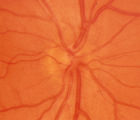 |
2-6b - Little Red Discs | Image | |
| 6 |
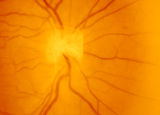 |
3-3 - Bergmeister Papilla | Image | |
| 7 |
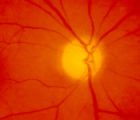 |
4-54a -Optic Neuropathy, Ischemic: Posterior | Image | |
| 8 |
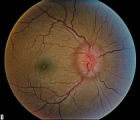 |
Stage 2 - Papilledema | Image | |
| 9 |
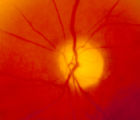 |
4-54b - Optic Neuropathy, Ischemic: Posterior | Image | |
| 10 |
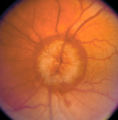 |
3-36a - Papilledema Stages | Grading Papilledema: Stage 5 Stage 5 = Dome-shaped appearance with all vessels being obscured. (Sometimes called "champagne cork" swelling--because of its dome shape.) | Image |
| 11 |
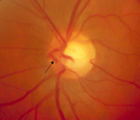 |
3-65 - Shunt Vessels (Glaucoma) | Chronic end-stage glaucoma produces high pressure that interferes with venous drainage from the disc and broad smooth venous collaterals drain the disc centrifugally to the disc margin where they drain. | Image |
| 12 |
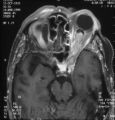 |
Shunt Vessel Meningioma - MRI | Meningiomas block venous egress and open potential venous channels known as retinochoroidal (optociliary) collateral vein. This meningioma extends from the back of the globe through the optic canal. | Image |
| 13 |
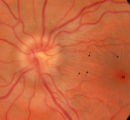 |
3-32b - Papilledema Stages | Grading Papilledema: Stage 1 Stage 1 = C shaped blurring of the nasal, superior and inferior borders. Usually the temporal margin is normal. Also notice the chorio-retinal folds (arrows) that eminate toward the macula (m) | Image |
| 14 |
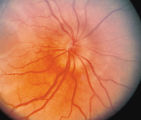 |
3-33b - Papilledema Stages | Grading Papilledema: Stage 2 = Elevation of the disc margin 360 degrees. Since the blood vessels at the disc margin are not swollen or obscured, this disc could be mistaken for pseudo-papilledema. | Image |
| 15 |
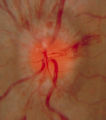 |
3-34c Papilledema Stages | Grading Papilledema: Stage 3 Stage 3 = Elevation of the entire disc with partial obscuration of the retinal vessels at the disc margin. Here the vessels are partly obscured and make the development into stage 3 easier to call. | Image |
| 16 |
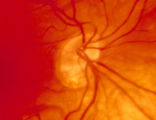 |
3-4 - Tilted Disc | Tilted discs are normal variants caused by oblique insertion of the optic nerve to the globe. They can be and frequently are mistaken for papilledema. In this case the superior edge of the disc is tilted and appears elevated. This disc exhibits a nasal inferior tilt. | Image |
| 17 |
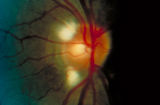 |
3-5b - Myelinated Nerve Fibers | Myelinated nerve fibers are frequently confused with papilledema. The feathery edge of the myelinated fibers that conceal the disc and vessel should provide the clue. These myelinated nerve fibers make the disc look blurred. | Image |
| 18 |
 |
3-60a - Meningioma | This 35 year old woman presented with slowly progressive loss of central acuity to 20/30. 3-60a: Her visual field shows progressive restriction over time. 3-60b: Her disc was chronically swollen, with refractile bodies on the disc surface. 3-60d: The CT axial scan showed an enlarged calcified optic... | Image |
| 19 |
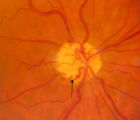 |
3-64a - Shunt Vessels (CRVO) | This man with a chronic CRVO and retino-choroidal collaterals developed AION and his collaterals disappeared. CRVO with retinochoroidal collaterals is almost always associated with multiple peripheral dot and blot hemorrhages as well as nerve fiber layer infarcts of various ages. Notice the retino-c... | Image |
| 20 |
 |
4-35 - Cupped Optic Nerve | Atrophic Glaucoma Atrophic glaucomatous discs show thinning of the neuro-retinal rim, "saucerization" (which is shallow cupping), evidence of peripapillary atrophy, and pallor of the very narrow neuroretinal rim. Notice that there is severe atrophy of the nerve fiber layer. | Image |
| 21 |
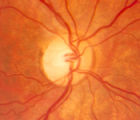 |
4-52b - Dominant Optic Neuropathy | A son presented with bilateral optic atrophy of unknown etiology after he failed a school visual exam. When looking for dominant optic atrophy, look at the parents. Mother was examined to find similar kind of atrophy. 4-52a mother, 4-52b son. | Image |
| 22 |
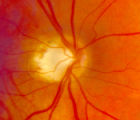 |
4-60a - Dominant Optic Neuropathy | A son presented with bilateral optic atrophy of unknown etiology after he failed a school visual exam. When looking for dominant optic atrophy, look at the parents. Mother was examined to find similar kind of atrophy. 4-60a mother, 4-60b son. | Image |
| 23 |
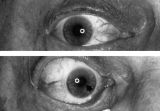 |
Aberrant Regeneration of the Right Pupil | Aberrant regeneration of the right pupil in a man with a large intracavernous sinus meningioma causing a pupil-involving, incomplete third cranial nerve palsy. His pupil is round when he gazes straight ahead (top). When he tries to rotate the eye medially, the pupil constricts, but a segment of the ... | Image |
| 24 |
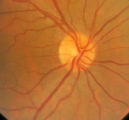 |
3-31b - Papilledema Stages | Grading Papilledema: Stage 0 GRADING PAPILLEDEMA GRADING PAPILLEDEMA We grade papilledema in order to tell us how severe it is. The most sensible grading scheme has been provided by Lars Frisén. STAGE 0: This woman had documented increased intracranial pressure of 340 mm water. Very little if any ... | Image |
| 25 |
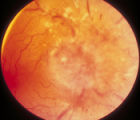 |
3-59a - Glioma | This 45-year-old man presented with vision loss in his right eye; his examination showed severe disc swelling in this eye and vision loss on visual field testing (3-59a). MRI with fat saturation and enhancement and MRI with T2 signals also confirm an enlarged optic nerve. (3-59c) Excisional biopsy o... | Image |
